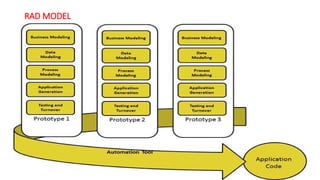
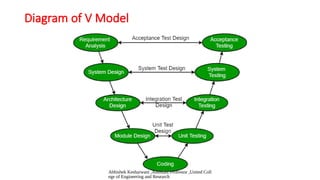
The document outlines the Rapid Application Development (RAD) model, emphasizing its prototyping and iterative approach, which allows for parallel component development and faster software delivery. It discusses business modeling, data modeling, process modeling, application generation, and testing, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of using RAD. Additionally, it describes the V-Model, which follows a sequential process with verification and validation phases for each development stage, specifying when each model is most applicable.














![Abhishek Kesharwani ,Assistant Professor ,United Coll
ege of Engineering and Research
Questions asked in different Software Companies
• What is the limitation of RAD Model?[TCS & Infosys]
• What are the merits of the incremental model?[HCL]
• What is the disadvantage of the spiral model? [TCS &
Infosys]
• Name the Evolutionary process Models.[Wipro]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extratopics-241218100126-28a73afc/85/Software-Engineering-unit-1-Notes-AKTU-ppt-17-320.jpg)