Embed presentation
Download to read offline





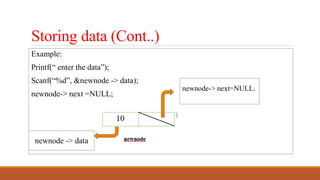


malloc() is used to allocate memory for nodes in a singly linked list. Each node contains a data field to store the data and a next pointer field pointing to the next node. The size of each node is 8 bytes, with 4 bytes for an integer data field and 4 bytes for a pointer next field. Data is stored in the data field of a node by using the arrow operator (->) to access the data field through a pointer to the node.







