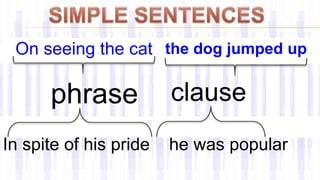
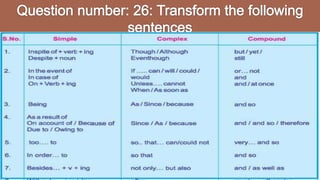
This document provides information about different types of clauses and sentences in English grammar. It defines independent clauses as main clauses that can stand alone as a complete sentence. Dependent clauses cannot stand alone and are part of a larger sentence. Complex sentences combine an independent clause with one or more dependent clauses using a subordinating conjunction. Compound sentences contain two independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction. The document gives numerous examples of simple, complex, and compound sentences and exercises to practice transforming between sentence types.