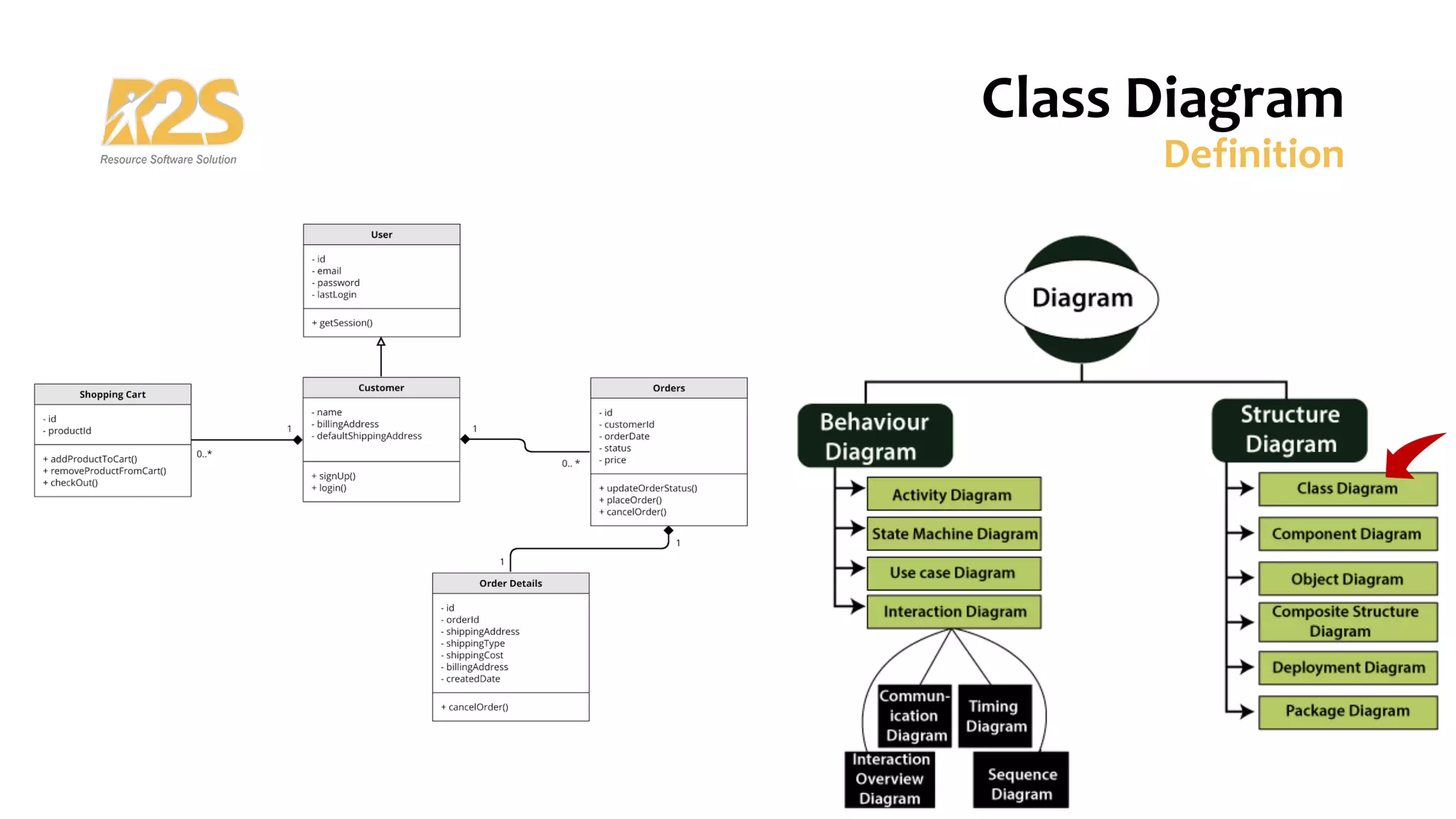
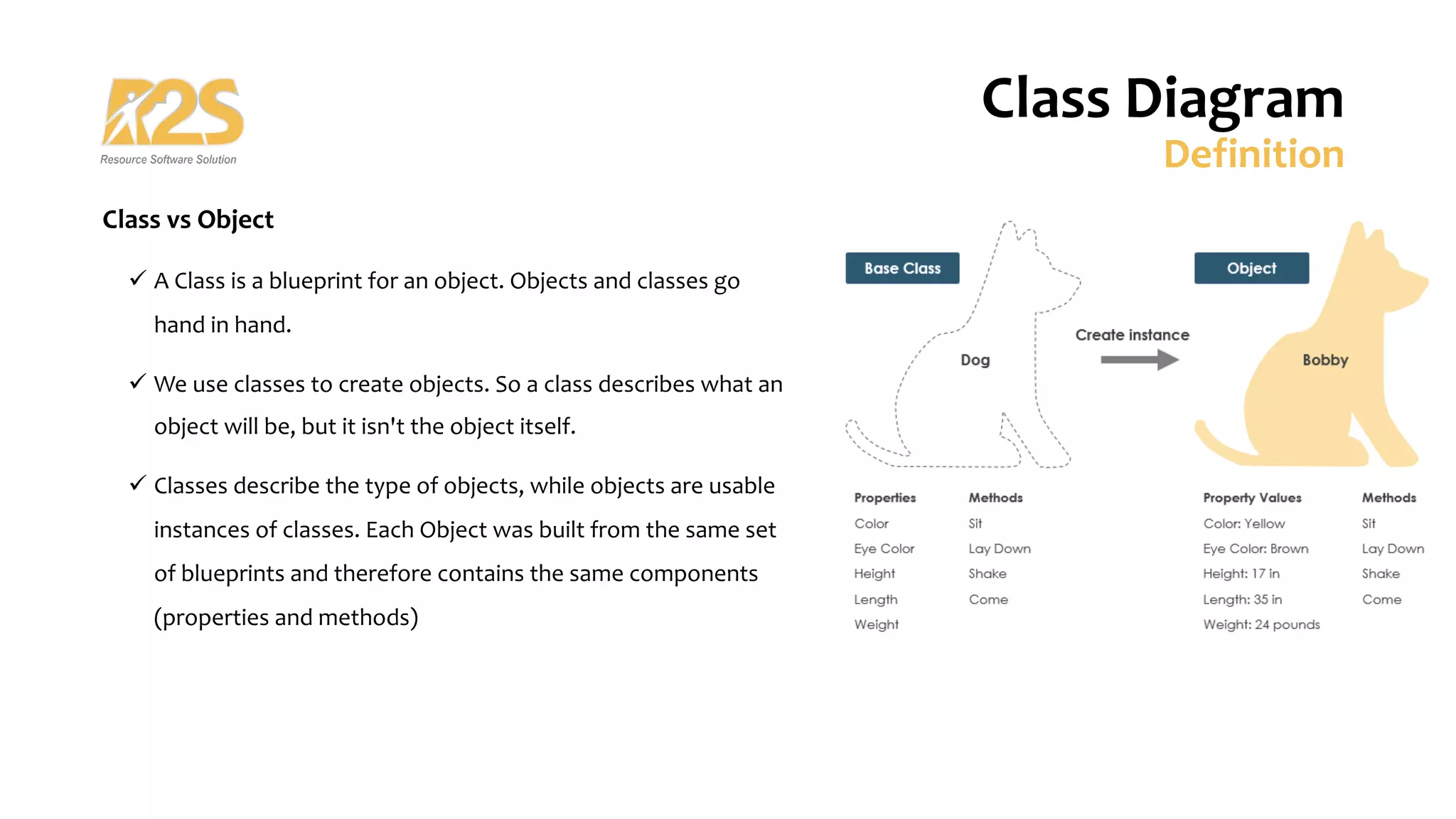
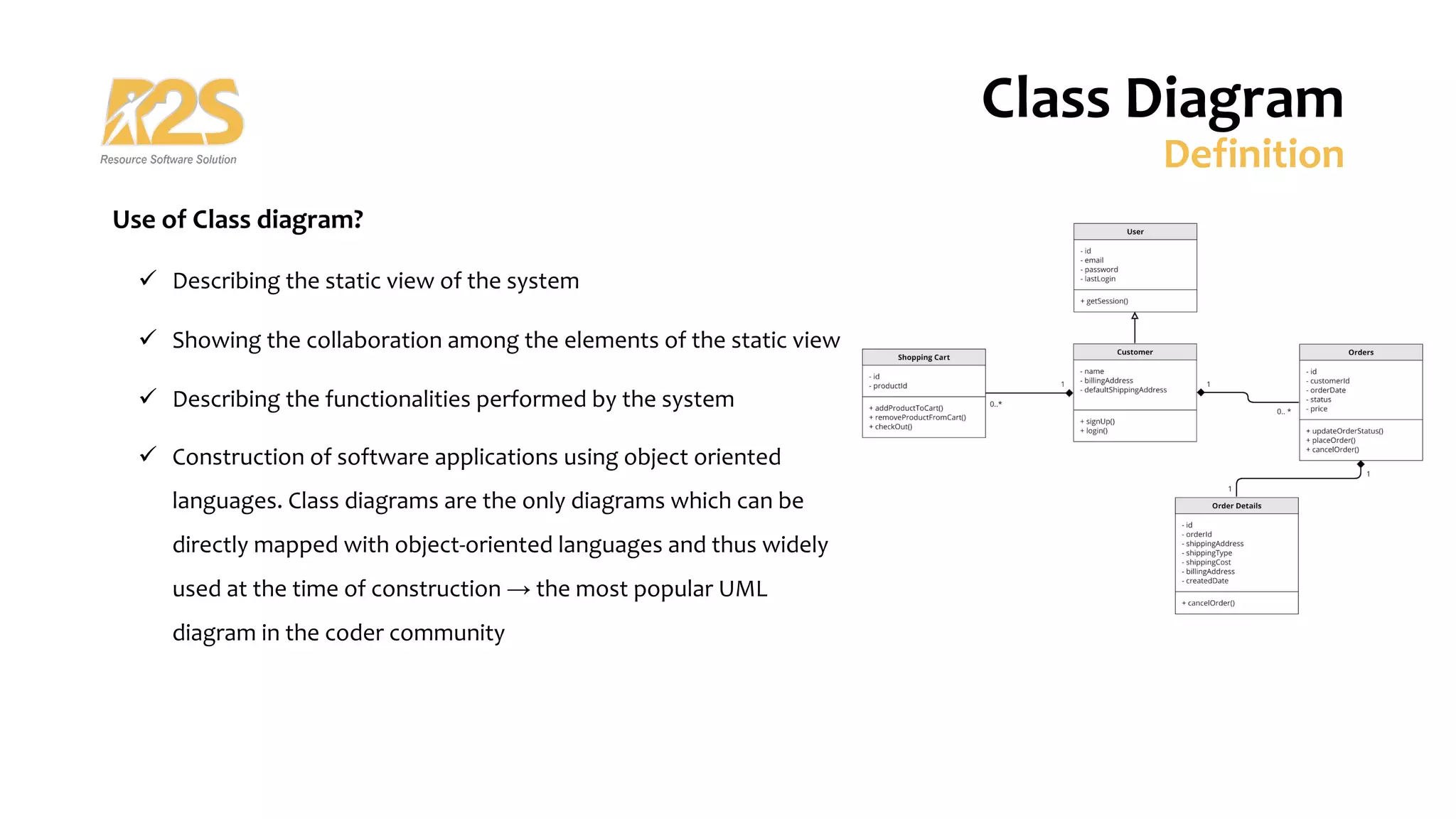
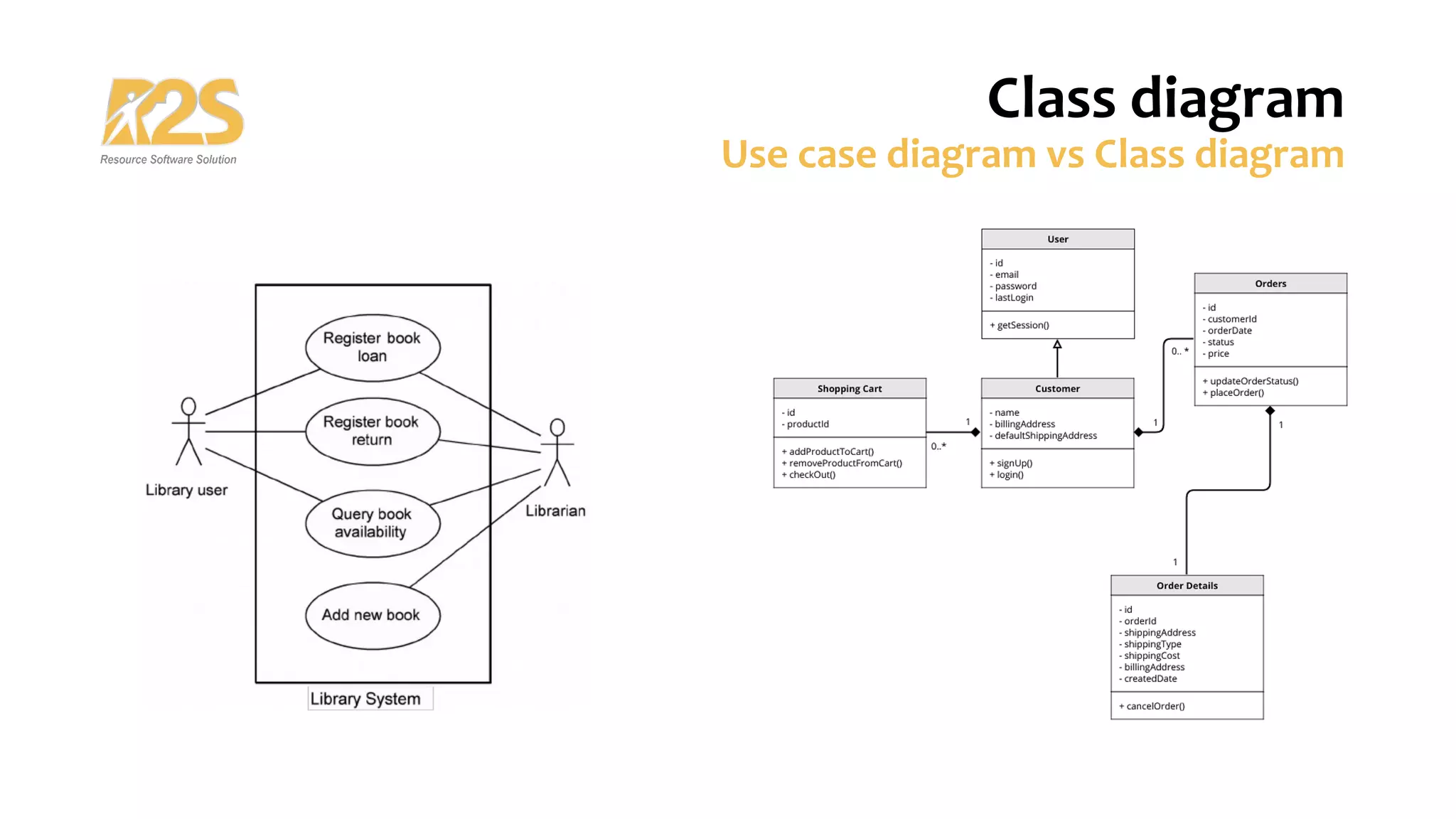
1. A class diagram shows classes, attributes, operations, and relationships between objects in a system. It describes the static structure of the system.
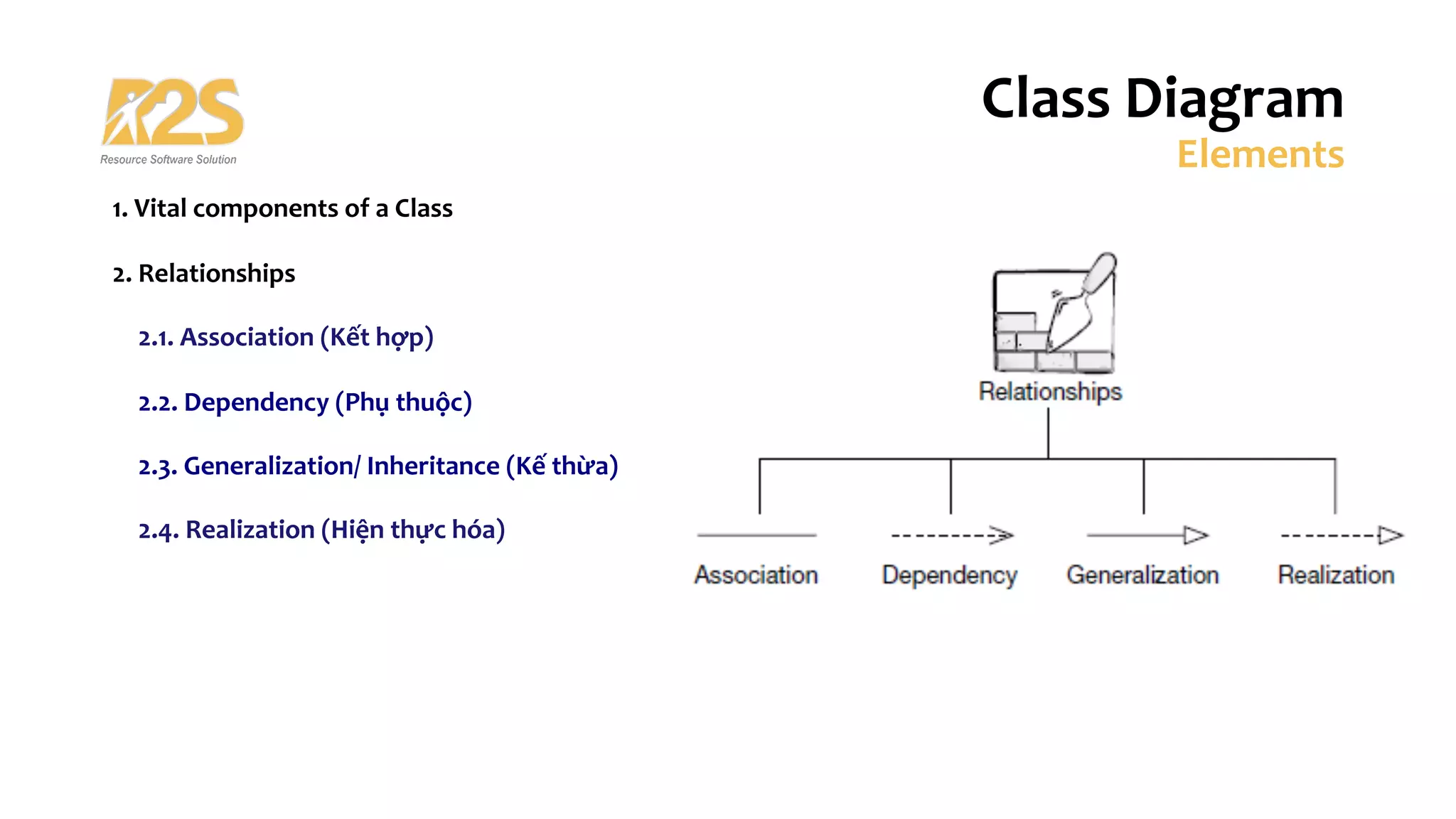
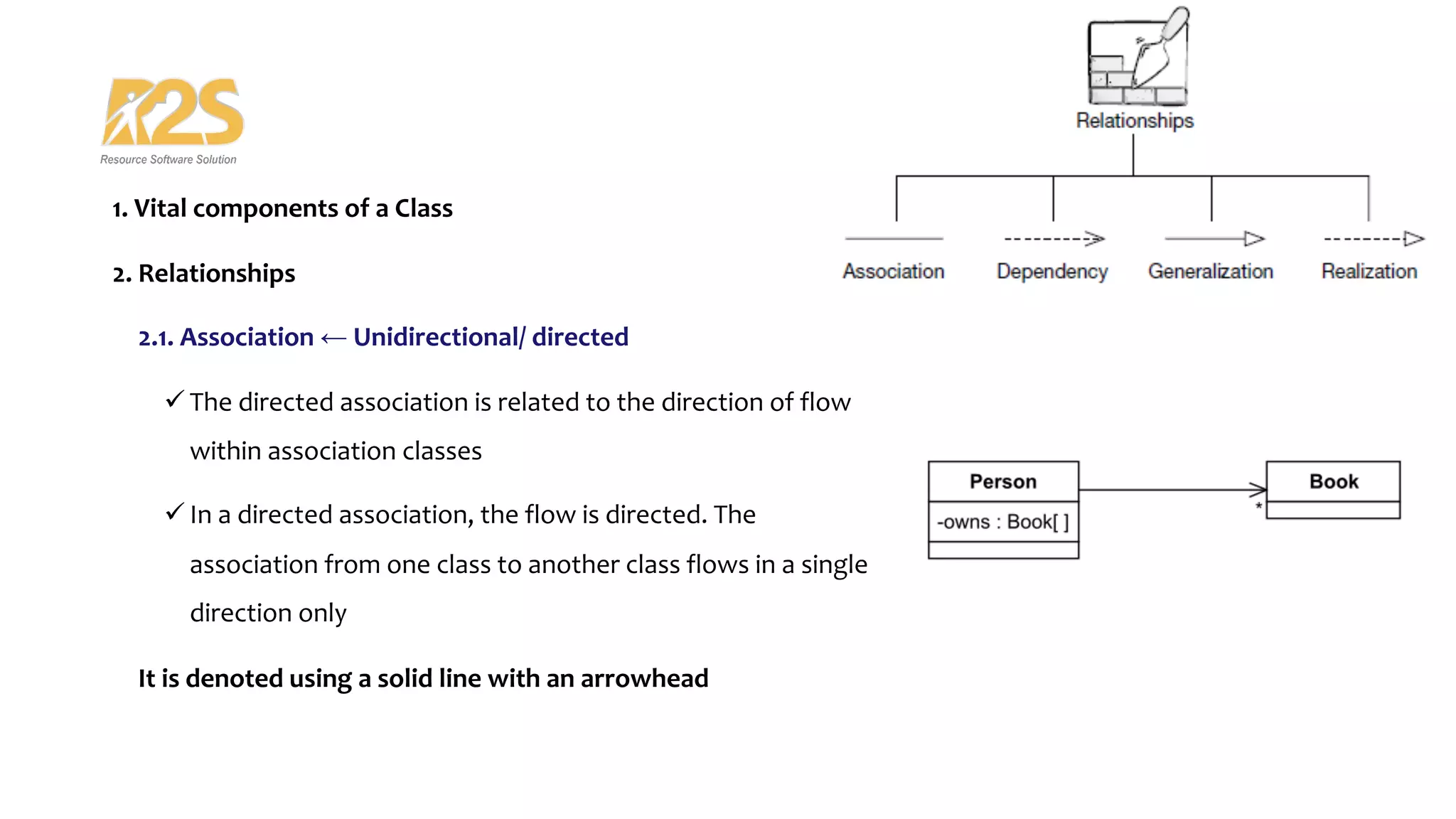
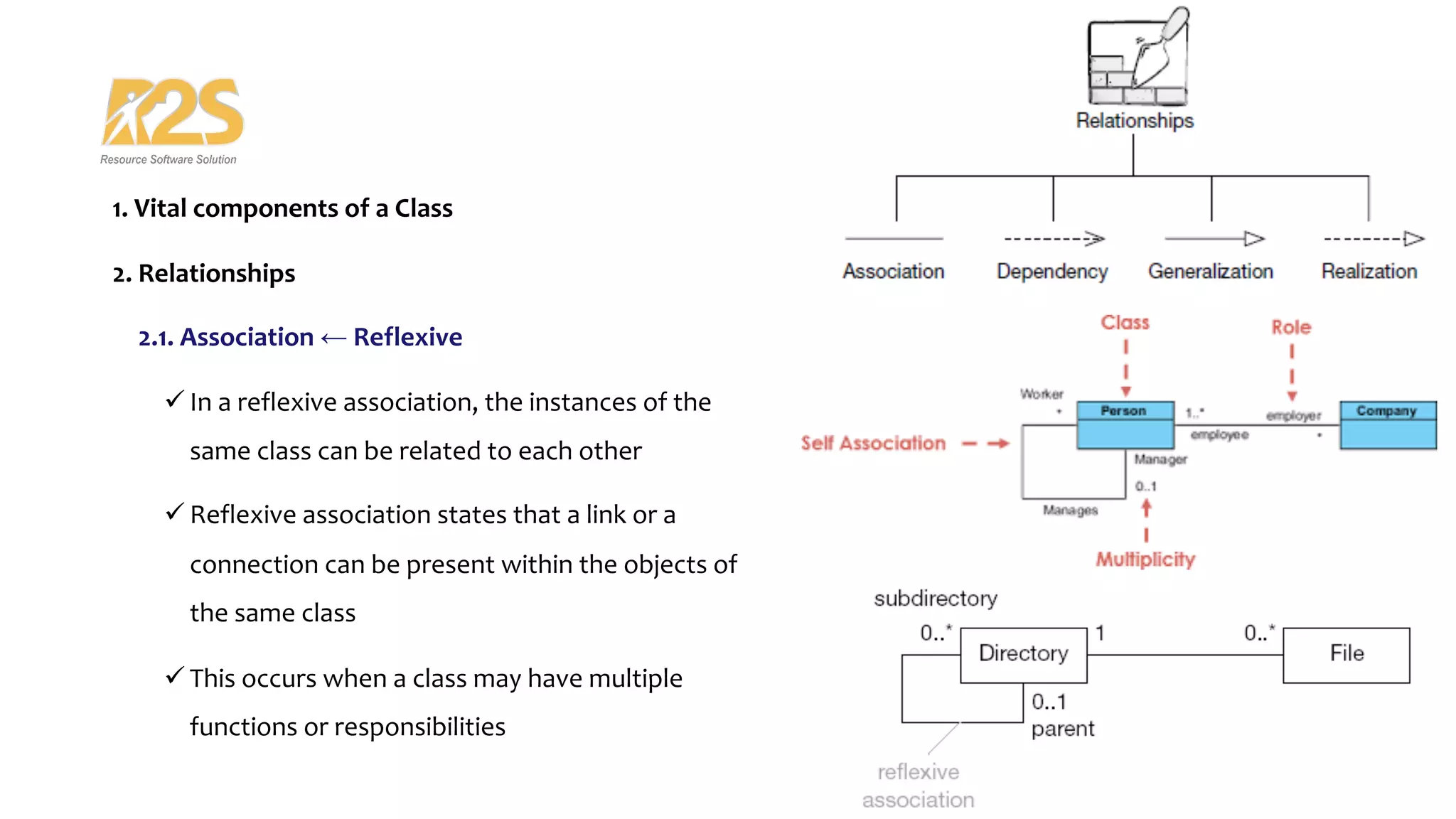
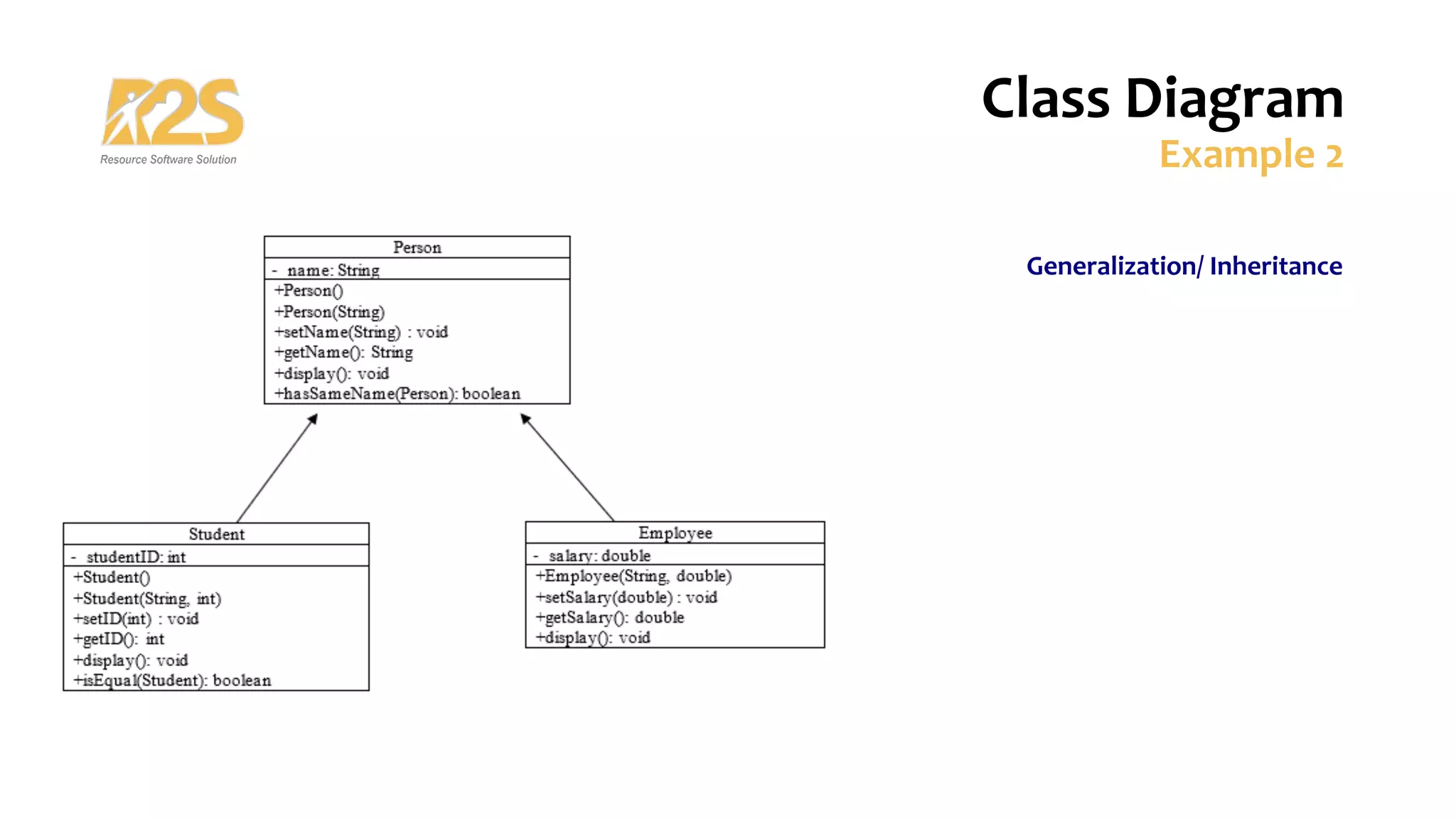
2. The main components of a class are its name, attributes, and operations. Relationships include association, dependency, generalization/inheritance, and realization.
3. Association examples include unidirectional, bidirectional, reflexive, and aggregation. Aggregation differs from composition based on whether parts can exist independently of the whole.