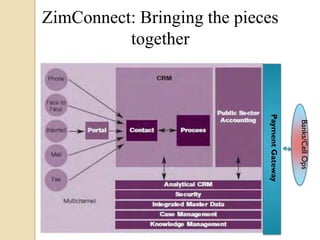
The document outlines the Zim-Connect e-government project in Zimbabwe aimed at creating a totally connected government to improve service delivery and enhance public sector accountability using a results-based management system. It emphasizes the need for efficient public service amidst rising citizen demands and limited resources, highlighting the role of e-government and technology in addressing these challenges. The project aims to integrate government operations across ministries, ultimately improving efficiency, reducing costs, and gathering citizen feedback.
















![A Totally Connected Government:
The Zim-Connect Project:
The Zim-Connect: e-
Government
Framework and
Implementation
Strategy [2011-2015]
Infrastructure
Systems/
Applications
Capacity
Building/
Change
Management
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solomonmhlangu-130704085702-phpapp01/85/Solomon-Mhlangu-17-320.jpg)

















![ZimConnect Project: A Totally
Connected Government
The ZimConnect: e-Government Framework and
Implementation Strategy [2011-2015]
Infrastructure
Systems/
Applications
Capacity
Building/
Change
Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solomonmhlangu-130704085702-phpapp01/85/Solomon-Mhlangu-35-320.jpg)