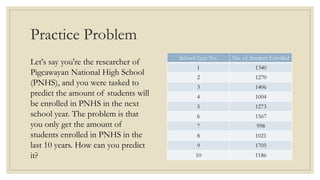
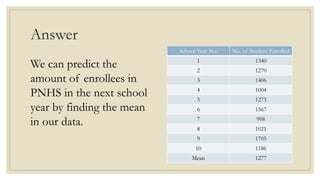
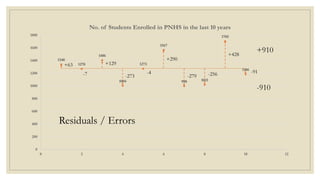
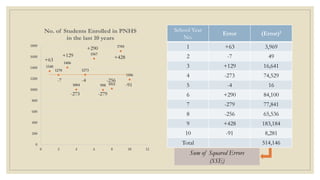
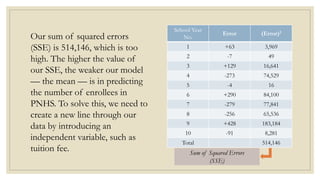
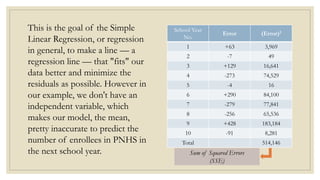
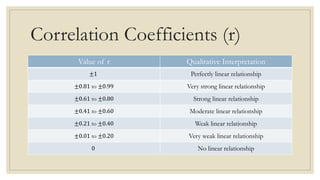
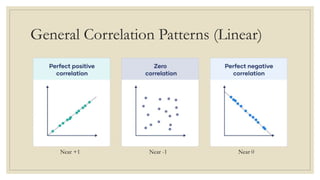
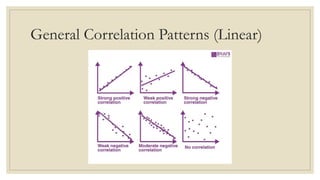
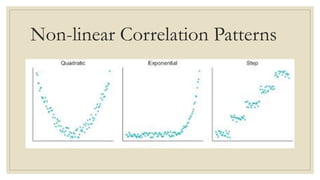
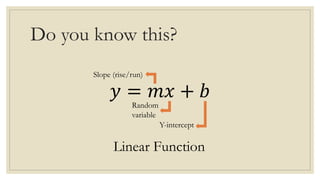
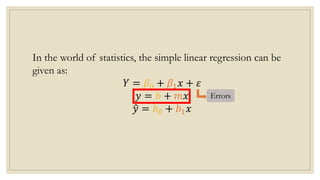
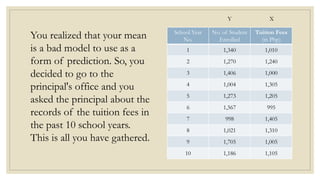
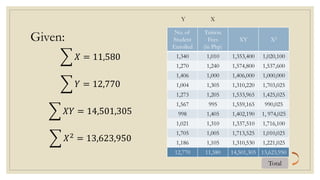
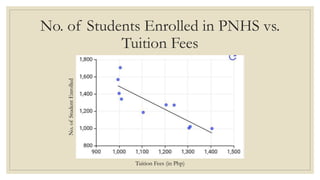
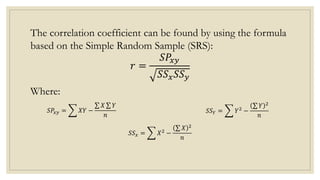
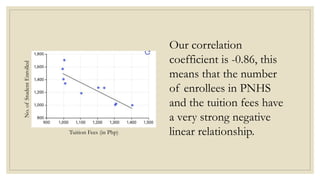
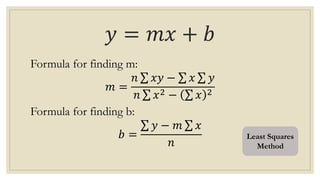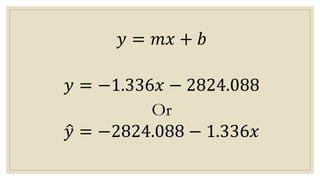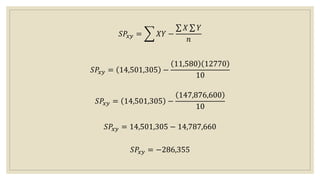This document discusses simple linear regression and correlation analysis. It begins by explaining simple linear regression as focusing on the relationship between two variables. It then provides an example using data on student enrollment in a school over 10 years to predict future enrollment. Several methods of simple linear regression are demonstrated, including finding the slope and y-intercept of the regression line. The document then discusses correlation analysis, explaining it as a measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Different correlation coefficients and their interpretations are provided. Finally, it returns to the student enrollment example to calculate the correlation between enrollment and tuition fees, finding a strong negative correlation between the two variables.