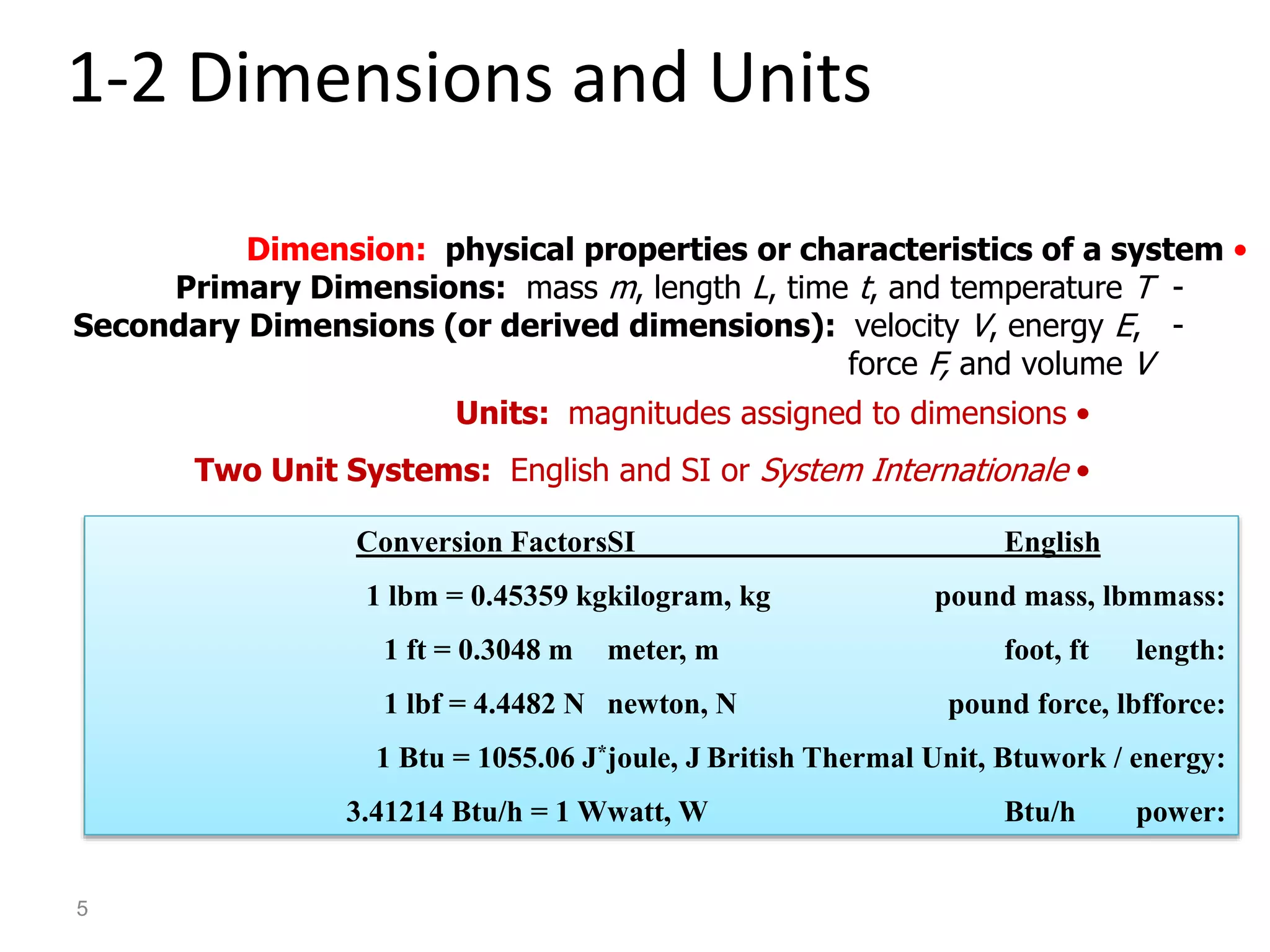
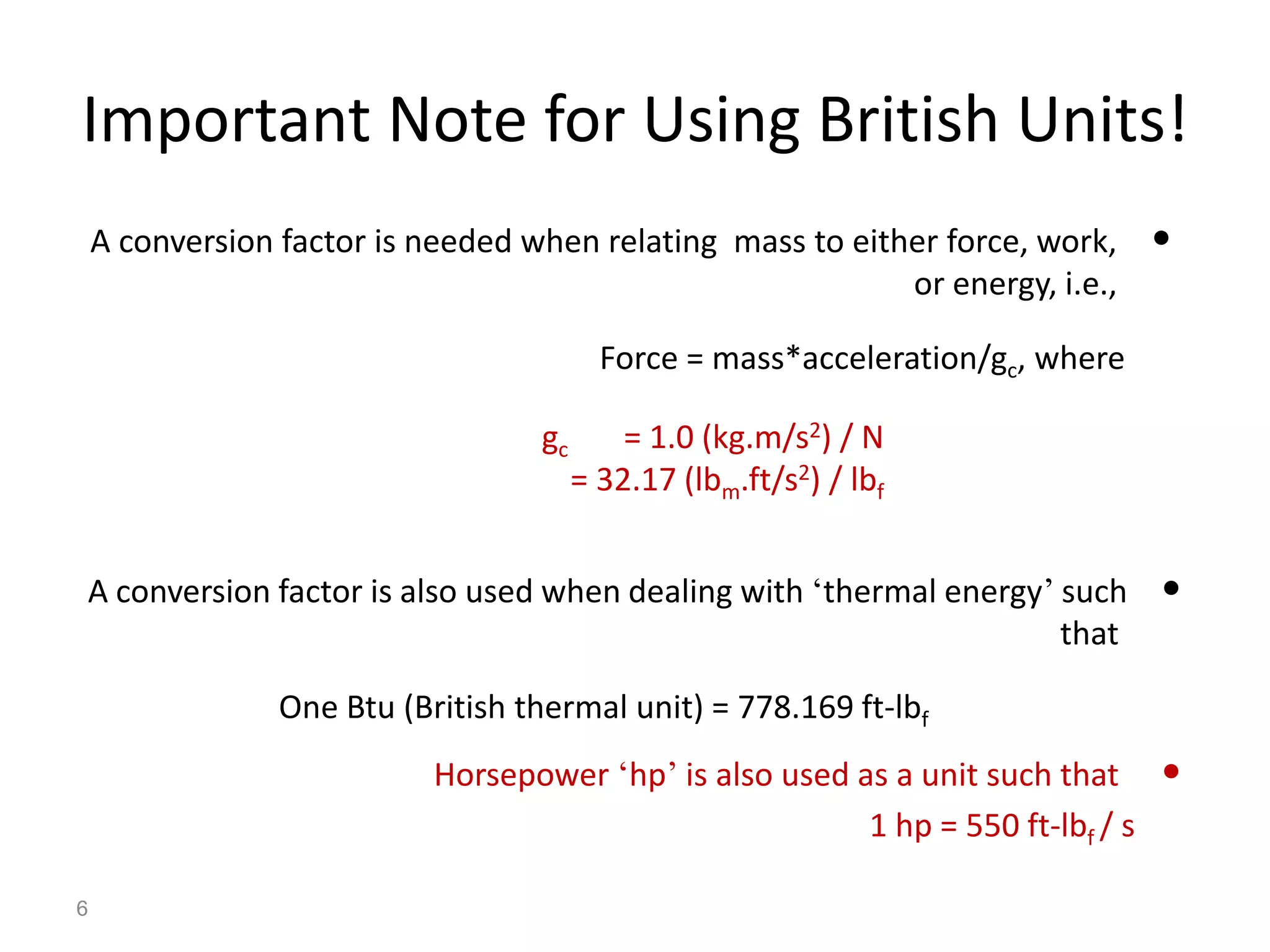
Thermodynamics is the science of energy and its transformation. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved during any process as it changes from one form to another. The second law states that the quality or usefulness of energy degrades as it is transformed. Thermodynamics applies to all natural processes and is important in engineering systems like power plants, refrigerators, and automobiles. Properties can be analyzed from a macroscopic or microscopic perspective, with classical thermodynamics taking a macroscopic approach useful for engineering applications. The state of a simple compressible system can be fully described by two intensive properties such as pressure and temperature.