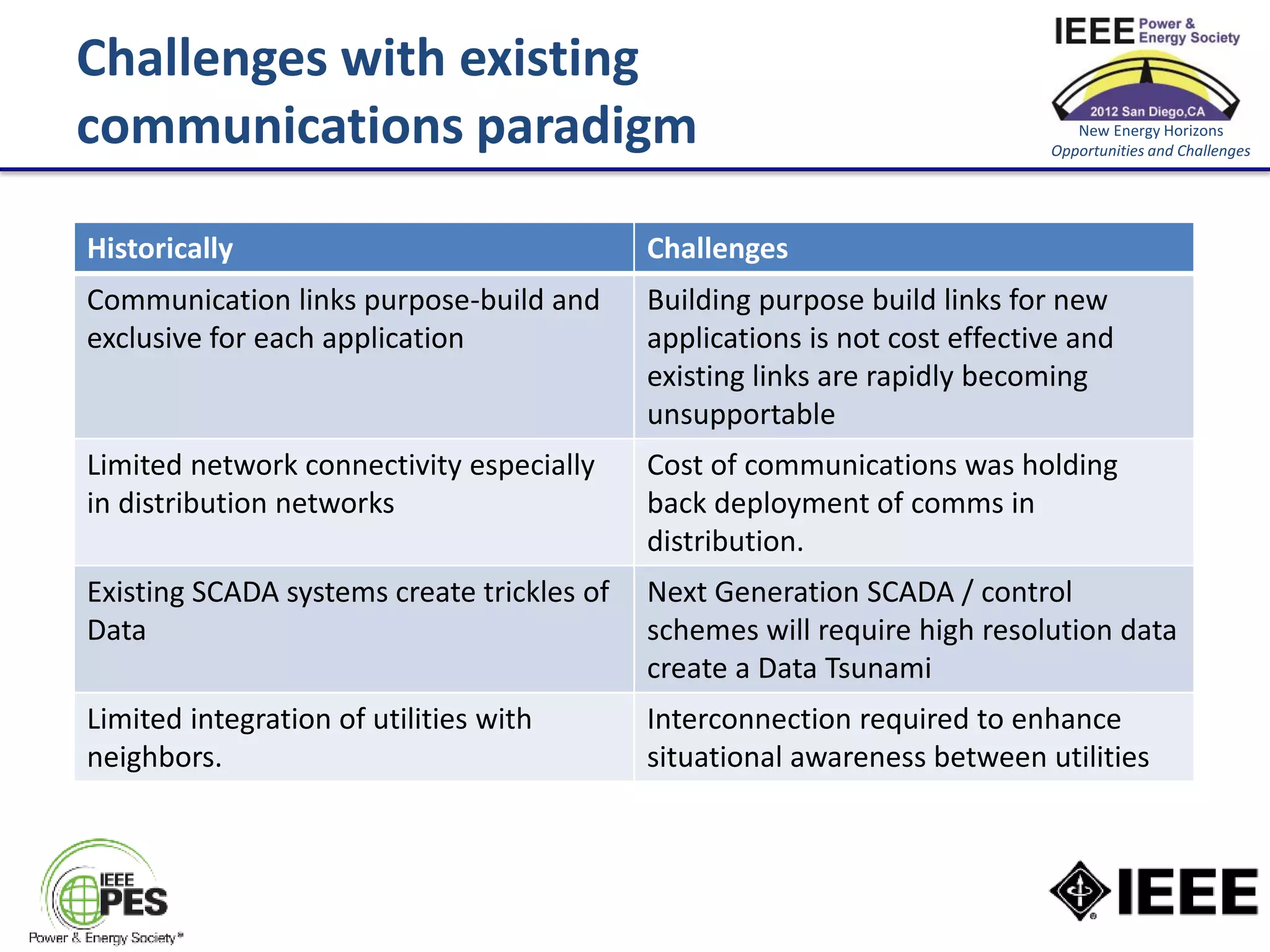
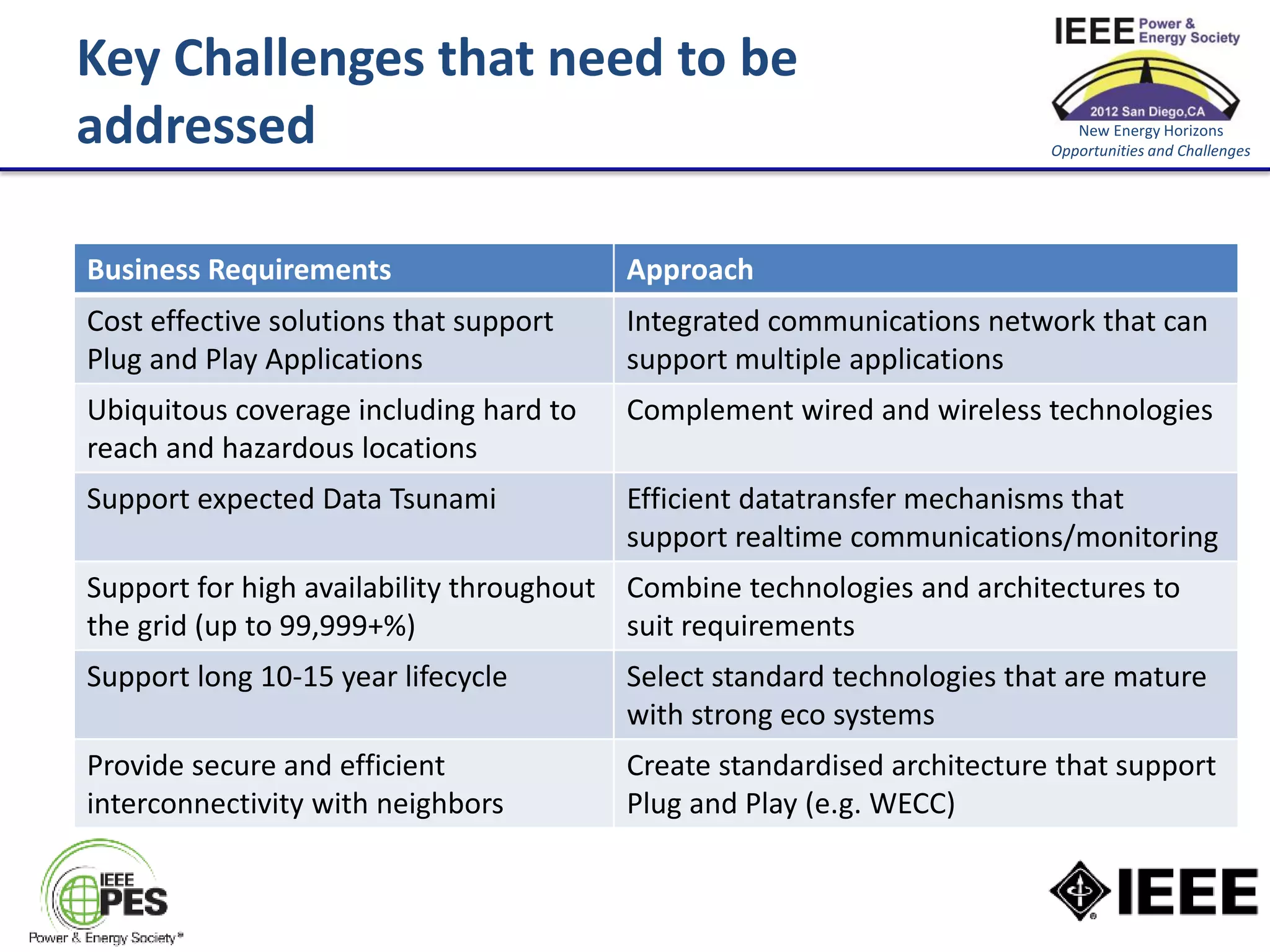
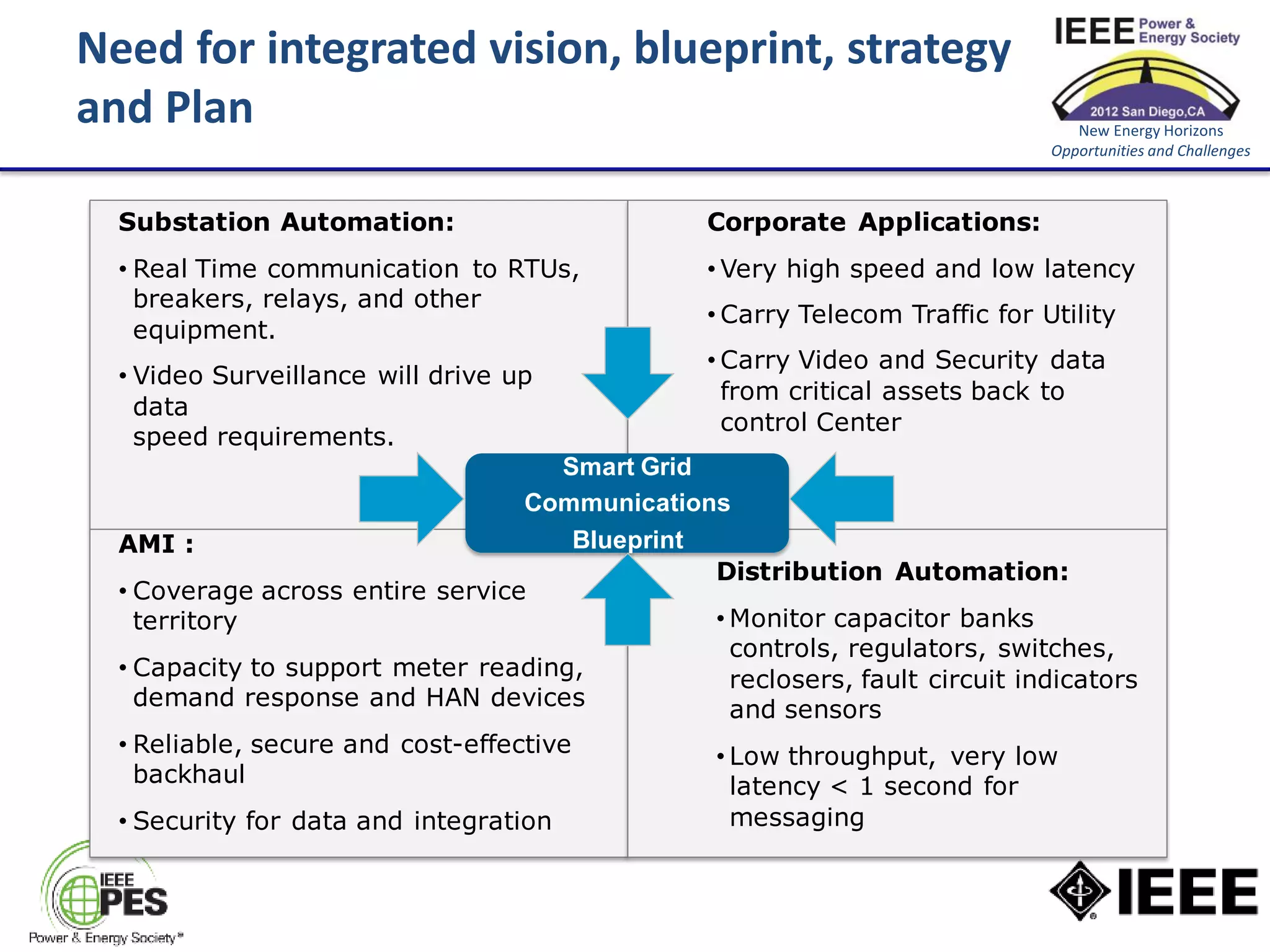
The document discusses the role of communications as a key enabler for the smart distribution network. It argues that power engineering innovation is increasingly dependent on communication capabilities. It outlines challenges with existing communication paradigms and key challenges that need to be addressed, including the need for cost-effective, ubiquitous, high-availability, and secure communications. It concludes that utilities, regulators, and the telecommunications industry need to work together to develop an integrated vision and strategy.