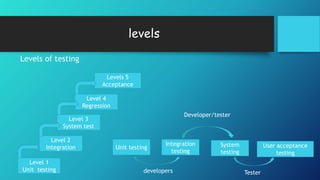
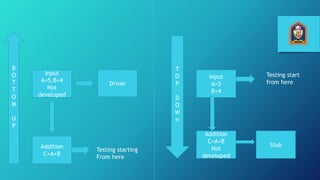
This document provides an overview of software testing. It defines software testing as evaluating software functionality to determine if it meets requirements and identifies defects. The document then describes different types of testing like unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing, and regression testing. It also discusses testing methods like static testing and dynamic testing. Finally, it covers topics like functional testing, performance testing, test drivers, test stubs, and top-down and bottom-up integration testing approaches.