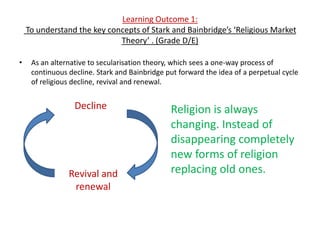
Stark and Bainbridge developed the Religious Market Theory to critique secularization theory. They believe religion is not declining as secularization predicts, but rather goes through perpetual cycles of decline and revival as religions adapt to meet consumer demand. Religious Market Theory views religion as operating in a competitive market, where churches provide compensators to attract followers. Stark and Bainbridge argue religion thrives in America's diverse religious market but declines in Europe due to historically dominant state churches creating religious monopolies with less incentive to adapt. While some evidence supports Religious Market Theory, critics argue factors beyond consumer choice also influence religious trends.