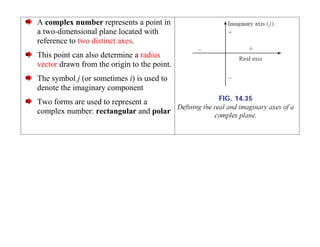
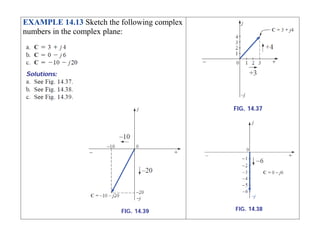
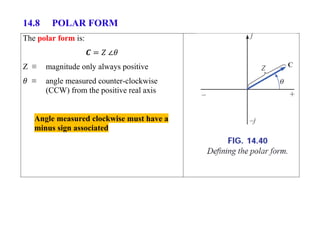
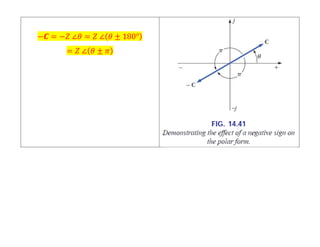
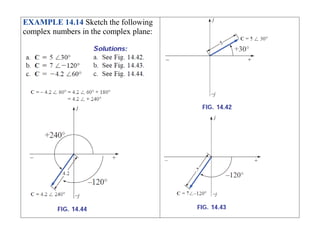
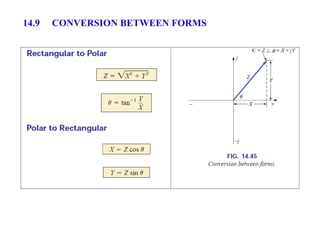
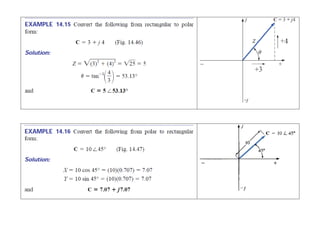
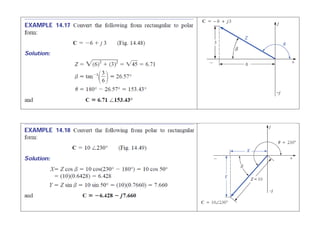
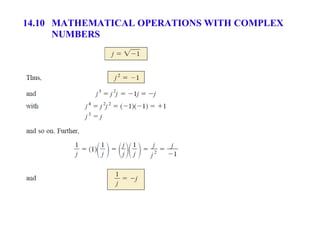
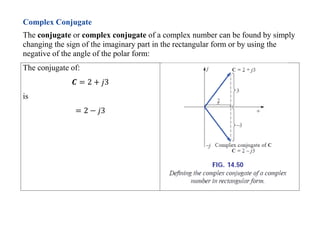
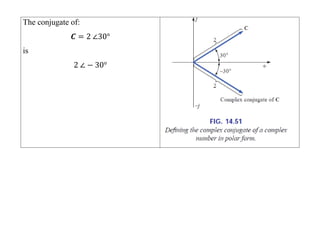
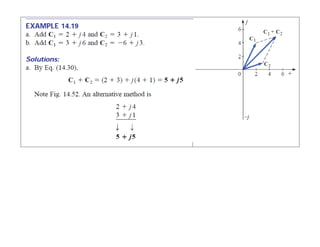
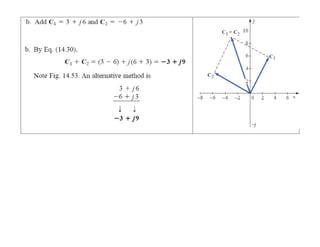
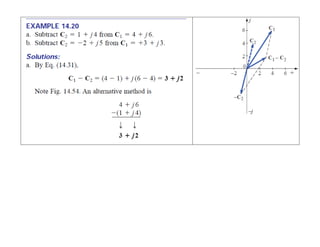
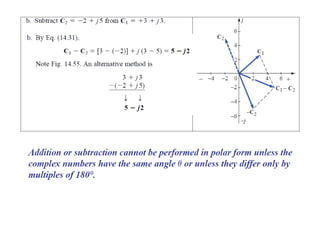
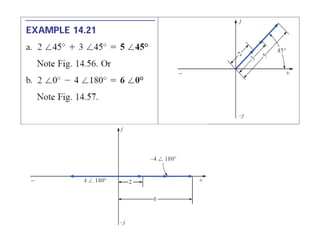
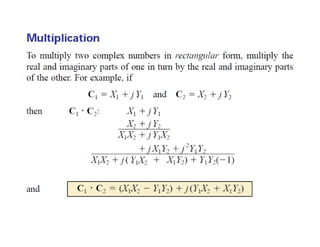
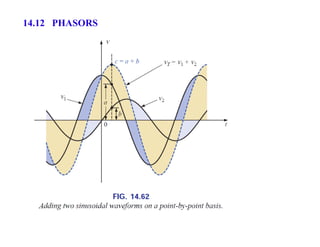
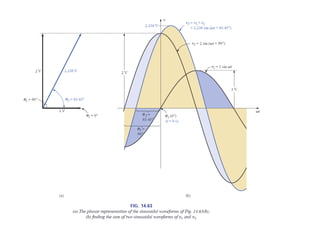
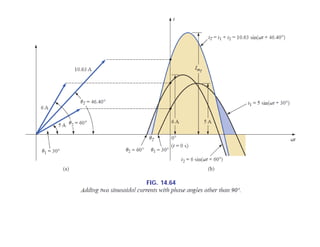
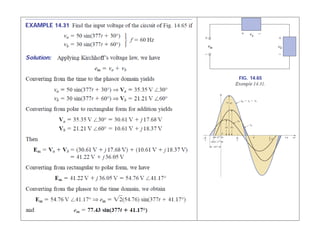
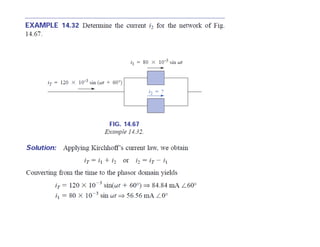
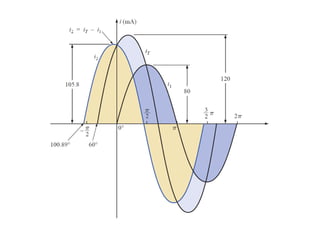
This document discusses complex numbers and phasors which are used to represent and calculate the sum of sinusoidal voltages and currents in AC circuit analysis. Complex numbers represent points in a two-dimensional plane and can be expressed in either rectangular form using real and imaginary components or polar form using magnitude and angle. Phasors are rotating radius vectors with constant magnitude that represent sinusoidal voltages and currents, where the phasor sum can be easily calculated using complex number algebra. This allows summation of sine waves much more easily than calculating point-by-point in the time domain.