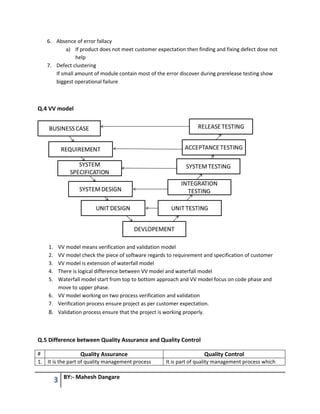
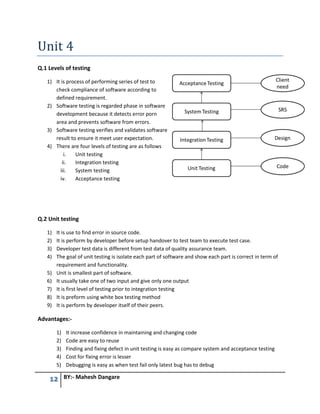
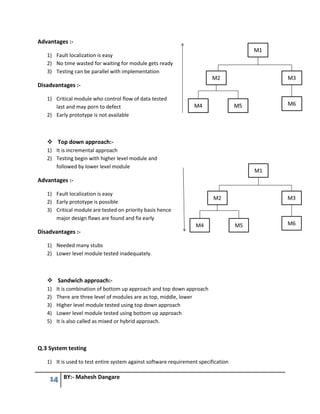
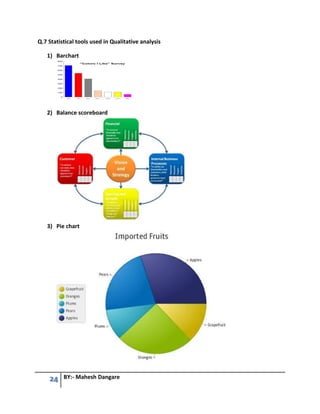
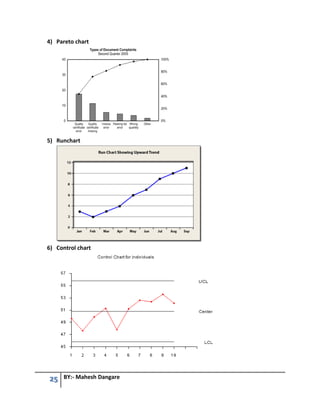
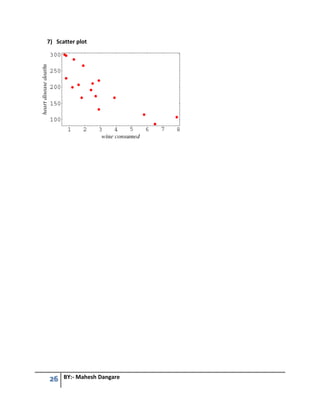
This document contains questions and answers related to software testing from a book authored by Mahesh Dangare. It covers topics like quality, testing principles, V-model, types of testing (black box vs white box, unit vs integration vs system testing), quality assurance vs quality control, and total quality management. The questions are divided into 6 units, with each unit covering a different testing concept and including multiple questions with detailed answers on that topic.