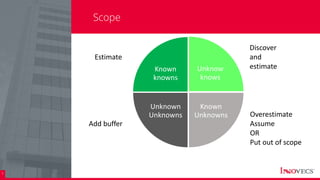
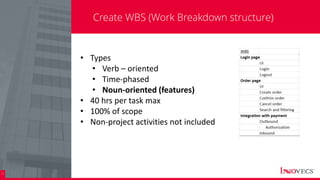
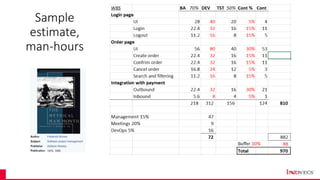
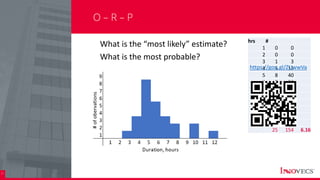
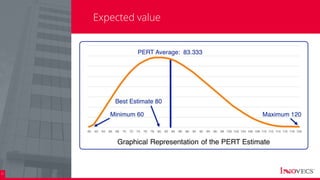
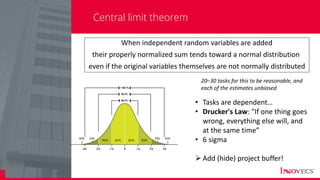
The document outlines the essential processes and considerations for software development project estimation, emphasizing the importance of accurate estimations for project success. It covers topics such as defining project scope, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), and handling risks and assumptions. Additionally, it provides practical tips and methodologies for estimating effort and duration, including the use of three-point estimation and various checklists.