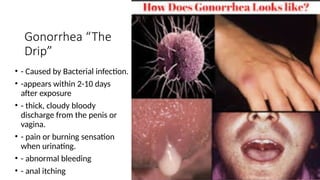
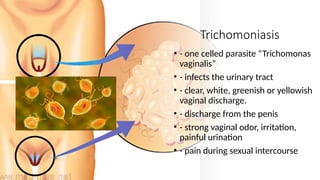
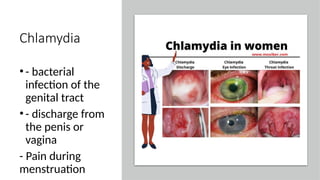
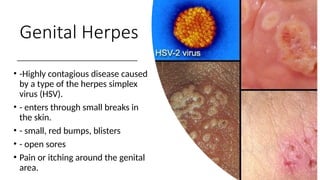
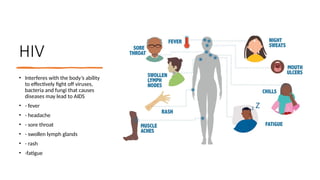
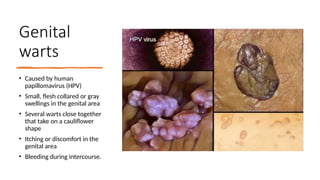
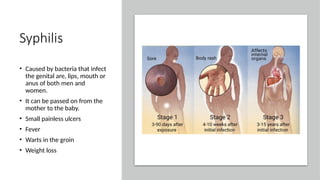
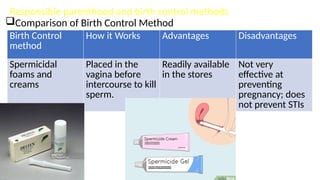
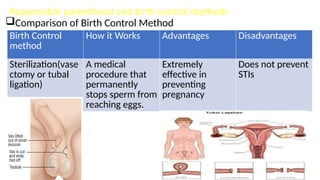
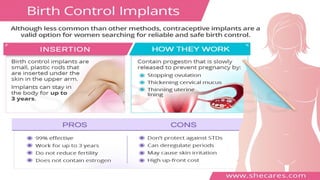
The document covers sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites, detailing symptoms and consequences if untreated, including HIV and its progression to AIDS. It also discusses various birth control methods, their mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages, emphasizing the importance of responsible parenthood. Methods include abstinence, contraceptive pills, IUDs, condoms, diaphragms, spermicidal foams, and sterilization, each with specific effectiveness and limitations.