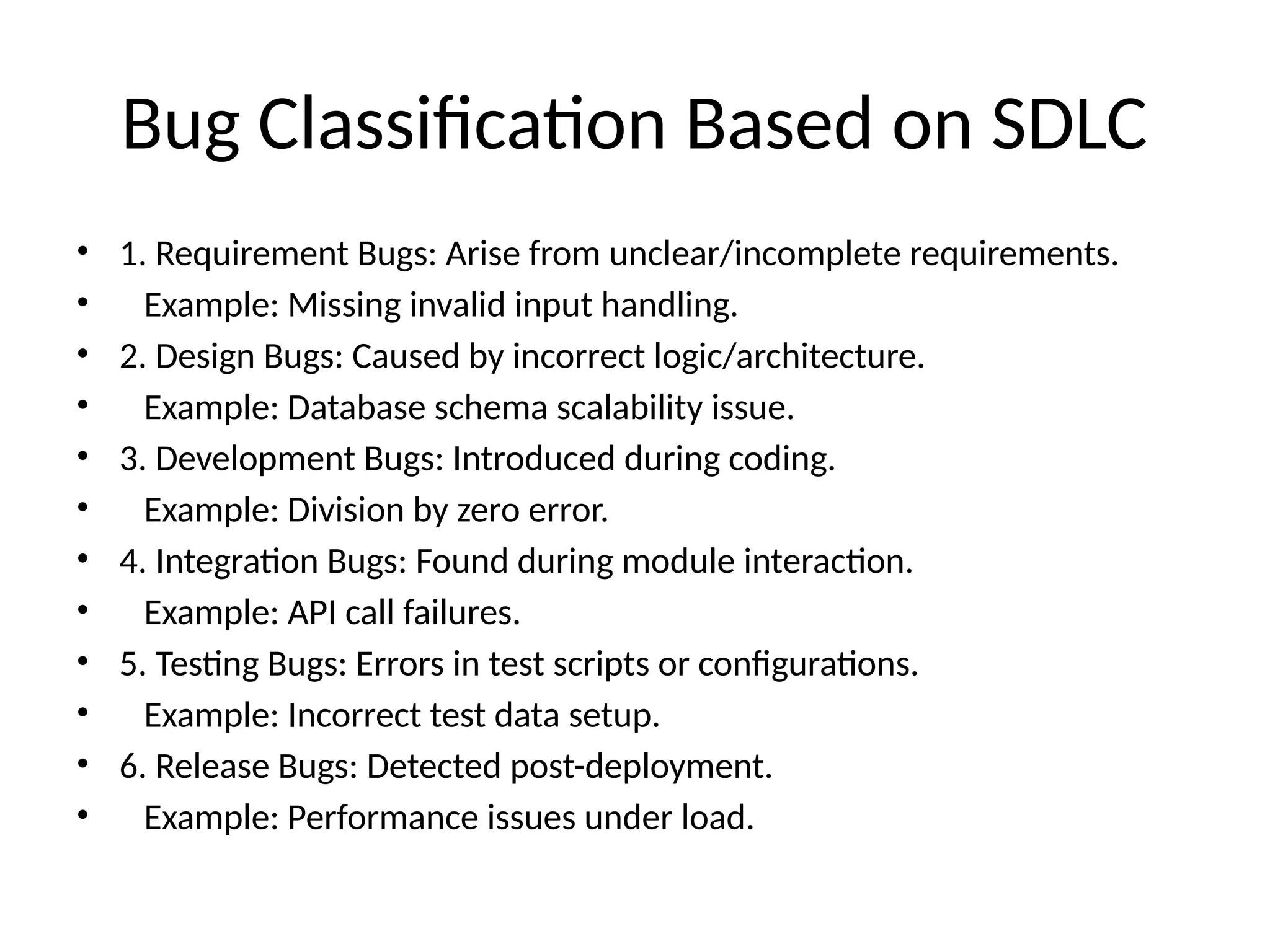
The document outlines the different states and classifications of software bugs, detailing 11 states from identification to closure. It categorizes bugs based on criticality into critical, major, minor, trivial, and blocker bugs, along with examples for clarity. Additionally, it classifies bugs according to the software development life cycle (SDLC), identifying six types, including requirement, design, and release bugs, with corresponding examples.