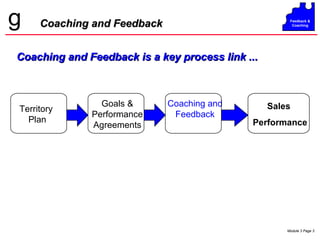
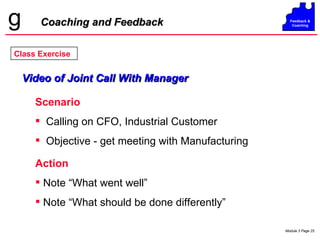
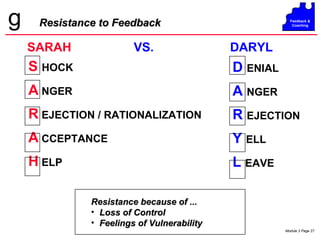
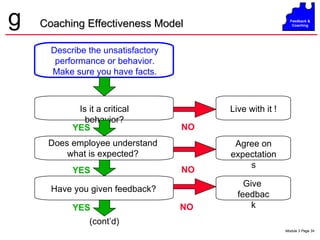
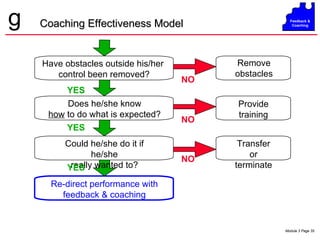
The document discusses coaching and feedback for salespeople. It emphasizes that coaching helps salespeople understand expectations while feedback reinforces or redirects behaviors. Effective feedback is specific, timely, and focuses on critical behaviors. When giving redirective feedback, managers should state facts objectively, get agreement, and help salespeople develop action plans to improve. Resistance to feedback can take various forms like denial, anger, intellectualizing or compliance, so managers must deliver feedback carefully.















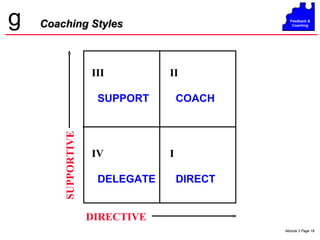











![PROFILE 1 George Landgrabe Seasoned sales veteran. Your most experienced employee. Consistent sales performance, but little evidence of real [sales-volume] growth. Jokes with the newer members of the sales team at the sales meetings: “ If you want to know how it’s done around here, just ask Ole’ George.” When you invite him to participate in the B.S.T. / All Sales Days, he “had a cannot- miss meeting with his best customer.” When you asked him last month if he was interested in attending training on ‘ Understanding Customer Financial Analyses’, he declined, remarking mildly, “ My customers buy from us because they know me and trust me.” Coaching Styles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smcfdbkcchgtab30403-120114124108-phpapp02/85/Smc-fdbk-cchg-tab-3-0403-36-320.jpg)



![PROFILE 5 R. L. “Bob” Sharp Has been on the sales team for four years. Has let it be known (privately) that “ I should have been promoted to Sales Manager [your job].” Good, solid--not spectacular--sales performance. No customer complaints. No evidence of a desire to transfer to another GE Business, or to accept another assignment within your Business. Says (publicly), “ I’ve put down some roots in the community…. I like it here.” You would be VERY hard put to classify Bob as a low performing (L10) player! In easier times, you might opt for a less pro-active stance with Bob, BUT, you are getting top-level pressure to increase Orders and Sales to Bob’s accounts. Coaching Styles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smcfdbkcchgtab30403-120114124108-phpapp02/85/Smc-fdbk-cchg-tab-3-0403-40-320.jpg)










