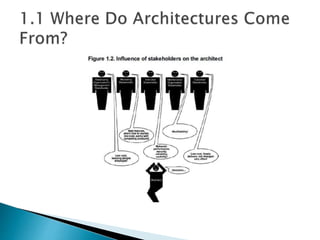
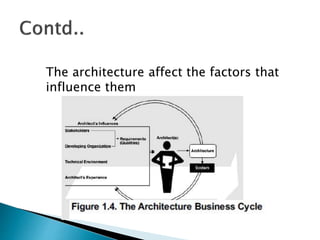
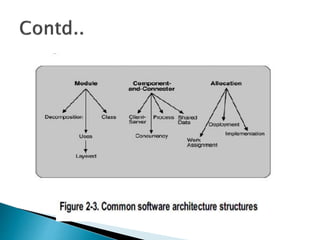
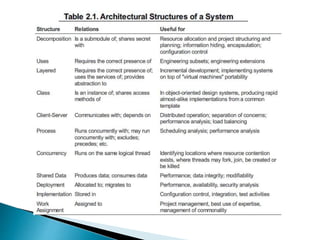
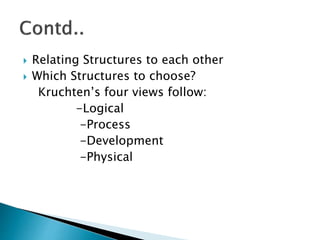
The document discusses the architecture business cycle (ABC) in software architecture, highlighting its definition and the influences that shape it, including system stakeholders and developers. It covers aspects such as defining good architecture, architectural patterns, reference models, and different structure categories like module and component-and-connector structures. Additionally, it outlines key architecture activities such as requirement understanding and architecture communication.