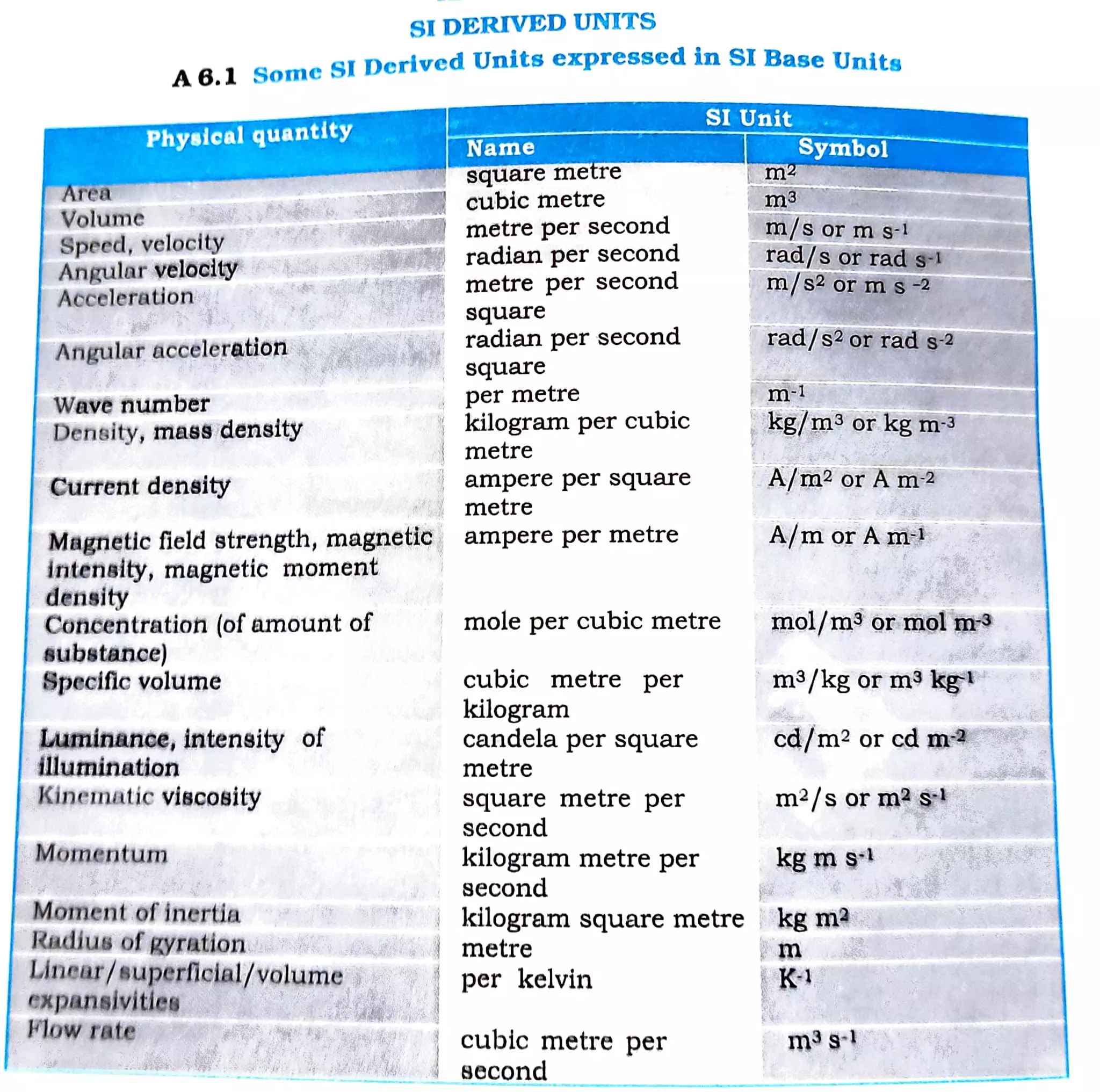
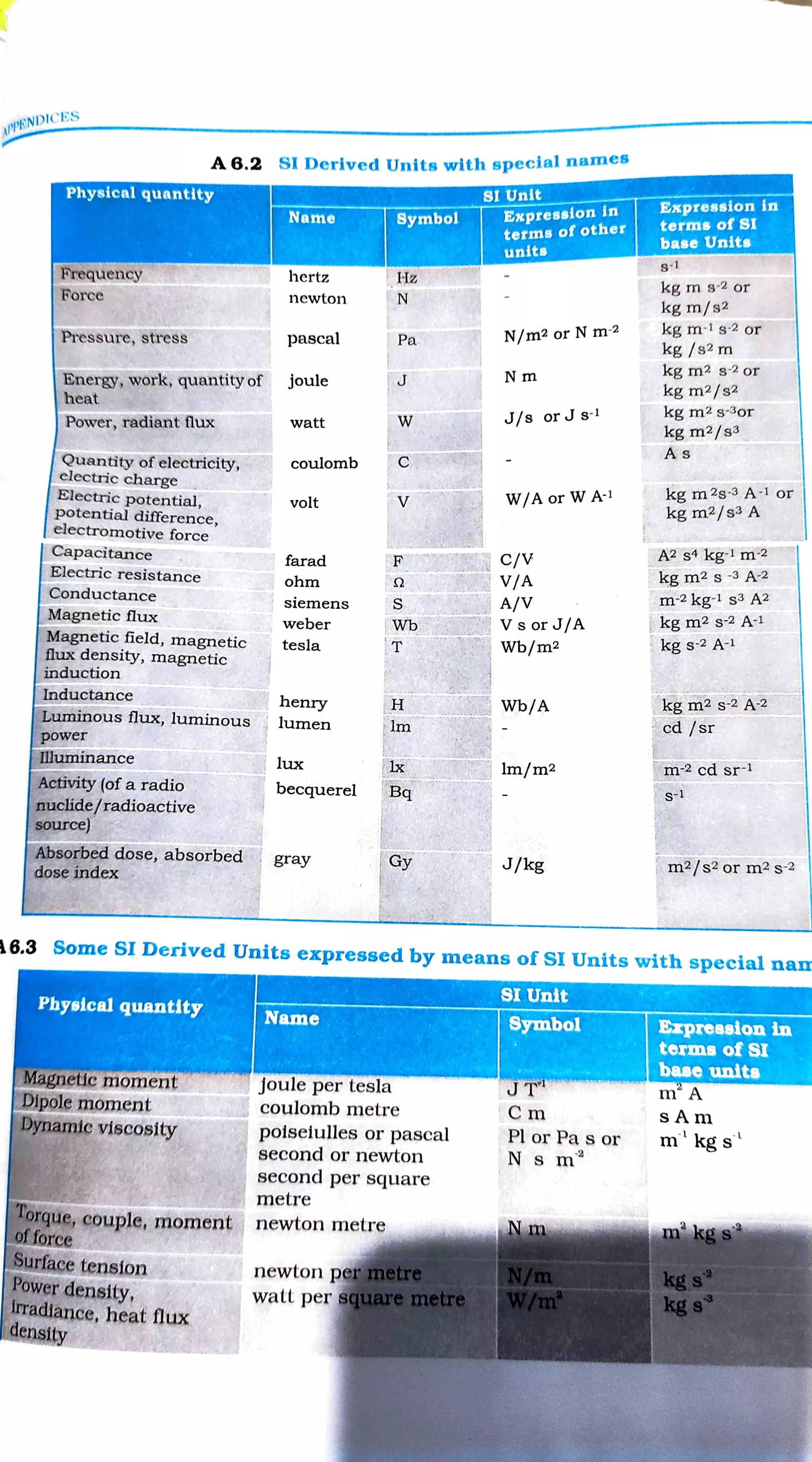
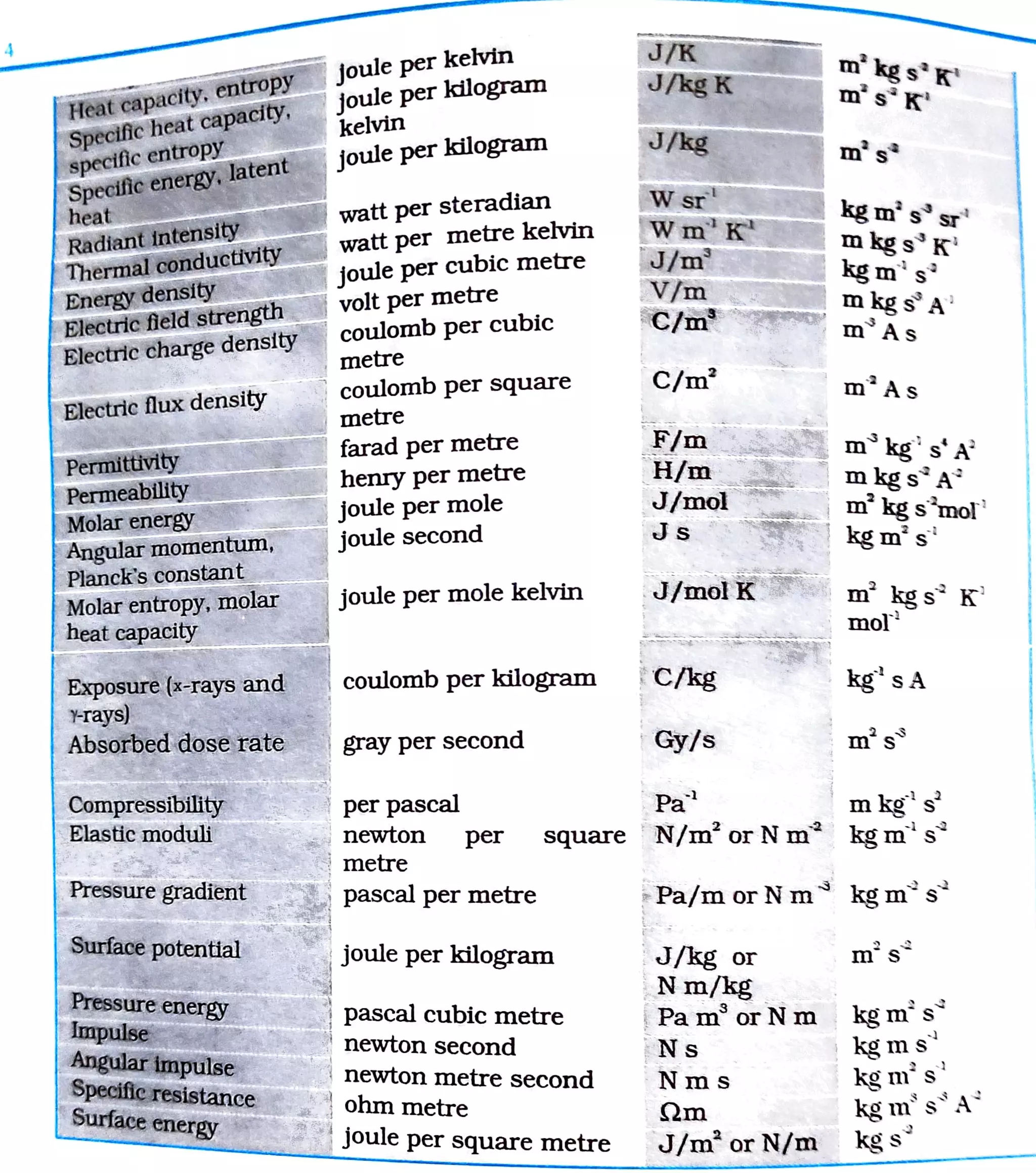
This document defines many SI derived units in terms of SI base units and provides their dimensional formulas. It lists units such as square metre for area, cubic metre for volume, metre per second for speed, newton for force, joule for energy, watt for power, pascal for pressure, and more. It expresses these derived units as combinations and ratios of dimensions of length, mass, and time.
![D I M E N S I O N A L F O R M U L A
Relationship with other
physical quantities
UANTITTES
Dimensions
imensional
Physical quantity
formula
S. No
Length x breadth
M 1T
Area
Length x breadth x height L' M°L T
Volume
Mass/volume [MV[L'] or[ML') ML'T
Mass density
1/timeperiod VIT [M° LT'
Frequency
Displacement/time [LIT M°LT'
Velocity, speed
Velocity /time Lr V[T] MLT
Acceleration
Mass x acceleration [M]LT' [M LT'
Force
Forcex time [M LT IT] [M LT'
Impulse
Forcexdistance MLT'1 L MLTT
Work, Energy
Work/time [MLTV [T [MLT]
10. Power
Mass xvelocity [M [LT' MLT
11
Momentum
Force/area [M LT VL [MLT
12.
Pressure, stress
Change in dimension L]/[L] or[L'j/[Lj M°LT
13 Strain
Oringinal dimension
MLT
[MLT
IM°L°T°]
14 Modulus ofelasticity Stress/strain
Surface tension Force/length [MLT VLI [MLT
15
Surface enerEy Energy/area [MLTVL MLT
16.
Velocity Velocity/distance [LTVL) MLT
17.
gradient
18 Pressure gradient Pressure/distance [MLT*V [MLT
19. Pressure energy Pressure x volume [MLT][L [MLT
20 Coefficient of
MLT
Force/area x velocityY
gradient
[MLT
LLT/LI
viscosity
21 Angle, Angular
displacement
[M'LTI
Arc/radius [L[LI
22 M'LT
Trigonometric ratio
(sine, cos0, tan6, etc.)
Length/length [LVILI
23 Angular velocity Angle/time L"VT] [M'L'TT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siderivedunits-230115054847-4bd8218d/75/Si-Derived-Units-pdf-4-2048.jpg)
![P P E N D I C E S
Angular acceleration Angular velocity/time TVT (M°LT'I
Radius of gyration L) [M'LT
Distance
Moment ofinertia Mass x (radius ofgyration [M][L'] [MI T
26
IMI T'
Moment of inertia x angular [ML'JIT'I
velocity
27 Angular momentum
Moment of force, Force x distance (MLT'J[LJ ML T'
28,
moment ofcouple
Torque Angular momentum/time, [ML'T']/[T] IML T'
Or or
Force x distance
[MLT' JL
30 Angular frequency 21t Frequency [T'] MLT
Wavelength Distance [L MLT
31.
Hubble constant Recession speed/distance LT'VLI MLT
Intensity ofwave Energy/timeyarea MIL' TTVLL'1 ML'T
Radiation pressure Intensityof wave
Speedoflight
[MTVLT' MLT1
34.
35 Energy density Energy/volume [MILTy L1 MLT
36. Critical velocity Reynold's umber x coefficient of viscocity
M°1T°MLT
[MLILI
[MLT'
Mass density x radius
37 Escape velocity (2 acceleration due to
gravity xearth'sradius) 2
[LTx[L MLT']
Heat energy, internal Work (Force x distance)
[MLT ]L] ML T
38.
energy
Kinetic energy (1/2) mass x (velocity) [M] [LT'} [MLT
40 Potential energy Mass x acceleration
due to gravity x height
[M LTIL [ML T
41 Rotational kinetic 4* moment ofinertia x
(angular velocityy
[ML'T][M }x[T"f ML'T
energy
42.
Efficiency [MLT*
Output work orenerg8y
Input work or energy
ML'T
[ML'T* 1
49 Angular impulse Torque x time [ML'T'1(T MLTI
44
Gravitational IMLT 1LC
M IM
Forcex(distance M'LT)
constant mass mass
Planck constant Energy/trequency [ML'T)/T [ML'T'1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siderivedunits-230115054847-4bd8218d/75/Si-Derived-Units-pdf-5-2048.jpg)
![PHYSICS
[ML TV[K]
Heat energy/temperature
MIT K
Heat capacity,
46
entropy
HeatEnergy [MLTVIMIK]
[MLTK
Specific heat capacity
Mass x temperature
[ML TVM
Heat energy/mass
[ML T
Latent heat
LI/LIK]
Changeindimension
Original dimensionx temperature [MLK 1
9
Thermal expansion
coefficient or
Thermal expansivity
[MLTIIL)
HeatenegY *thickness
Area x temperature x time MLTK'
S0
Thermal conductivity
Volume x(changeinpressure)
(changein volume)
Lj[ML 'T*]
[L
[MLT)
Bulk modulus
or(compressibility)
(Velocity) lradius [LT' /[L] [M'LT
Centripetal
acceleration
(Energy/areaxtime))
(Temperature)
[MT
(T] K
M TK
Stefan constant
Wavelength x temperature L [K) M LT°K
Wien constant
Energy/temperature [MIL T*VK] LML' TK1
Boltzmann constant
[MLTL
mol) [K]
[MTK
Pressurexvolume
mole xtemperature
Universal gas
constant
mol ]
Charge Currentx time [A] [T [MLTA]
Current density Current/area [A]/[L' MLTA
Work/charge [ML'TV[AT] ML TA]
Voltage, electric
potential,
electromotive force
59
ML T A
IMLT A']
[A
60 Resistance Potential difference
Current
61 Capacitance Charge/potential difference
[ML'T A
[AT]
[ML T'A]
ML' T A
[ML' TA*]
LVLI
62 Electrical
resistivity
or (electrical
Resistance x area
length
conductivity'
Electric field IMLTA
Electrical force/charge [MLTV[AT]
64 Electric flux EML T A"]
Electric ficld xarea MLT AL']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siderivedunits-230115054847-4bd8218d/75/Si-Derived-Units-pdf-6-2048.jpg)
![[M LTA]
Electric dipole Torque/electric field [ML T
65
moment (MLT' A"]
[MLTA*
Electricfield strength
or electric intensity
[ML'TA)
L
66.
Potential difference
distance
[MLTV[A]L) MLTA
Magnetic field,
magnetic flux density,
magnetic induction
67. Force
Current length
[MTA) L MLTA1
68 Magnetic flux Magnetic field xarea
[MT AA
Magnetic fux
Current
[ML'TA"
[A]
69 Inductance
Torque/magneticfield [MLT]/[MT A*][M'LTA}
70 Magnetic dipole
moment
or Or
CuITentxarea
AJL
L'A]
'
MLTAJ
Magnetic moment
Magnetic field
strength, magnetic
intensity or magnetic
moment density
Volumee
MLTA
Permittivity constant Charge x charge
[AT][AT]
[MLTJLF
(offree space) 4T xelectricforcex (distance)
Permeability constant
(of free space)
[M°L'TIMLTIUMTA
[A][AJL]
27 forcexdistance
current currentxlength
LT LT] [M°LT]
Speedofightinvacuum
Speed oflightinmedium
Refractive index
[ATmol] M'LTAmol
Avogadro constantx
elementary charge
Faraday
constant
27t/wavelength [MLT|/[ [MLT
Wave number
[MLTV[T] MI'T
Radiant flux, RadiantBnergyemitted/time
power
[ML'T/ [M°LTI IML T
Luminosity ofradiant Radiant powerorradiantfhusofsource
flux or radiant
18
Solid angle
intensity
[ML TVIT [MLT
Luminous energy emited
Luminous power or
luminous flux of time
Source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siderivedunits-230115054847-4bd8218d/75/Si-Derived-Units-pdf-7-2048.jpg)
![[ML T']
[MLT
2 Luminousflux
ML T
Luminousintensityor
illuminatingpowerof
Soildangie
80.
[ML' TVL
[ML'T
S O u r c e
Luninous intensity
Intensityof
illumination or
81
(distance)
[ML'T]
[MILT']
luminance
Luminous fiux ofa source of
gvenwavelength
Juminous filx ofpeaksensitivityy
wavelength (555 nm) source of
same powver
MLT)
82
Relative luminosity
[ML' T/[MLT] MLT
Total luminous flux
83.
Luminous efficiency
Total radiant flux
Luminous flux incident
[MLTVL [ML'T)
Iluminance or
illumination
84 area
(sum ofmasses ofnucleons)-
(mass ofthe nucleus)
[M
[ML'T
85. Mass defect
Binding energy of
nucleus
Mass defect x (speed oflight [M[LTr
in vacuum
86. [ML' T']
Decay constant 0.693/halflife [T] [MLT
87.
88. Resonant frequency [M'L' A°T
(Inductance x capacitance) 2
[MLTA?
[MLTA?J
89 Quality factor or Q
factor of coil
Resonant frequency x inductance
[T]MLTA] [M'LT]
Resistance
[MLPTA
90 Power of lens (Focallength
[ML'T]
91.
Magnification Image distance
Object distance
[L]/L] [M'LT]
92 Fluid flow rate
(T/8) (pressure)x (radius
viscosity coefficient)x length
(ML T] M'L'T]
IML'T] li
93
Capacitive reactance (Angular frequency x
capacitance ITTM'L'T'AT' [MLT A
94
Inductive reactance
(Angular frequency x
inductance) ITIML T A) [MLT A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siderivedunits-230115054847-4bd8218d/75/Si-Derived-Units-pdf-8-2048.jpg)