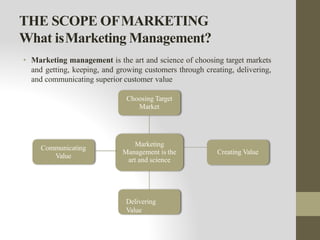
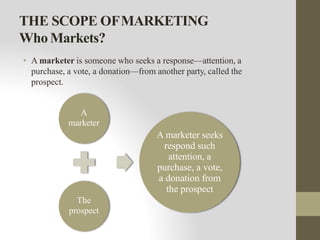
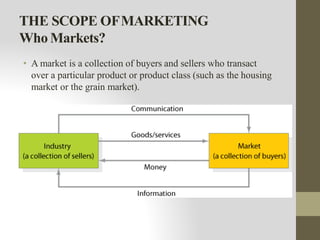
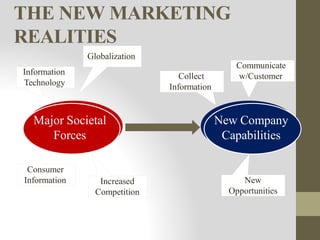
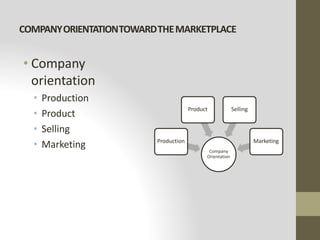
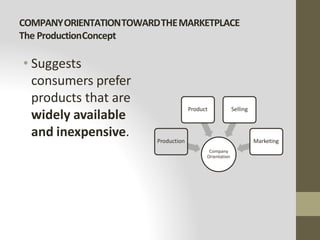
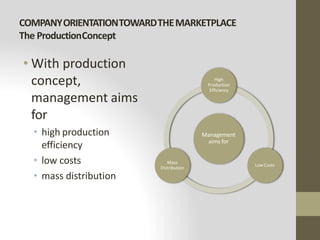
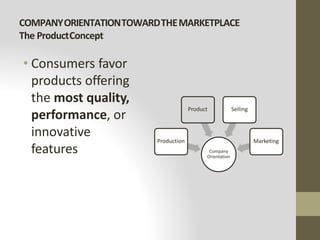
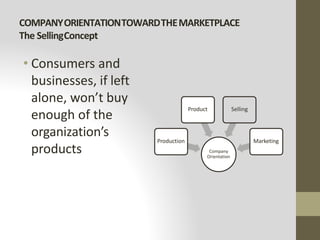
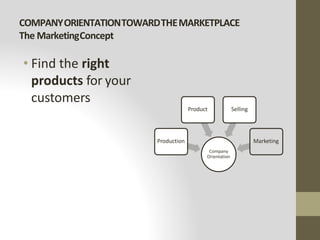
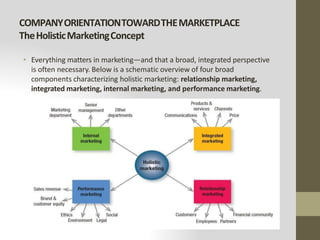
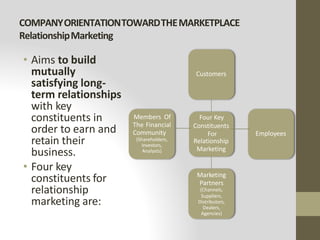
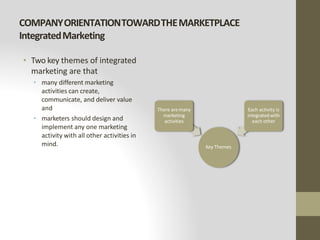
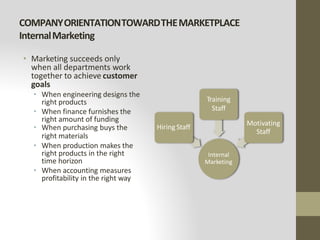
This document provides an introduction to marketing. It defines marketing as meeting needs profitably and discusses how marketing is a basic function of all businesses. Traditionally, small businesses did not prioritize marketing but it is now seen as important as other functions. The document also discusses how marketing has shifted from a product orientation to a customer orientation. It provides definitions of marketing from various sources and discusses the scope of marketing, including what can be marketed and who engages in marketing activities.