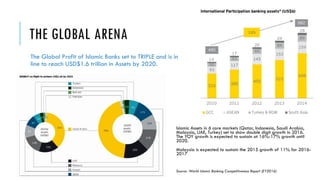
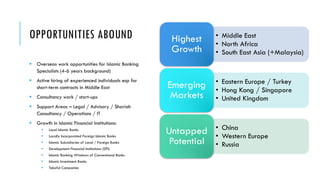
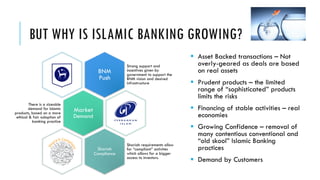
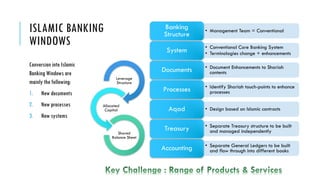
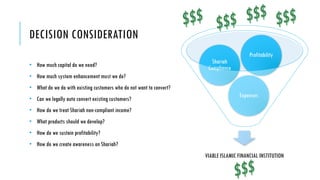
The document outlines the evolution and growth of Islamic banking, emphasizing its increasing acceptance and potential for expansion compared to conventional banking. It highlights opportunities in various global markets, Malaysia's position as a leader in Islamic finance, and the importance of Shariah compliance in product development. Additionally, it discusses the challenges faced by institutions in balancing Shariah requirements with business needs and the implications of the Islamic Financial Services Act 2013.