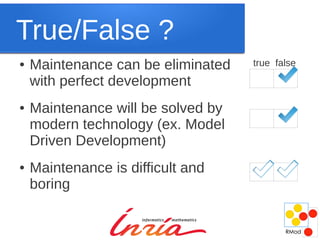
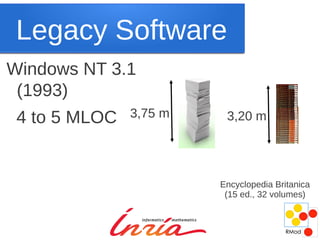
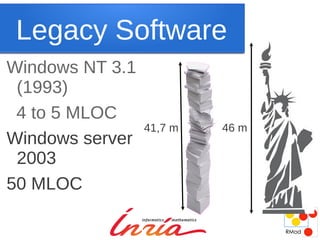
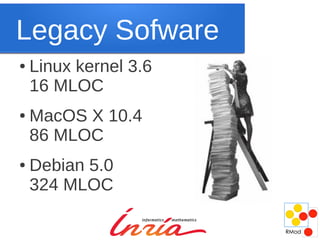
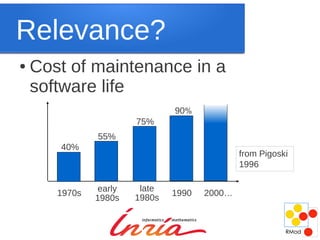
Maintenance is inevitable as software systems must evolve to adapt to changing needs and environments over time. While new development techniques may improve quality, they do not eliminate the need for maintenance, which accounts for a large portion of total costs in software engineering. Maintenance is challenging due to missing information and the need for backward compatibility, but it is not inherently boring and can provide interesting problems to solve. Changing the cultural perception of maintenance as punishment or of legacy systems as inferior is needed.















![Software systems must be
continually adapted or they become
progressively less satisfactory
First law of software evolution
[Lehman, 1974]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soft-evola-130119160505-phpapp01/85/Software-evolution-evangelisation-20-320.jpg)














![New techniques
● Cobol > 60% of all code in the
world [eWeeks, 2001]
● 180 GLOC in use, + 1GLOC/year
[Gartner, 2006]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soft-evola-130119160505-phpapp01/85/Software-evolution-evangelisation-35-320.jpg)