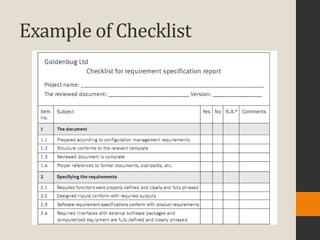
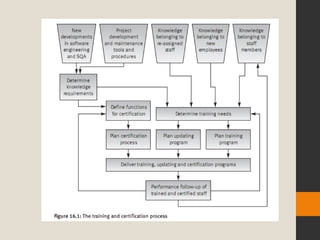
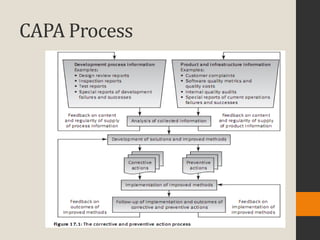
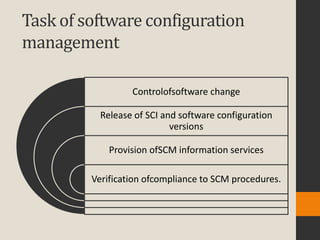
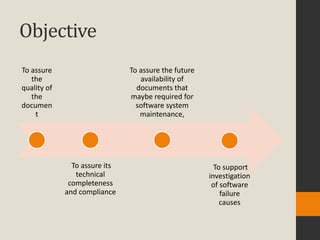
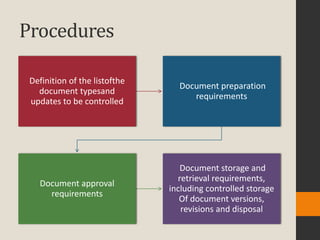
The document discusses various aspects of software quality infrastructure including procedures, work instructions, templates, checklists, staff training and certification, corrective and preventive actions, configuration management, and documentation control. It defines these terms and describes activities related to preparing, implementing, updating and using them to facilitate software development and quality assurance processes. The infrastructure aims to standardize processes, assure completeness and compliance, integrate new team members, and improve efficiency.