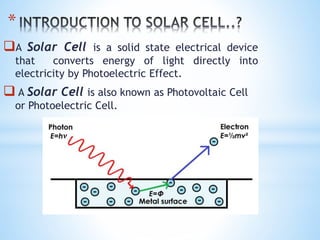
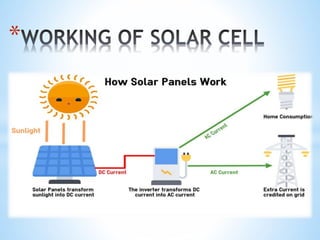
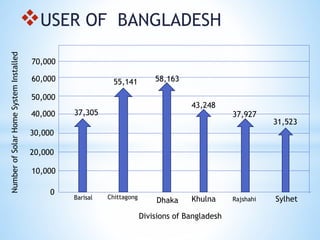
This document discusses solar cells, including their history, types, uses, advantages, and disadvantages. A solar cell converts light directly into electricity via the photoelectric effect. Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect in 1905. The modern solar cell was developed in 1954 at Bell Laboratories and first used in 1958 on the Vanguard I satellite. There are three main types of solar cell technologies: discrete cell, integrated thin film, and multi-crystalline silicon. Solar cells have various uses and advantages such as being renewable, pollution-free, and having a long lifespan. However, their initial costs are high and efficiency can be affected by weather and requiring large land areas.