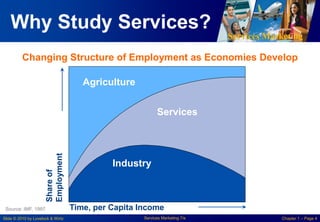
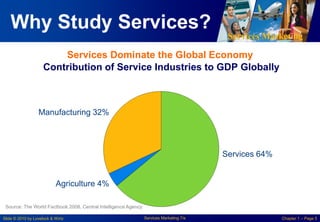
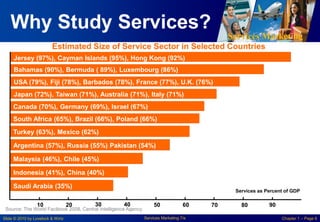
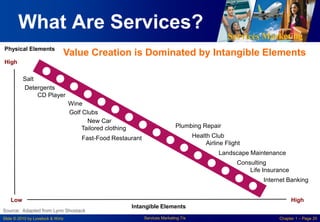
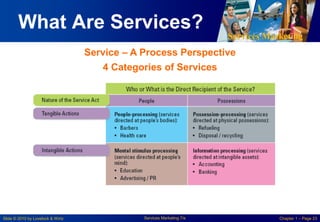
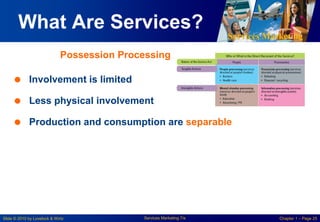
This chapter discusses the importance of services marketing. Services now dominate most economies and are the strongest growth area for marketing. Understanding services gives a competitive advantage. Services are distinct from goods in that they are intangible and customers may participate in production. Developing effective services marketing requires an extended marketing mix that integrates marketing with operations, human resources, and customers.