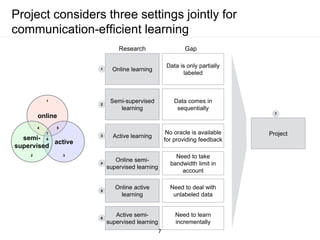
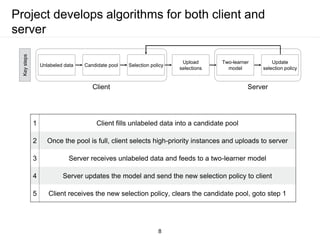
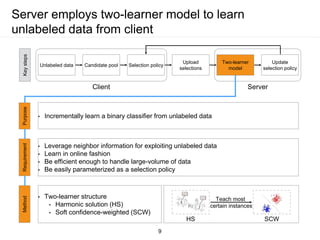
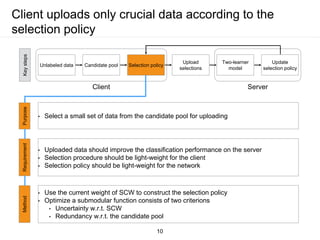
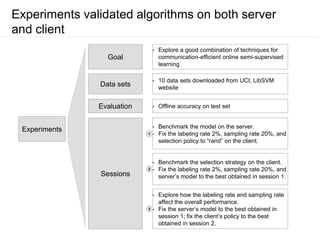
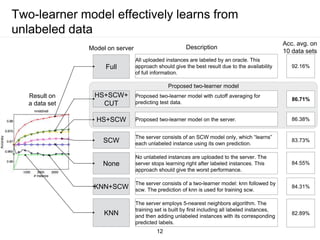
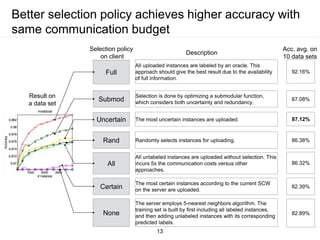
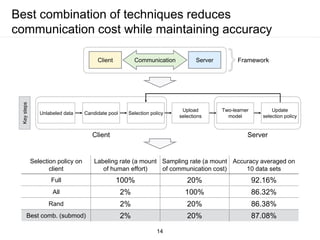
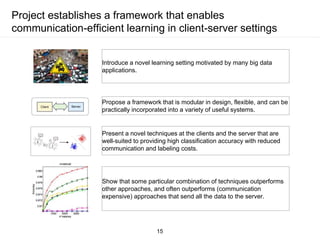
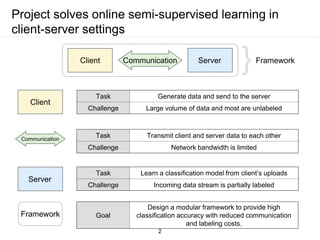
The document presents a framework for communication-efficient online semi-supervised learning in client-server settings. The framework consists of a client that selects and uploads unlabeled data to a server based on a selection policy. The server employs a two-learner model to learn from the unlabeled data and updates the selection policy. Experiments show the proposed approach achieves higher accuracy than alternatives while reducing communication costs between client and server.

![Project shares characteristics of online, semi-
supervised, and active learning
Online learning
Semi-supervised
learning
Active learning
• Passive aggressive [JMLR03],
• confidence weighted [ICML06,NIPS07],
• adaptive regularization of weights [NIPS09],
• exact soft confidence weight [ICML12]
• Semi-supervised suport vector machines,
• harmonic function solution [ICML03],
• SSL with max-margin graph cuts [AISTATS10]
• Submodularity function [AAAI07,ICRA10]
Online semi-
supervised learning
• Harmonic function on quantized graph [UAI09],
• bootstrap AROW [ACML12]
Online active
learning
• Unbiased online active learning [KDD11]
Active semi-
supervised learning
• Graph risk on harmonic function solution [ICML04]
online
active
semi-
supervised
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
2 3
4 5
6
7
Research Previous work
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/862b3309-446d-466b-a6e5-0eb6321ab468-160325081245/85/slides-sd-6-320.jpg)