1) The document defines key terms related to trends in media ownership and control, new media technologies, news selection and moral panics, audience reception of media, and representations of gender, ethnicity, age, disability, and social class in media.
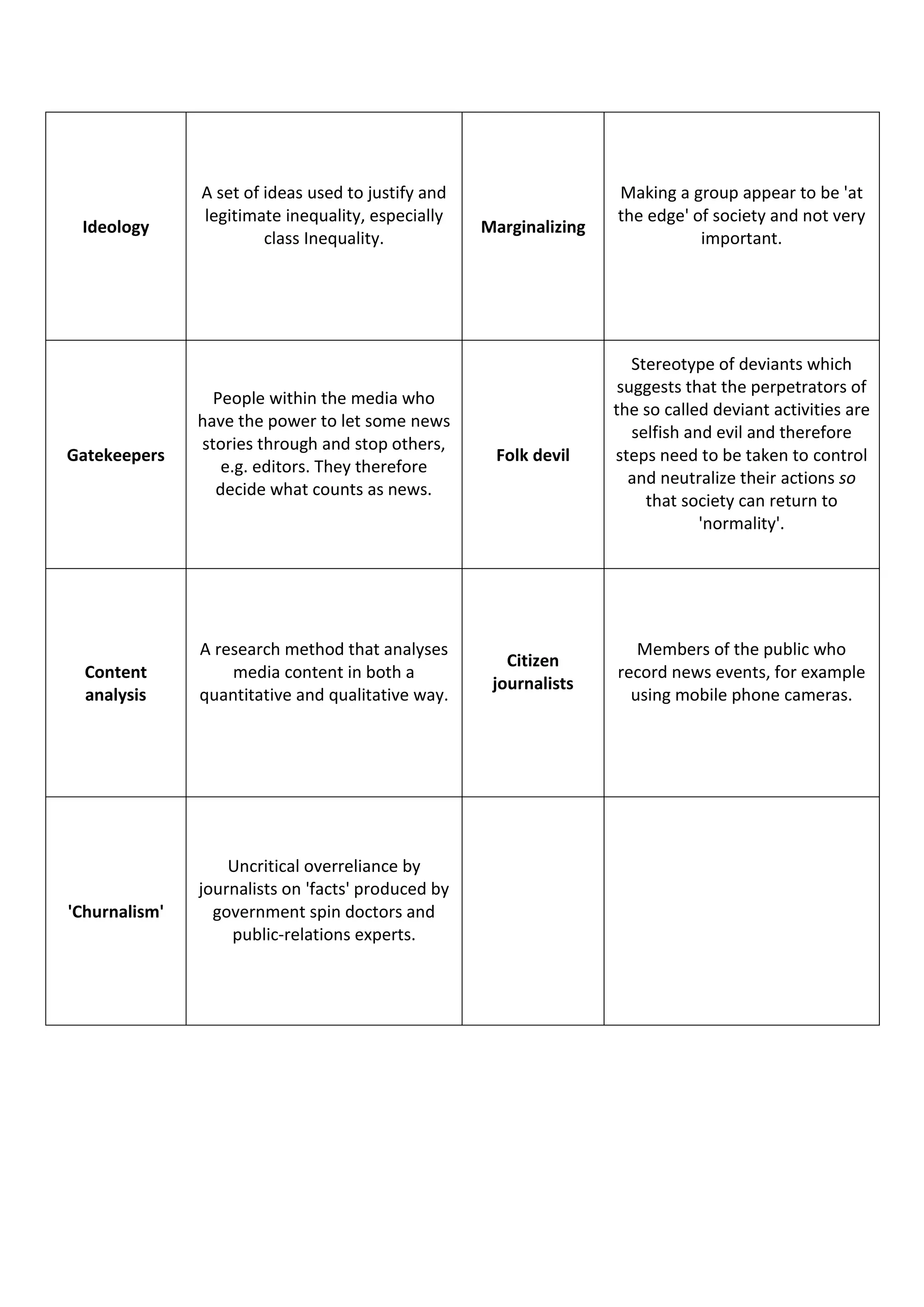
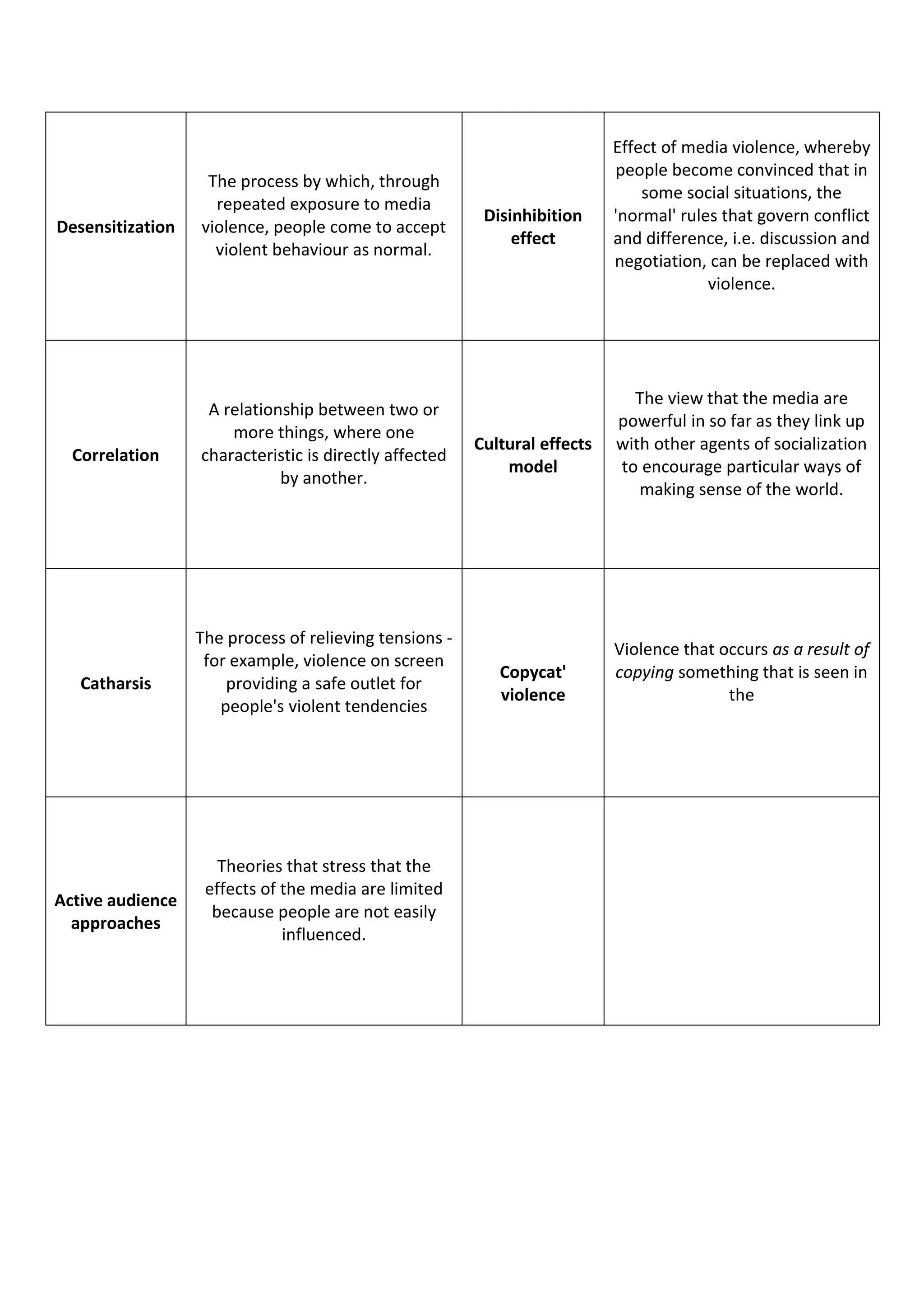
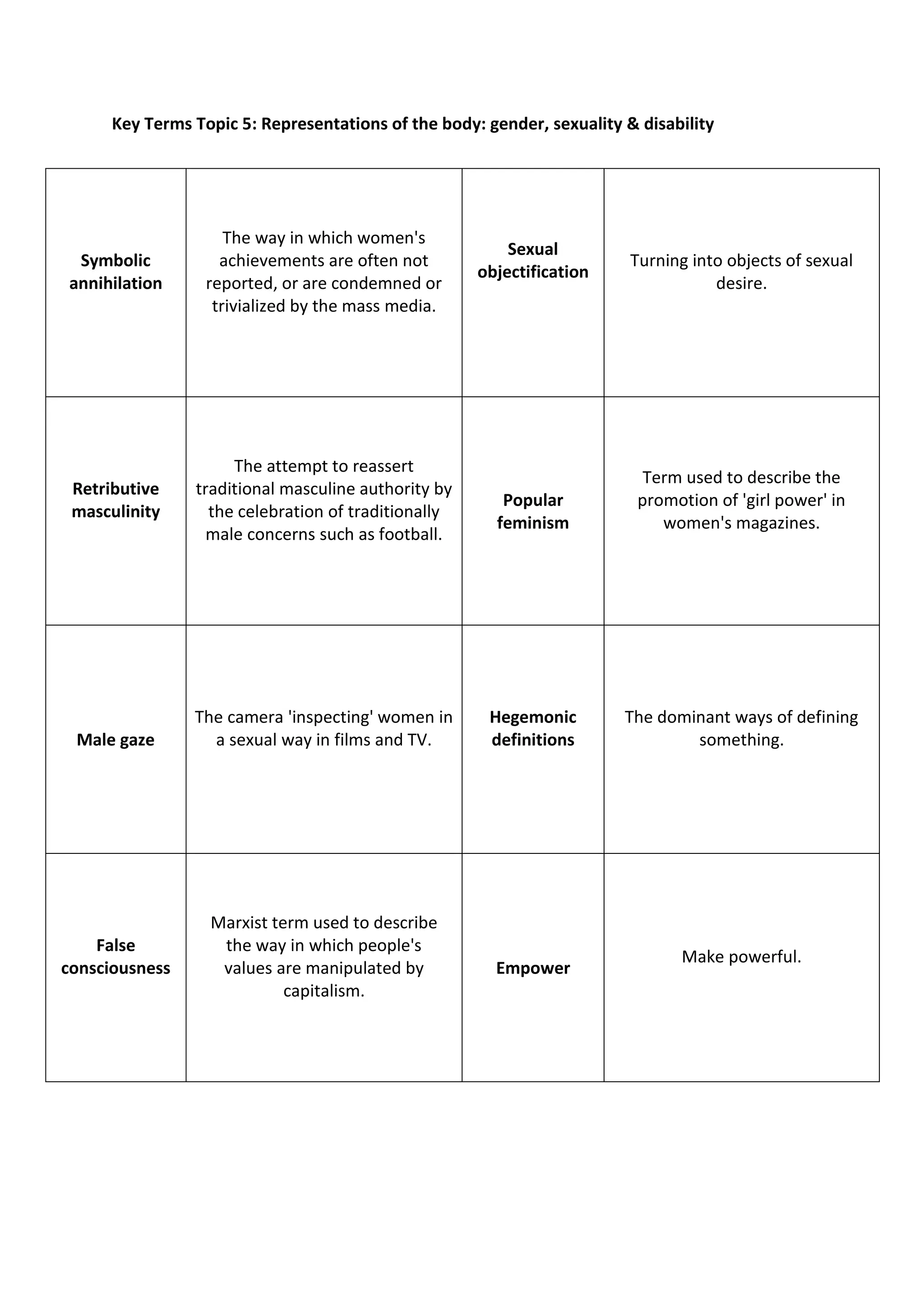
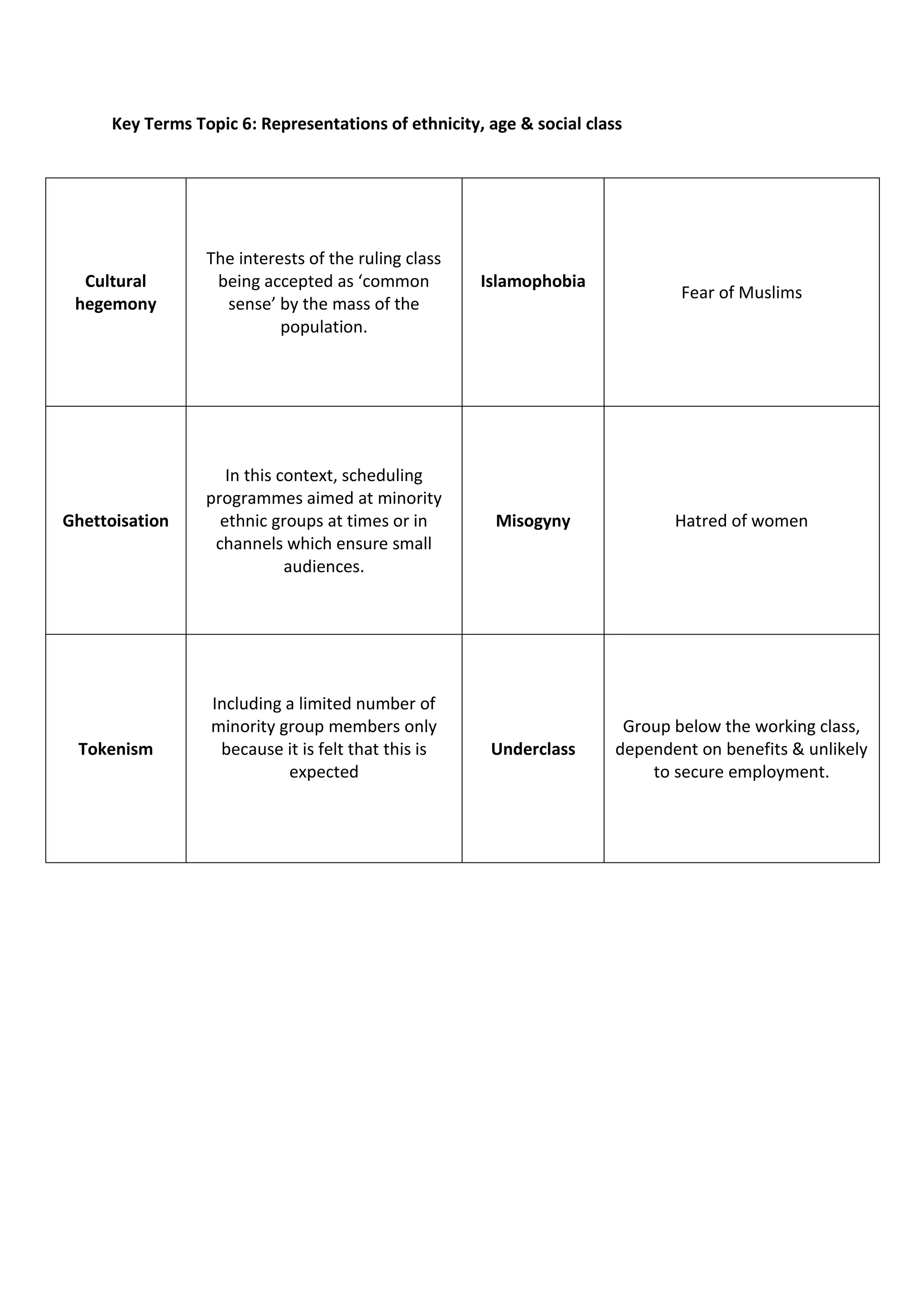
2) Some of the terms discussed include synergy, public service broadcasting, media concentration, agenda setting, collective intelligence, convergence, moral panics, gatekeepers, symbolic annihilation, male gaze, cultural hegemony, Islamophobia, and underclass.
3) The document provides definitions for over 50 key terms related to analyzing and understanding media industries and effects.