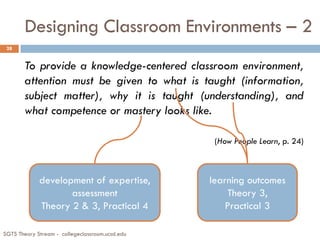
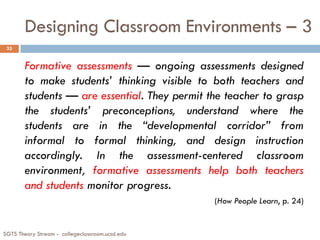
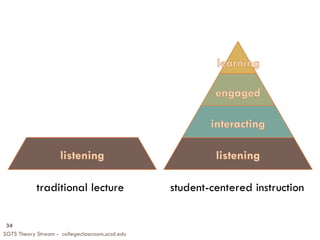
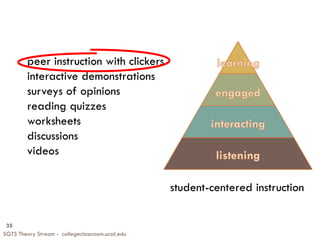
The document summarizes key points from a presentation on effective teaching methods based on how people learn. It discusses three main findings from research: 1) Students come with preexisting understandings that must be engaged, 2) Students learn best when topics are taught in depth within a conceptual framework, and 3) Teaching metacognitive skills helps students control their own learning. The presentation provides implications for designing learner-centered classrooms and using techniques like formative assessments, interactive demonstrations, and peer instruction with clicker questions to replace traditional lectures.









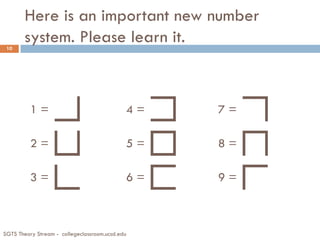


![How People Learn [1]
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-16-320.jpg)



![Learning requires interaction [2]
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-21-320.jpg)
![Learning requires interaction [2]
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
22
% of class time
NOT lecturing
Normalized learning gain:
pre-test
0
100%
post-test
0.50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-22-320.jpg)
![Learning requires interaction [2]
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
23
1 2
3 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-23-320.jpg)




![Aside: metacognition
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
30
Metacognition refers to one’s knowledge concerning one’s
own cognitive processes or anything related to them.
For example, I am engaging
in metacognition if I notice
that I am having more
trouble learning A than B.
([3], [4])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-30-320.jpg)





![How People Learn [1]
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-39-320.jpg)



![References
SGTS Theory Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu
43
1. National Research Council (2000). How People Learn: Brain, Mind,
Experience, and School: Expanded Edition. J.D. Bransford, A.L Brown & R.R.
Cocking (Eds.),Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
2. Prather, E.E, Rudolph, A.L., Brissenden, G., & Schlingman, W.M. (2009). A
national study assessing the teaching and learning of introductory
astronomy. Part I. The effect of interactive instruction. Am. J. Phys. 77, 4,
320-330.
3. Flavell, J. H. (1976). Metacognitive aspects of problem solving. In L. B.
Resnick (Ed.), The nature of intelligence (pp.231-236). Hillsdale, NJ:
Erlbaum.
4. Brame, C. (2013). Thinking about metacognition. [blog] January, 2013,
Available at: http://cft.vanderbilt.edu/2013/01/thinking-about-
metacognition/ [Accessed: 14 Jan 2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theory1introhpl-130426113529-phpapp01/85/SGTS-Theory-1-43-320.jpg)