- SOA performance testing is challenging due to the distributed nature of SOA architectures and the need to test multiple applications, databases, technologies, and protocols.
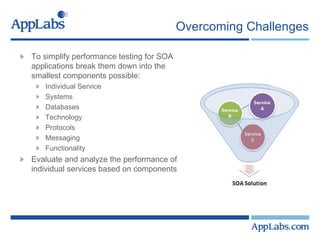
- A key part of SOA performance testing is breaking applications into their smallest components like individual services, systems, databases, and technologies and testing each component.
- The methodology involves discovery of services and components, test planning, automation for load generation, monitoring of performance under increasing load, and analysis of results.
- Automated testing tools are needed to simulate traffic at scale and monitor performance across the SOA infrastructure under varying loads.