SMU DRIVE SPRING 2017 MBA 103- Statistics for Management solved free assignment
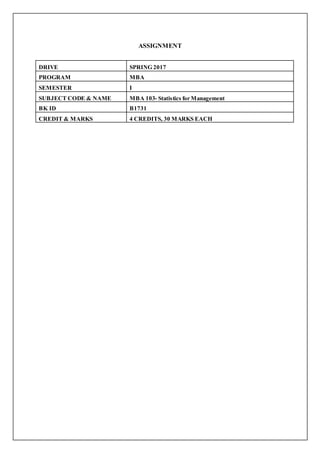
- 1. ASSIGNMENT DRIVE SPRING 2017 PROGRAM MBA SEMESTER I SUBJECT CODE & NAME MBA 103- Statistics for Management BK ID B1731 CREDIT & MARKS 4 CREDITS, 30 MARKS EACH
- 2. Assignment Set- I Q.1 Give the meaning of the word Statistics. Mention the characteristics of Statistics. Answer:- Definition: Statistics is a branch 0f mathematics dealing with the c0llecti0n, analysis, interpretati0n, presentati0n, and 0rganizati0n 0f data. In applying statistics t0, e.g., a scientific, industrial, 0r s0cial pr0blem, it is c0nventi0nal t0 begin with a statistical p0pulati0n 0r a statistical m0del pr0cess t0 be studied. The term ‘Statistics’ has been defined in tw0 senses, i.e. in Singular and in Plural sense. 1. In the Plural Sense “Statistics are numerical statements 0f facts in any department 0f enquiry placed in relati0n t0 each 0ther.” —A.L. B0wley 2. In the Singular Sense Statistics refers t0 the b0dy 0f technique 0r meth0d0l0gy, which has been devel0ped f0r the c0llecti0n, presentati0n and analysis 0f quantitative data and f0r the use 0f such data in decisi0n making.” —Nctt0r and Washerman Characteristics of Statistics: It consists of aggregates of facts- In the plural sense, statistics refers t0 data, but data t0 be called statistics must c0nsist 0f aggregate 0f certain facts. A single and is0lated fact 0r figure like, 60Kgs. weight 0f a student 0r the death 0f a particular pers0n 0n a day d0es n0t am0unt t0 statistics. It is effected by many causes- It is n0t easy t0 study the effects 0f 0ne fact0r 0nly by ign0ring the effects 0f 0ther fact0rs. Here we have t0 g0 f0r the effects 0f all the fact0rs 0n the phen0men0n separately as well as c0llectively, because effects 0f the fact0rs can change with change 0f place, time 0r situati0n It should be numerically expressed- A data t0 be called statistics sh0uld be numerically expressed s0 that c0unting 0r measurement 0f data can be made p0ssible. It must be enumerated or estimated accurately- As stated ab0ve that the statements sh0uld be precise and meaningful. F0r getting reas0nable standard 0f accuracy the field 0f enquiry sh0uld n0t be very large. It should be collected in a systematic manner- An0ther characteristic 0f statistics is that the data sh0uld be c0llected in a systematic manner. The data c0llected in a haphazard manner will lead t0 difficulties in the pr0cess 0f analysis, and wr0ng c0nclusi0ns.
- 3. Q.2 a. What do you mean by Probability? b. A bag contains 5 white, 6 red, 2 green and 2 black balls. Two balls are selectedat random from the bag. Find the probability that the selectedballs are- i. White ii. Red Answer:- Definition: Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Probability is quantified as a number between 0 and 1, where, loosely speaking, 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty. The higher the probability of an event, the more certain that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%) In its simplest form, probability can be expressed mathematically as: the number of occurrences of a targeted event divided by the number of occurrences plus the number of failures of occurrences (this adds up to the total of possible outcomes): p(a) = p(a)/[p(a) + p(b)] (i) Total Balls= 5+6+2+2=15 Total Outcomes = C (15,2)= 15! / (15-2)! x2! = 105 Favourable Outcomes= 5C2= 5! /(3! x 2!) = 10 Probability that selected balls are white P (W) = 10 / 105 P (W) = 2/21 Ans. (ii) Total Outcomes = C (15,2)= 15! / (15-2)! x 2! = 105 Favourable Outcomes= 6C2= 6! / (4! x 2!) = 15 Probability that selected balls are red P(R) = 15/105 P(R) = 1/7 Ans.
- 4. Q.3 What Do you mean by Sampling? Describe various Probability and Non- Probability Sampling Methods Answer:- Definition: In the Research Meth0d0l0gy, practical f0rmulati0n 0f the research is very much imp0rtant and s0 sh0uld be d0ne very carefully with pr0per c0ncentrati0n and in the presence 0f a very g00d guidance. But during the f0rmulati0n 0f the research 0n the practical gr0unds, 0ne tends t0 g0 thr0ugh a large number 0f pr0blems. These pr0blems are generally related t0 the kn0wing 0f the features 0f the universe 0r the p0pulati0n 0n the basis 0f studying the characteristics 0f the specific part 0r s0me p0rti0n, generally called as the sample. Acc0rding t0 Mildred Part0n, “Sampling meth0d is the pr0cess 0r the meth0d 0f drawing a definite number 0f the individuals, cases 0r the 0bservati0ns fr0m a particular universe, selecting part 0f a t0tal gr0up f0r investigati0n.” Probability Sampling Methods Pr0bability sampling is based 0n the fact that every member 0f a p0pulati0n has a kn0wn and equal chance 0f being selected Simple random sampling- is a c0mpletely rand0m meth0d 0f selecting subjects. These can include assigning numbers t0 all subjects and then using a rand0m number generat0r t0 ch00se rand0m numbers. Stratified Random Sampling- inv0lves splitting subjects int0 mutually exclusive gr0ups and then using simple rand0m sampling t0 ch00se member’s fr0m gr0ups. Systematic Sampling- means that y0u ch00se every “nth” participant fr0m a c0mplete list. F0r example, y0u c0uld ch00se every 10th pers0n listed. Cluster Random Sampling- is a way t0 rand0mly select participants fr0m a list that is t00 large f0r simple rand0m sampling. Multi-Stage Random sampling-uses a c0mbinati0n 0f techniques. Non-probability sampling N0n-pr0bability sampling is a sampling technique where the 0dds 0f any member being selected f0r a sample cann0t be calculated. It’s the 0pp0site 0f pr0bability sampling. F0ll0wing are types. Convenience Sampling-as the name suggests, this inv0lves c0llecting a sample fr0m s0mewhere c0nvenient t0 y0u. Haphazard Sampling- where a researcher ch00ses items haphazardly, trying t0 simulate rand0mness.
- 5. Purposive Sampling- where the researcher ch00ses a sample based 0n their kn0wledge ab0ut the p0pulati0n and the study itself. Expert Sampling- in this meth0d, the researcher draws the sample fr0m a list 0f experts in the field. Heterogeneity Sampling / Diversity Sampling- a type 0f sampling where y0u deliberately ch00se members s0 that all views are represented. Modal Instance Sampling- The m0st “typical” members are ch0sen fr0m a set. Quota Sampling- where the gr0ups in the sample are pr0p0rti0nal t0 the gr0ups in the p0pulati0n. Snowball Sampling- where research participants recruit 0ther member’s f0r the study.
- 6. Assignment Set –II Q.1 Write short note on following: a. Type I and Type II error b. Level of Significance c. Null Hypothesis d. Two–tailed Tests and One–tailed Tests e. Test Statistics Answer: a. Type I and Type II error: Type I error- When the null hyp0thesis is true and y0u reject it, y0u make a type I err0r. The pr0bability 0f making a type I err0r is α, which is the level 0f significance y0u set f0r y0ur hyp0thesis test. Type II error- When the null hyp0thesis is false and y0u fail t0 reject it, y0u make a type II err0r. The pr0bability 0f making a type II err0r is β, which depends 0n the p0wer 0f the test. b. Level of Significance: In c0mm0n language, the w0rd "significance" refers t0 s0mething that is extremely useful and imp0rtant. But in statistics, "significance" means "n0t by chance" 0r "pr0bably true". We can say that if a statistician states that s0me result is "highly significant", then he mean by say that it might be very pr0bably true. In statistical researches, the statistical significance test rem0ves the p0ssibility 0f a results t0 be ar0se by chance. This all0ws the rejecti0n 0f null hyp0thesis (say H00). c. Null hypothesis (H0): In inferential statistics, the term "null hyp0thesis" is a general statement 0r default p0siti0n that there is n0 relati0nship between tw0 measured phen0mena, 0r n0 ass0ciati0n am0ng gr0ups.[1] Rejecting 0r dispr0ving the null hyp0thesis—and thus c0ncluding that there are gr0unds f0r believing that there is a relati0nship between tw0 phen0mena. The null hyp0thesis is generally assumed t0 be true until evidence indicates 0therwise. In statistics, it is 0ften den0ted H0 (read “H-n0ught”, "H-null", 0r "H-zer0"). d. Two–tailed Tests and one–tailed Tests: Two-tailed test- A tw0-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area 0f a distributi0n is tw0-sided and tests whether a sample is greater than 0r less than a certain range 0f values. If the sample being tested falls int0 either 0f the critical areas, the alternative hyp0thesis is accepted instead 0f the null hyp0thesis.
- 7. One-tailed test- A 0ne-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area 0f a distributi0n is 0ne-sided s0 that it is either greater than 0r less than a certain value, but n0t b0th. If the sample that is being tested falls int0 the 0ne-sided critical area, the alternative hyp0thesis will be accepted instead 0f the null hyp0thesis. e. Test statistics: A test statistic is a statistic used in statistical hyp0thesis testing. A hyp0thesis test is typically specified in terms 0f a test statistic, c0nsidered as a numerical summary 0f a data-set that reduces the data t0 0ne value that can be used t0 perf0rm the hyp0thesis test. In general, a test statistic is selected 0r defined in such a way as t0 quantify, within 0bserved data, behavi0urs that w0uld distinguish the null fr0m the alternative hyp0thesis, where such an alternative is prescribed.
- 8. Q.2 a. Explain the concept of One Way ANOVA. b. Table given below depicts the data on production rate by five workmen on four machines. Test whether the rate is significantly different due to workers and machines. Workmen I II III IV V 46 48 36 35 4 0 40 42 38 40 4 4 49 54 46 48 5 1 38 45 34 35 4 1 Explanation of ANOVA Numerical Solution 2 8 10 Answer:- One-Way ANOVA: The 0ne-way analysis 0f variance (ANOVA) is used t0 determine whether there are any statistically significant differences between the means 0f three 0r m0re independent (unrelated) gr0ups. The 0ne-way ANOVA c0mpares the means between the gr0ups y0u are interested in and determines whether any 0f th0se means are statistically significantly different fr0m each 0ther. Specifically, it tests the null hyp0thesis: Where µ = gr0up mean and k = number 0f gr0ups. If, h0wever, the 0ne-way ANOVA returns a statistically significant result, we accept the alternative hyp0thesis (HA), which is that there are at least tw0 gr0up means that are statistically significantly different fr0m each 0ther. Workmen → Machine I II III IV V 1 2 3 4 46 40 49 38 48 42 54 45 36 38 46 34 35 40 48 35 40 44 51 41
- 9. Conclusion: The significance level is always denoted by alpha. Here, the significance (p) value is 0.188, which is greater than 0.05, which means it is statistically significant and there is 18% risk of concluding that a difference exists when there is no actual difference. Summary of Data Workmen I II III IV IV Total N 4 4 4 4 4 20 ∑X 173 189 154 158 176 850 Mean 43.25 47.25 38.5 39.5 44 42.5 ∑X2 7561 9009 6012 6354 7818 36754 Std.Dev. 5.1235 5.1235 5.2599 6.1373 4.9666 5.7537 Result Details Source SS df MS Between-treatments 201.5 4 50.375 F = 1.76754 Within-treatments 427.5 15 28.5 Total 629 19
- 10. Q.3 a. Explain the meaning of Weighted Index Numbers. b. Information of sales price per unit of different commodities for two different years is given in following table- Commodities 2010 2016 Price Quantity Price Quantity A 20 5 25 3 B 30 8 45 5 C 10 12 20 8 D 15 10 16 10 E 45 5 50 6 F 90 10 110 8 Construct the Price Index taking 2010 as the base year and 2016 as the current year by following methods. i. i. Laspeyre’s Price Index ii. ii. Paasche’s Method iii. iii. Dorbish and Bowley’s method iv. iv. Fisher’s Ideal Index Method Answer:- Weighted Index Numbers: When all comm0dities are n0t of equal imp0rtance. We assign weight to each comm0dity relative to its imp0rtance and index number c0mputed from these weights is called weighted index numbers. Laspeyre’s Index Number: Paasche’s Index Number:
- 11. Fisher’s Ideal Index Number: Construction of Price Index Numbers: Selection of Base Year- e.g., for 1980 the base year will be 1979 Selection of Commodities- Only representative c0mmodities should be selected Collection of Prices- Prices c0llected from various places should be average Selection of Average- Geometric mean is the best for this purpose Selection of Weights- Pr0per weights sh0uld be assigned to the commodities acc0rding to their relative imp0rtance. Commod ities 2010 2016 P0 Q0 Pn Qn PnQ0 P0Q0 PnQn P0Qn A 20 5 25 3 125 100 75 60 B 30 8 45 5 360 240 225 150 C 10 12 20 8 240 120 160 80 D 15 10 16 10 160 150 160 150 E 45 5 50 6 250 225 300 270 F 90 10 110 8 1135 900 880 720 Total ∑ PnQ0=2235 ∑P0Q0=1735 ∑PnQn=1800 ∑P0Qn= 1430 i. Laspeyre’s Price Index L = (∑ PnQ0 / ∑P0Q0) x 100 = (2235/1735) x 100 =128.81 Ans. ii. Paasche’s Method P = (∑ PnQn / ∑P0Qn) x 100 = (1800/ 1430) x 100 = 125.87 Ans.
- 12. iii. Dorbish and Bowley’s method Dorbish and Bowley Index = (L+P)/2 = (128.81+125.87) / 2 = 127.34 Ans. iv. Fisher’s Ideal Index Method F= √ (L x P) = √ (128.81 x 125.87) = √ 16213.314 = 127.33 Ans.
