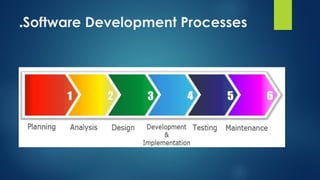
The document provides an overview of software design, detailing its definition, processes, levels, objectives, and approaches. It emphasizes that software design transforms user requirements into structured forms, moving through architectural, high-level, and detailed design. Key design principles discussed include abstraction, modularity, and information hiding, aiming for correctness, completeness, and efficiency in software development.