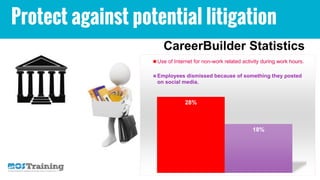
The document outlines essential guidelines for creating and implementing a social media policy in organizations, emphasizing the need to educate employees about proper social media use and the risks involved. It discusses the legal implications, best practices, and the importance of protecting both employees and the company's reputation. Various resources and case studies are provided to assist in developing relevant social media guidelines.