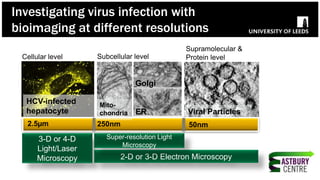
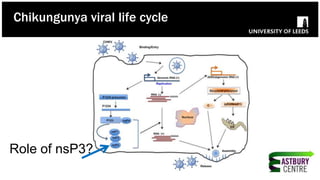
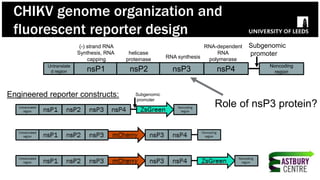
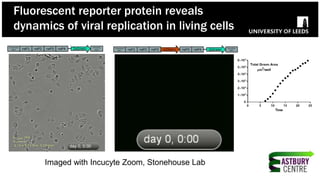
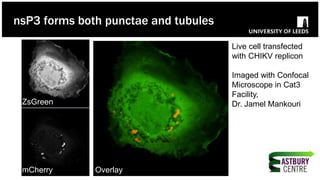
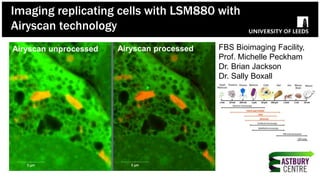
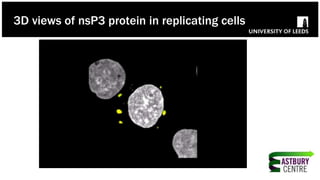
The document discusses high-resolution microscopy techniques used to study chikungunya virus (CHIKV) replication and its life cycle, emphasizing advanced bioimaging methods like live-cell fluorescence and confocal microscopy. Researchers examine the role of the nsp3 protein in viral replication, using engineered fluorescent reporter constructs and various microscopy approaches to track protein localization and interactions. Future research plans include investigating nsp3 dynamics and its implications for chikungunya infection, supported by various institutional and funding collaborations.