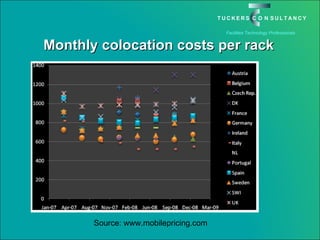
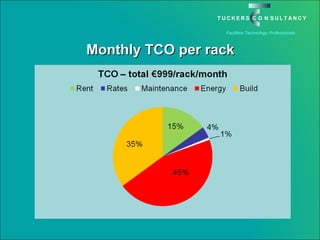
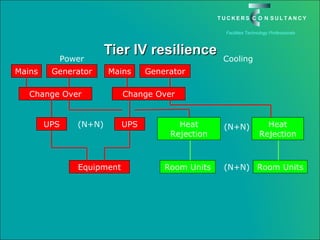
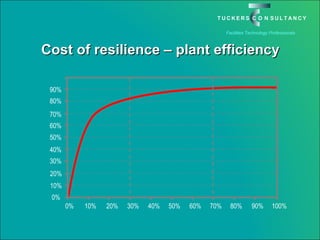
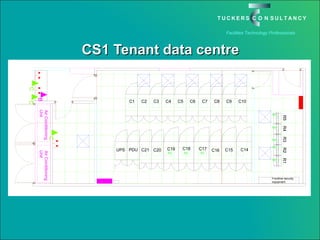
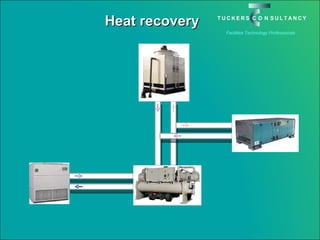
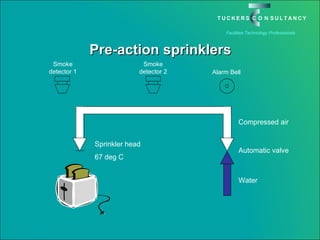
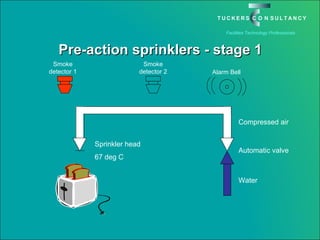
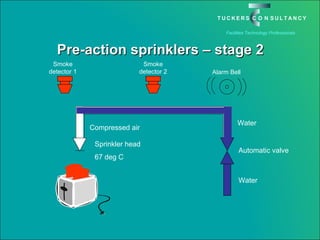
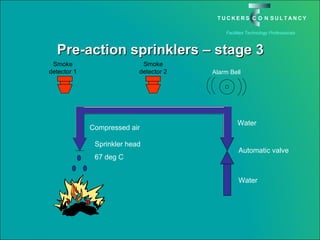
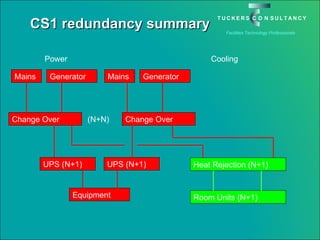
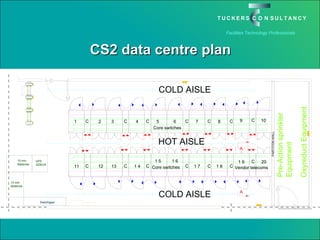
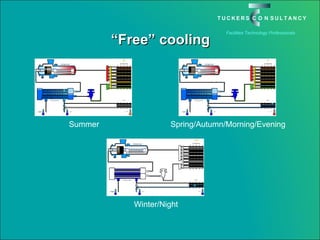
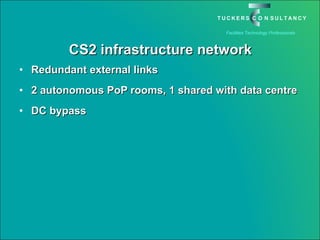
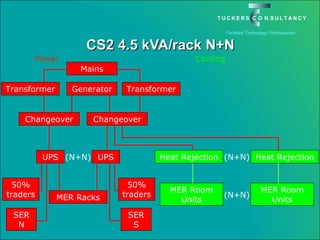
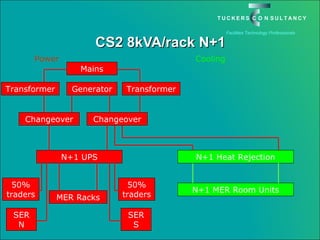
This document discusses the benefits and challenges of locating data centers in shared buildings. It presents two case studies of different types of shared buildings housing data centers. Case study 1 involves a bespoke design for a large tenant, with the landlord providing redundant power and cooling infrastructure. Case study 2 examines a speculative building with multiple tenants, where compromises are needed for redundancy due to space and cost constraints. Shared infrastructure and design tradeoffs between resilience and efficiency are explored for both examples.