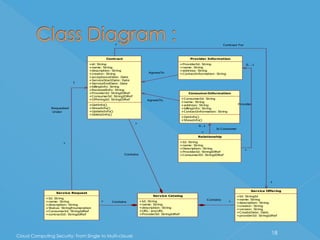
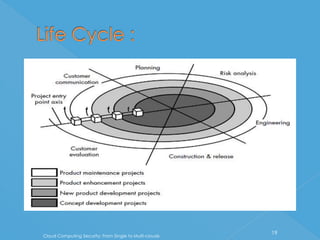
The document discusses developing a system for smart cloud security from single to multi-clouds. It outlines the introduction, literature survey, existing systems, problem definition, software architecture, requirements, UML diagrams, SDLC process, and conclusions. The problem is ensuring security and availability when data is stored and processed across single or multiple cloud systems. The goal is to develop a system that provides features like availability even during cloud failures, ability to handle multiple requests, and data security across single or multi-cloud environments.