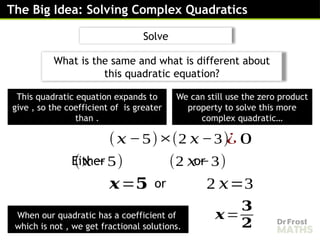
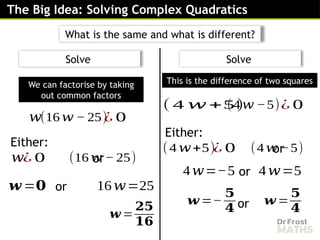
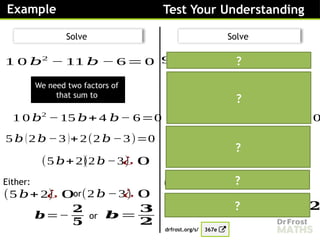
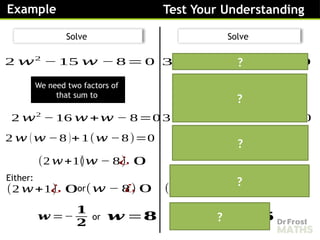
Solving complex quadratic equations by factorising involves rewriting the quadratic expression into a product of two brackets, then using the fact that if a product equals zero, at least one of the factors must be zero. The process is similar to solving regular quadratics, but it may include complex numbers.
To factorise a complex quadratic, you look for two expressions whose product gives the original quadratic and whose terms match the middle coefficient. Once the quadratic is written in its factorised form, you can set each bracket equal to zero and solve for the variable. This often leads to solutions that include complex numbers, especially when the quadratic does not cross the x-axis.
Factorising is helpful because it gives an exact, simplified way to find the roots of the equation and understand how the quadratic behaves in the complex number system.












![Exam Question
[Edexcel GCSE June 2016 1H Q22]
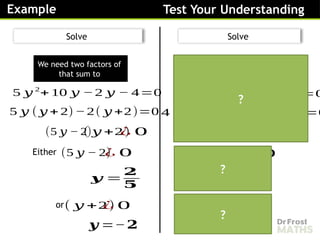
Solve
[3 marks]
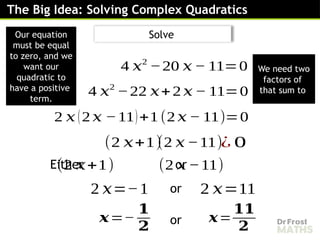
𝑥2
=4(𝑥2
−6 𝑥+9)
?
𝑥2
=4 𝑥2
−24 𝑥+36
3 𝑥2
−24 𝑥+36=0
𝑥2
−8𝑥+12=0
(𝑥−6)(𝑥 −2)=0
or
?
?
?
?
?
367e
drfrost.org/s/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solvingcomplexquadraticsbyfactorising-lesson-260127164848-b62b859c/85/Solving-Complex-Quadratic-by-Factorising-28-320.jpg)
![𝒘 =−𝟏, 𝒙=−
𝟒
𝟓
𝒚 =−
𝟏
𝟑
, 𝒚 =
𝟑
𝟒
𝒂=
𝟏
𝟐
, 𝒂=
𝟔
𝟓
𝒕=−
𝟓
𝟑
, 𝒕=
𝟑
𝟓
?
?
?
?
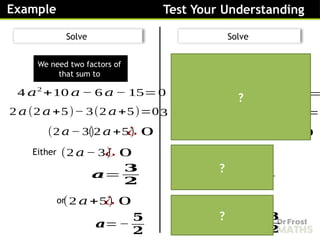
1
a
Solve:
3
𝒂=
𝟏
𝟑
, 𝒂=𝟓
(3𝑎 −1)(𝑎−5)=0
b ( 𝑥+7) (2𝑥+5)=0
c (2 𝑦 −1)(3 𝑦+7)=0
d 5 𝑑(2 𝑑+1)=0
e (3 𝑥+2)(6−5 𝑥)=0
𝒙=− 𝟕,𝒙=−
𝟓
𝟐
𝒚 =
𝟏
𝟐
, 𝒚=−
𝟕
𝟑
𝒅=𝟎, 𝒅=−
𝟏
𝟐
𝒙=−
𝟐
𝟑
, 𝒙=
𝟔
𝟓
𝒙=𝟏𝟏 ,𝒙=−
𝟑
𝟐
[OCR GCSE(9-1) Nov 2018 1H Q16]
Solve by factorisation
?
4
𝒙=−
𝟑
𝟓
, 𝒙=
𝟏
𝟒
[WJEC Additional Maths June 2017 Q1]
Factorise and hence solve
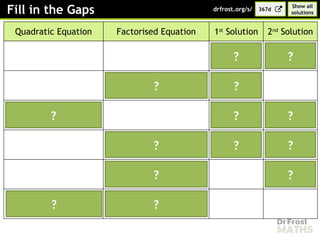
Exercise (Available as a separate worksheet)
Show all
solutions
?
?
?
?
2
a
Solve:
𝒙=
𝟏
𝟐
, 𝒙=−𝟐
2 𝑥2
+3 𝑥− 2=0
b 5𝑤2
+9𝑤 +4=0
c 12 𝑦2
−5 𝑦 − 3=0
d 10𝑎2
−17𝑎+6=0
e 15𝑡2
+16 𝑡 −15=0
?
(𝒙−𝟏𝟏)(𝟐𝒙 +𝟑)=𝟎
?
(𝟓 𝒙+𝟑) (𝟒 𝒙 −𝟏)
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solvingcomplexquadraticsbyfactorising-lesson-260127164848-b62b859c/85/Solving-Complex-Quadratic-by-Factorising-29-320.jpg)