Sniper rifles
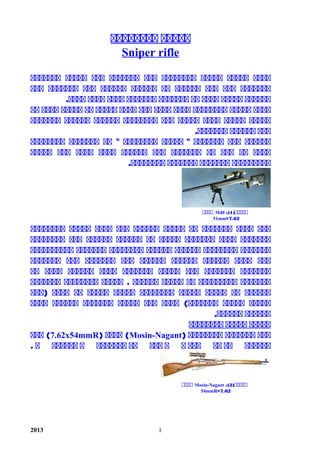
- 1. ققققققققققققق Sniper rifle ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.قققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققق.ققققققق قققققققققققققققق"ققققققققققققققق "ققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققق.قققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق .ققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق)ققق قققققققققققققق (قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققق.قققققق قققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققق)Mosin-Nagantقققق ()7.62x54mmRققق ( قق ققققققققق ققق ققق قققق قققققققق قققققق. 2013 )للللل1:(M40لللل 7.62×51mm )للللل2:(Mosin-Nagantلللل 7.62×54mmR 1
- 2. قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق)XM21( ققققققققق)M40.( ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق)Whitworth rifleققققققق ( ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق730ققققق قققققققققققققققققق.ققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققق)peep sightsققققققققق (قققققققققققققققق ()قققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق .قققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققق.قققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققق2.5xقق3xققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققق.ققققق قققققققققق:قققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق:ققق )1(قققققققققققققققققق )2(ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.ققققققق )3(ققققققققققق.ققققق )4(ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.قققققققق )5(قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق)Prone position.( قققققققققق:قققققققق )1(قققققققققققق)Anti-personnel( )2(قققققققققققق)Anti-material Rifleققققق (ققققققققققق :ققققق .قققققققققق.50BMG. 2013 )للللل3:(XM21 لM40 )للللل4:(Whitworth rifle 2
- 3. .قققققققققق20mm. ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق:ققققققق )1(قققققققققققققققققق)Parked Aircraft.( )2(قققققققققققققققق)TelecommunicationMasts.( )3(قققققققققق)Power Lines.( )4(قققققققققققققققققق)Missile Sites.( )5(قققققققققققققق)Radar Installations.( )6(قققققققققققق)Refineries.( )7(ققققققققققققققققققققق)Satellite Dishes.( )8(قققققققققققق)Gun Emplacements.( )9(ققققققققققققققق)Bunkers and Personnel.( )10(ققققققققق)Counter Sniping.( )11(قققققققققققققق)Ordnance Disposal.( قققققققققققققققققققق:قققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققق)Prone position.( قققققققققق:قققققققق .قققققققققققققق)ققققققققMilitary:( ققققققققققققققققققققققق:ققققققق )1(قققققققققققققققق.ققققق )2(ققققق.ققققق 2013 )للللل5للللللللللللللل :( للللللللللللل 3
- 4. )3(قققققققققققققققققق.قققققققق )4(ققققققققققق.قققققققق )5(ققققق.ققققققق )6(ققققق.ققققق )7(قققققق.ققققق .قققققققققققققققققق)Law enforcement:( )1(ققققققققققققق.قققق )2(ققق.ققققق ققققققق)ققققققTelescopic sight:( ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققق.ققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققق)4قققق (ققق)40ققق (ققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققق40قققققق50ققققققققققققققق قققققققق.قققققق 2013 )للللل6للللللللل :( 4
- 5. ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق )7قققق (قققققققققققققققققققققPSO-1ققققققققققققققققق قققققققق)Dragonovقققققق (قققققققققق:ققققققق 1قققق .قققققققق 2.قققققققققققققققق 3.قققققققققققققق 4.ققققققققق قققققققققققق:قققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققق:قققققققق قققققققققق :ققققققق)bolt-actionقققققق .(قققققق: )1(قققققققققققققققق.قققققققق )2(ققققققق.ققققق )3(قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.قققققق )4(قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.ققققق 2013 )للللل7لللللللللللللللل :( 5
- 6. قققققققققق :ققققققققققق)semi-automaticقققققق .(قققققق: )1(قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق. )2(ققققققققققققققققققققققققق.ققققق )3(ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق) Anti-material Rifle.( )4(ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققق)target-rich environments.( قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق ققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق.ققققق قققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققققق :قققققق ققق ققققققق قققققق ققققققق قق قققققق ققق ققققق ققققققق قق ققققق قققققق ققق ققققق ققققققق ققققق قق 30-06 Springfield 7.62×63mmAnti- personal USA1906-1970 & قققققققق M1903springfield M1917enfield Browning Automatic Rifle (BAR( 8mm Mauser 7.92×57mmAnti- personal Germany1905ققق قققق Zastava M76 MG 42 Gewehr 43 .303British7.7×56mmRAnti- personal United Kingdom 1889-1950Lee-Metford Lee Enfield .307.62×54mm RAnti- personal Russia1891Mosin-Nagant Dragunov sniper rifle .308 Winchester 7.62×51mm NATO. Anti- personal USA1950M14 rifle M60 machine gun 7mm Remington Magnum 7.2×64mmAnti- personal USA1962– Present Remington Model 700 2013 6
- 7. ععع ععععععع عععععع ععععععع عع عععععع ععع ععععع ععععععع عع ععععع عععععع ععع ععععع ععععععع ععععع عع .338Lapua Magnum 8.6×70mmAnti- personal Finland .50BMG12.7×99mm NATO Anti- material Rifle USA1921M2 Browning Accuracy International AS50 Barrett M82/M107 12.7× 108mm Russian 14.5× 114mm Russian Certain commercial cartridges designed with only performance in mind, without the logistical constraints of most armies, have also gained popularity in the 1990s. These include the 7 mm Remington Magnum (7.2×64mm), .300 Winchester Magnum (7.8/7.62×67mm), and the .338 Lapua Magnum (8.6×70mm). These cartridges offer better ballistic performance and greater effective range than the 7.62×51mm. Though they are not as powerful as .50 caliber cartridges, rifles chambered for these cartridges are not as heavy as rifles chambered for .50 caliber ammunition, and are significantly more powerful than rifles chambered for 7.62×51mm. Jaguar AMR of Bolivian origin. M82A1 SASR (Special Applications Scoped Rifle or Semi-Automatic Sniper Rifle), a .50 caliber sniper rifle used as an anti-materiel rifle. Snipers may also employ anti-materiel rifles in sniping roles against targets such as vehicles, equipment and structures, or for the long-range destruction of explosive devices; these rifles may also be used against personnel. 2013 7
- 8. Anti-materiel rifles tend to be semi-automatic and of a larger caliber than anti-personnel rifles, using cartridges such as the .50 BMG, 12.7×108mm Russian or even 14.5×114mm Russian and 20mm. These large cartridges are required to be able to fire projectiles containing payloads such as explosives, armor piercing cores, incendiaries or combinations of these, such as the Raufoss Mk211 projectile. Due to the considerable size and weight of anti-materiel rifles, 2- or 3-man sniper teams become necessary. Most telescopic lenses employed in military or police roles have special reticles to aid with judgment of distance, which is an important factor in accurate shot placement due to the bullet's trajectory. Sniper rifle From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from World war 1 sniper rifles) Jump to: navigation, search The 7.62×51mm M40, United States Marine Corps standard-issue sniper rifle. The Accuracy International Arctic Warfare series of sniper rifles is standard issue in the armies of many countries, including those of Britain and Germany (picture shows a rifle of the German Army). Bor – the 7.62×51 mm Polish bolt-action sniper rifle. In military and law enforcement terminology, a sniper rifle is a precision-rifle used to ensure more accurate placement of bullets at longer ranges than other small arms. A typical sniper rifle is built for optimal levels of accuracy, fitted with a telescopic sight and chambered for a military centerfire cartridge. The term is often used in the media to describe any type of accurized firearm fitted with a 2013 8 ععععع)1:(Mosin-Nagant
- 9. telescopic sight that is employed against human targets, although "sniping rifle" or "sniper's rifle" is the technically correct term for such a rifle. The military role of a sniper (a term derived from the snipe, a bird which was difficult to hunt and shoot) dates back to the turn of the 18th century, but the true sniper rifle is a much more recent development. Advances in technology, specifically that of telescopic sights and more accurate manufacturing, allowed armies to equip specially trained soldiers with rifles that enable them to deliver precise shots over greater distances than regular infantry weapons. The rifle itself could be based on a standard rifle (at first, a bolt-action rifle); however, when fitted with a telescopic sight, it becomes a sniper rifle. Contents [hide] • 1 History • 2 Classification o 2.1 Military o 2.2 Law enforcement • 3 Distinguishing characteristics o 3.1 Telescopic sight o 3.2 Action o 3.3 Cartridge o 3.4 Barrel o 3.5 Stock o 3.6 Accessories • 4 Capabilities o 4.1 Accuracy o 4.2 Maximum effective range • 5 See also • 6 Notes • 7 References • 8 External links [edit] History During World War II, the (7.62×54mmR) Mosin-Nagant rifle mounted with a telescopic sight was commonly used as a sniper rifle by Russian snipers. Vietnam War era sniper rifles, US Army XM21 (top) and USMC M40 (bottom) 2013 9
- 10. In the American Civil War, Confederate troops equipped with barrel-length three power scopes mounted on the exceptionally accurate British Whitworth rifle had been known to kill Union officers at ranges of about 800 yards (731.5m), an unheard-of distance at that time.[1][2][3][4] The earliest sniper rifles were little more than conventional military or target rifles with long-range "peep sights" and Galilean 'open telescope' front and rear sights, designed for use on the target range. Only from the beginning of World War I did specially adapted sniper rifles come to the fore. Germany deployed military caliber hunting rifles with telescopic sights, and the British used Aldis, Winchester and Periscopic Prism Co. sights fitted by gunsmiths to regulation SMLE Mk III and Mk III* or Enfield Pattern 1914 rifles; the Canadian Ross rifle was also employed by snipers after it had been withdrawn from general issue. Typical World War II-era sniper rifles were generally standard-issue battle rifles, selected for accuracy, with a 2.5× or 3× telescopic sight and cheek-rest fitted and the bolt turned down if necessary to allow operation with the scope fitted. Australia's No.1 Mk III* (HT) rifle was a later conversion of the SMLE fitted with the Lithgow heavy target barrel at the end of WW2. By the end of the war, forces on all sides had specially trained soldiers equipped with sniper rifles, and they have played an increasingly important role in military operations ever since. [edit] Classification Modern sniper rifles can be divided into two basic classes: military and law enforcement. [edit] Military U.S. Marine Corps SRT sniper team with an M24 sniper rifle, during sniper training. Macedonian special policeman holding a Zastava M76. Sniper rifles manufactured for military service are often designed for very high durability, range, reliability, sturdiness, serviceability and repairability under adverse environmental and combat conditions, at the sacrifice of a small degree of accuracy. Military snipers and sharpshooters may also be required to carry their rifles and other equipment for long distances, making it important to minimize weight. Military organizations often operate under strict budget constraints, which influences the type and quality of sniper rifles they purchase. 2013 10
- 11. [edit] Law enforcement Sniper rifles built or modified for use in law enforcement are generally required to have the greatest possible accuracy, more than military rifles, but do not need to have as long a range. As law enforcement-specific rifles are usually used in non-combat (often urban) environments, they do not have the requirement to be as hardy or portable as military versions; nevertheless they may be smaller, as they do not need very long range. Some of the first sniper rifles designed specifically to meet police and other law-enforcement requirements were developed for West German police after the Munich massacre at the 1972 Summer Olympics. Many police services and law enforcement organizations (such as the U.S. Secret Service) now use rifles designed for law enforcement purposes. The Heckler & Koch PSG1 is one rifle specifically designed to meet these criteria and is often referred to as an ideal example of this type of sniper rifle. The FN Special Police Rifle was built for, and is marketed to, law enforcement rather than military agencies. [edit] Distinguishing characteristics Looking through a telescopic sight. PSO-1 Sniper Scope Reticle 1 - Lead/deflection scale 2 - Main targeting chevron 3 - Bullet drop chevrons 4 - Rangefinder The features of a sniper rifle can vary widely depending on the specific tasks it is intended to perform. Features that may distinguish a sniper rifle from other weapons are the presence of a 2013 11
- 12. telescopic sight, unusually long overall length,[5] a stock designed for firing from a prone position, and the presence of a bipod and other accessories. [edit] Telescopic sight The single most important characteristic that sets a sniper rifle apart from other military or police small arms is the mounting of a telescopic sight, which is relatively easy to distinguish from smaller optical aiming devices found on some modern assault rifles and submachine guns. This also allows the user to see farther. The telescopic sights used on sniper rifles differ from other optical sights in that they offer much greater magnification (more than 4× and up to 40×), and have a much larger objective lens (40 to 50 mm in diameter) for a brighter image. Most telescopic lenses employed in military or police roles have special reticles to aid with judgment of distance, which is an important factor in accurate shot placement due to the bullet's trajectory. [edit] Action The choice between bolt-action and semi-automatic (more commonly known as recoil or gas operation) is usually determined by specific requirements of the sniper's role as envisioned in a particular organization, with each design having advantages and disadvantages. For a given cartridge, a bolt-action rifle is cheaper to build and maintain, more reliable, and lighter, due to fewer moving parts in the mechanism. In addition, the absence of uncontrolled automatic cartridge case ejection helped to avoid revealing the firer's position. Semi-automatic weapons can serve both as battle rifle and sniper rifle, and allow for a greater rate (and hence volume) of fire. As such rifles may be modified service rifles, an additional benefit can be commonality of operation with the issued infantry rifle. A bolt action is most commonly used in both military and police roles due to its higher accuracy and ease of maintenance. Anti-materiel applications such as mine clearing and special forces operations tend to use semi-automatics. A Marine manually extracts an empty cartridge and chambers a new 7.62×51mm round in his bolt- action M40A3 sniper rifle. The bolt handle is held in the shooter's hand and is not visible in this photo. A designated marksman rifle (DMR) is less specialized than a typical military sniper rifle, often only intended to extend the range of a group of soldiers. Therefore, when a semi-automatic action is used it is due to its ability to cross over into roles similar to the roles of standard issue weapons. There may also be additional logistical advantages if the DMR uses the same ammunition as the more common standard issue weapons. These rifles enable a higher volume of fire, but sacrifice some long range accuracy. They are frequently built from existing selective fire battle rifles or assault rifles, often simply by adding a telescopic sight and adjustable stock. 2013 12
- 13. A police semi-automatic sniper rifle may be used in situations that require a single sniper to engage multiple targets in quick succession, and military semi-automatics such as the M110 SASS are used in similar "target-rich" environments. [edit] Cartridge In a military setting, logistical concerns are the primary determinant of the cartridge used, so sniper rifles are usually limited to rifle cartridges commonly used by the military force employing the rifle and match grade ammunition. Since large national militaries generally change slowly, military rifle ammunition is frequently battle-tested and well-studied by ammunition and firearms experts. Consequently, police forces tend to follow military practices in choosing a sniper rifle cartridge instead of trying to break new ground with less-perfected (but possibly better) ammunition. Before the introduction of the standard 7.62×51mm NATO (.308 Winchester) cartridge in the 1950s, standard military cartridges were the .30-06 Springfield or 7.62×63mm (United States), .303 British (7.7×56mmR) (United Kingdom) and 7.92×57mm (8mm Mauser) (Germany). The .30-06 Springfield continued in service with U.S. Marine Corps snipers during the Vietnam War in the 1970s, well after general adoption of the 7.62×51mm. At the present time, in both the Western world and within NATO, 7.62×51mm is currently the primary cartridge of choice for military and police sniper rifles. Worldwide, the trend is similar. The preferred sniper cartridge in Russia is another .30 caliber military cartridge, the 7.62 × 54 mm R, which has similar performance to the 7.62×51mm. This cartridge was introduced in 1891, and both Russian sniper rifles of the modern era, the Mosin- Nagant and the Dragunov sniper rifle, are chambered for it. Certain commercial cartridges designed with only performance in mind, without the logistical constraints of most armies, have also gained popularity in the 1990s. These include the 7 mm Remington Magnum (7.2×64mm), .300 Winchester Magnum (7.8/7.62×67mm), and the .338 Lapua Magnum (8.6×70mm). These cartridges offer better ballistic performance and greater effective range than the 7.62×51mm. Though they are not as powerful as .50 caliber cartridges, rifles chambered for these cartridges are not as heavy as rifles chambered for .50 caliber ammunition, and are significantly more powerful than rifles chambered for 7.62×51mm. Jaguar AMR of Bolivian origin. M82A1 SASR (Special Applications Scoped Rifle or Semi-Automatic Sniper Rifle), a .50 caliber sniper rifle used as an anti-materiel rifle. 2013 13
- 14. Snipers may also employ anti-materiel rifles in sniping roles against targets such as vehicles, equipment and structures, or for the long-range destruction of explosive devices; these rifles may also be used against personnel. Anti-materiel rifles tend to be semi-automatic and of a larger caliber than anti-personnel rifles, using cartridges such as the .50 BMG, 12.7×108mm Russian or even 14.5×114mm Russian and 20mm. These large cartridges are required to be able to fire projectiles containing payloads such as explosives, armor piercing cores, incendiaries or combinations of these, such as the Raufoss Mk211 projectile. Due to the considerable size and weight of anti-materiel rifles, 2- or 3-man sniper teams become necessary. [edit] Barrel Barrels are normally of precise manufacture and of a heavier cross section than more traditional barrels in order to reduce the change in impact points between a first shot from a cold barrel and a follow-up shot from a warm barrel. Unlike many battle and assault rifles, the bores are usually not chromed to avoid inaccuracy due to an uneven treatment. When installed, barrels are often free-floated: i.e., installed so that the barrel only contacts the rest of the rifle at the receiver, to minimise the effects on impact point of pressure on the fore-end by slings, bipods, or the sniper's hands. The end of the barrel is usually crowned or machined to form a rebated area around the muzzle proper to avoid asymmetry or damage, and consequent inaccuracy. Alternatively, some rifles such as the Dragunov or Walther WA2000 provide structures at the fore- end to provide tension on the barrel in order to counteract barrel drop and other alterations in barrel shape. External longitudinal fluting that contributes to heat dissipation by increasing surface area, while simultaneously decreasing the weight of the barrel, is sometimes used on sniper-rifle barrels. Sniper-rifle barrels may also utilise a threaded muzzle or combination device (muzzle brake or flash suppressor and attachment mount) to allow the fitting of a sound suppressor. These suppressors often have a means of adjusting the point of impact while fitted. Military sniper rifles tend to have barrel lengths of 609.6 mm (24 inches) or longer, to allow the cartridge propellant to fully burn, reducing the amount of revealing muzzle flash and increasing bullet velocity. Police sniper rifles may use shorter barrels to improve handling characteristics. The shorter barrels' velocity loss is unimportant at closer ranges; projectile energy is more than sufficient. 2013 14
- 15. [edit] Stock The most common special feature of a sniper rifle stock is the adjustable cheek piece, where the shooter's cheek meets the rear of the stock. For most rifles equipped with a telescopic sight, this area is raised slightly, because the telescope is positioned higher than iron sights. A cheek piece is simply a section of the stock that can be adjusted up or down to suit the individual shooter. To further aid this individual fitting, the stock can sometimes also be adjusted for length, often by varying the number of inserts at the rear of the stock where it meets the shooter's shoulder. Sniper stocks are typically designed to avoid making contact with the barrel of the weapon. [edit] Accessories An adjustable sling is often fitted on the rifle, used by the sniper to achieve better stability when standing, kneeling, or sitting. The sniper uses the sling to "lock-in" by wrapping his non-firing arm into the sling forcing his arm to be still. Non-static weapon mounts such as bipods, monopods and shooting sticks are also regularly used to aid and improve stability and reduce operator fatigue. [edit] Capabilities [edit] Accuracy 2013 15
- 16. Comparison of 0.5, 1, and 3 MOA extreme spread levels against a human torso at 800 m (left) and a human head at 100 m (right) A military-issue battle rifle or assault rifle is usually capable of between 3-6 minute of angle (MOA) (1-2 mrad) accuracy.[6] A standard-issue military sniper rifle is typically capable of 1-3 MOA (0.3-1 mrad) accuracy, with a police sniper rifle capable of 0.25-1.5 MOA (0.1-0.5 mrad) accuracy. For comparison, a competition target or benchrest rifle may be capable of accuracy up to 0.15-0.3 MOA (0.05-0.1 mrad). A 1 MOA (0.3 mrad) average extreme spread for a 5-shot group (meaning the center-to-center distance between the two most distant bullet holes in a shot-group) translates into a 69% probability that the bullet's point of impact will be in a target circle with a diameter of 23.3 cm (9.2 in) at 800 m (875 yd).[7] This average extreme spread for a 5-shot group and the accompanying hit probability are considered sufficient for effectively hitting a human shape at 800 m distance. In 1982 a U.S. Army draft requirement for a Sniper Weapon System was: "The System will: (6) Have an accuracy of no more than 0.75 MOA (0.2 mrad) for a 5-shot group at 1,500 meters when fired from a supported, non-benchrest position".[8] Actual Sniper Weapon System (M24) adopted in 1988 has stated maximum effective range of 800 meters and a maximum allowed average mean radius (AMR) of 1.9 inches at 300 yards from a machine rest, what corresponds to a 0.6 MOA (0.5 mrad) extreme spread for a 5-shot group when using 7.62 × 51 mm M118 Special Ball cartridges.[9] [10][11] Precision Weapon Engagement Ranges & Dispersion according to the US Army. 2013 16
- 17. A 2008 United States military market survey for a Precision Sniper Rifle (PSR) calls for 1 MOA (0.3 mrad) extreme vertical spread for all shots in a 5-round group fired at targets at 300, 600, 900, 1,200 and 1,500 meters.[12][13] In 2009 a United States Special Operations Command market survey calls for 1 MOA (0.3 mrad) extreme vertical spread for all shots in a 10-round group fired at targets at 300, 600, 900, 1,200 and 1,500 meters.[14][15] The 2009 Precession Sniper Rifle requirements state that the PSR when fired without suppressor shall provide a confidence factor of 80% that the weapon and ammunition combination is capable of holding 1 MOA extreme vertical spread. This shall be calculated from 150 ten (10) round groups that were fired unsuppressed. No individual group shall exceed 1.5 MOA (0.5 mrad) extreme vertical spread. All accuracy will be taken at the 1,500 meter point.[16][17] In 2008 the US military adopted the M110 Semi-Automatic Sniper System which has corresponding maximum allowed extreme spread of 1.8 MOA (0.5 mrad) for a 5-shot group on 300 feet, using M118LR ammunition or equivalent.[9][10][18] In 2010 maximum bullet dispersion requirement for M24 .300 Winchester Magnum corresponds[9][10] 1.4 MOA extreme spread for 5 shot group on 100 meters.[19] Although accuracy standards for police rifles do not widely exist, rifles are frequently seen with accuracy levels from 0.5-1.5 MOA (0.2-0.5 mrad).[20] For typical policing situations, an extreme spread accuracy level no better than 1 MOA (0.3 mrad) is usually all that is required. This is because police typically employ their rifles at short ranges.[21] At 100 m or less, a rifle with a relatively low accuracy of only 1 MOA (0.3 mrad) should be able to repeatedly hit a 3 cm (1.2 inch) target. A 3 cm diameter target is smaller than the brain stem which is targeted by police snipers for its quick killing effect.[22] [edit] Maximum effective range Cartridge Maximum effective range[23] 7.62×39mm 600 m 5.56×45mm 800 m [24] 7.62×51mm (.308 Winchester) 800 m 7.62×54mm R 800 m .30-06 Springfield 800 m 7 mm Remington Magnum 900–1,100 m .300 Winchester Magnum 900–1,200 m .338 Lapua Magnum 1,200-1,500 m .50 BMG (12.7×99mm NATO) 12.7×108mm (Russian) 1,500–2,000 m 14.5×114mm 1,800–2,300 m Unlike police sniper rifles, military sniper rifles tend to be employed at the greatest possible distances so that range advantages like the increased difficulty to spot and engage the sniper can be exploited. The most popular military sniper rifles (in terms of numbers in service) are chambered for 7.62 mm (0.30 inch) caliber ammunition, such as 7.62×51mm and 7.62×54mm R. Since sniper rifles of this class must compete with several other types of military weapons with similar range, snipers invariably must employ skilled fieldcraft to conceal their position. .338Lapua Magnum.50BMG14.5×114mm The recent trend in specialized military sniper rifles is towards larger calibers that offer relatively favorable hit probabilities at greater range, such as the anti-personnel .338 Lapua Magnum cartridge 2013 17
- 18. and anti-materiel cartridges like the .50 BMG and the 14.5×114mm. This allows snipers to take fewer risks, and spend less time finding concealment when facing enemies that are not equipped with similar weapons. Maximum range claims made by military organizations and materiel manufacturers regarding sniper weapon systems are not based on consistent or strictly scientific criteria. The problem is only the bullet interacts after a relatively long flight path with the target (can also be a materiel target for a sniper bullet). This implies that variables such as the minimal required hit probability, local atmospheric conditions, properties and velocity of the employed bullet (parts), properties of the target and the desired terminal effect are major relevant factors that determine the maximum effective range of the employed system. [edit] See also • Longest recorded sniper kills Related military roles • Sniper • Scout Sniper • Designated marksman Related military weapons • List of sniper rifles • Assault rifle • Battle rifle • Carbine rifle • Marksman rifle • Anti-tank rifle • Anti-materiel rifle [edit] Notes 1. ^ Snipers in History 2. ^ Whitworth Rifle No. C529 3. ^ Whitworth Sharpshooter Rifle 4. ^ Artillery of the Civil War 5. ^ The Ultimate Sniper: an Advanced Training Manual for Military and Police Snipers, Maj. John L. Plaster, 1993. The information about counter-sniper operations describes techniques for identifying snipers amongst groups of other soldiers. The most easily recognizable feature of a sniper from a great distance is the fact that the sniper's rifle is longer than all the others. 6. ^ T.W. Lee. Military Technologies of the World. p. 237. 7. ^ Statistical notes on rifle group patterns by Robert E. Wheeler 8. ^ AMSAA Technical report No. 461 9. ^ a b c http://www.bobwheeler.com/guns/GroupStat.pdf Statistical notes on rifle group patterns 10. ^ a b c http://enotus.blog.tut.by/2009/04/09/rasseivanie-vyistrelov-kuchnost-pokazateli-i-zavisimost/ (in Russian) 11. ^ MIL-R-71126(AR) at everyspec.com 12. ^ US Special Operations Considers A ".338" Sniper Rifle 13. ^ Precession Sniper Rifle - Solicitation Number: H92222-09-PSR 14. ^ Precision Sniper Rifle (PSR) - Solicitation Number: H92222-09-PSR2 2013 18
- 19. 15. ^ SOCOM PSR Contenders 16. ^ Precision Sniper Rifles Systems (PSR) Draft Go/No-Go Requirements 17. ^ Precision Sniper Rifle (PSR) Vendor Questionnaire 18. ^ http://www.everyspec.com/MIL-PRF/MIL-PRF+%28030000+-+79999%29/MIL-PRF- 32316_AMENDMENT-1_25025/ 19. ^ M24 Sniper Weapon System Reconfiguration 20. ^ The FBI, a national-level policing organization, has recently specified an accuracy level of 0.5 MOA for 5 shots at 100 yd for sniper rifles issued to their SWAT teams: Johnson, D: Precision Pair, Guns & Ammo, February 2005.[1] 21. ^ Minimum documented range is 5 yards, maximum documented range is 187 yards: Police Sniper Utilization Survey, American Sniper Association, 2006, full report available to military and law enforcement agencies only.[2] [3] Some information publicly available from The Ultimate Sniper: an Advanced Training Manual for Military and Police Snipers, Major John Plaster, 1993. 22. ^ Police Sniper Training, Major John Plaster, 1990.[4] 23. ^ Approximate maximum effective ranges of common cartridges when used in an adequately accurate rifle system with special long-range high accuracy ammunition at International Standard Atmosphere sea level conditions Common Calibers Used by Snipers<references/> 24. ^ "Philippine MSSR - Marine Scout Sniper Rifle - Sniper Central.com". http://www.snipercentral.com/mssr.htm. Retrieved 2009-05-22."Marine Scout Sniper Rifle". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marine_Scout_Sniper_Rifle. Retrieved 2011-09-19.] [edit] References • Tobias, Ronald (1981). They Shoot to Kill: A Psycho-History of Criminal Sniping. Boulder, Colorado: Paladin Press. ISBN 0-87364-207-4. • De Haas, Frank (1995). Bolt Action Rifles. Krause Publications. ISBN 0-87349-168-8. [edit] External links Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Sniper rifles • Modern Firearms list of sniper rifles • SniperCentral list of sniper rifles • Mcmillan Tactical Stocks — Images of tactical stocks from the world's leading supplier manufacturer • Tack Driving Tactical Rifle from Tac Ops — Detailed overview of the accurization process for a .25 MOA rifle • Detailed accuracy articles, by famous barrel maker Dan Lilja • Detail of Russian snipers and sniper rifles of World War Two by Chris Eger, military historian • demigodllc.com: Practical long-range rifle shooting Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php? title=Sniper_rifle&oldid=532573927#History" Categories: • Sniper rifles Navigation menu Personal tools • Create account 2013 19
- 20. • Log in Namespaces • Article • Talk Variants Views • Read • Edit • View history Actions Search Navigation • Main page • Contents • Featured content • Current events • Random article • Donate to Wikipedia Interaction • Help • About Wikipedia • Community portal • Recent changes • Contact Wikipedia Toolbox • What links here • Related changes • Upload file • Special pages • Permanent link • Page information • Cite this page • Add your feedback • View feedback 2013 20
- 21. Print/export • Create a book • Download as PDF • Printable version Languages • • Azərbaycanca • Беларуская • Български • Català • Česky • Dansk • Deutsch • Eesti • Español • Esperanto • • Français • 한국어 • Hrvatski • Bahasa Indonesia • Italiano • • • Bahasa Melayu • Nederlands • 日本語 • Norsk (bokmål) • Polski • Português • Русский • • Simple English • Slovenčina • Slovenščina • Српски / srpski • Srpskohrvatski / српскохрватски • Suomi • Svenska • ไไไ • Türkçe • Українська • Tiếng Việt • 中文 • This page was last modified on 11 January 2013 at 18:13. 2013 21
- 22. • Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. See Terms of Use for details. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization. • Contact us • Privacy policy • About Wikipedia • Disclaimers • Mobile view • • ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة)ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة(ةة3-6MOA ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة1-3MOA ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة0.25-1.5 MOA ةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةةة0.15-0.3 MOA 2013 22