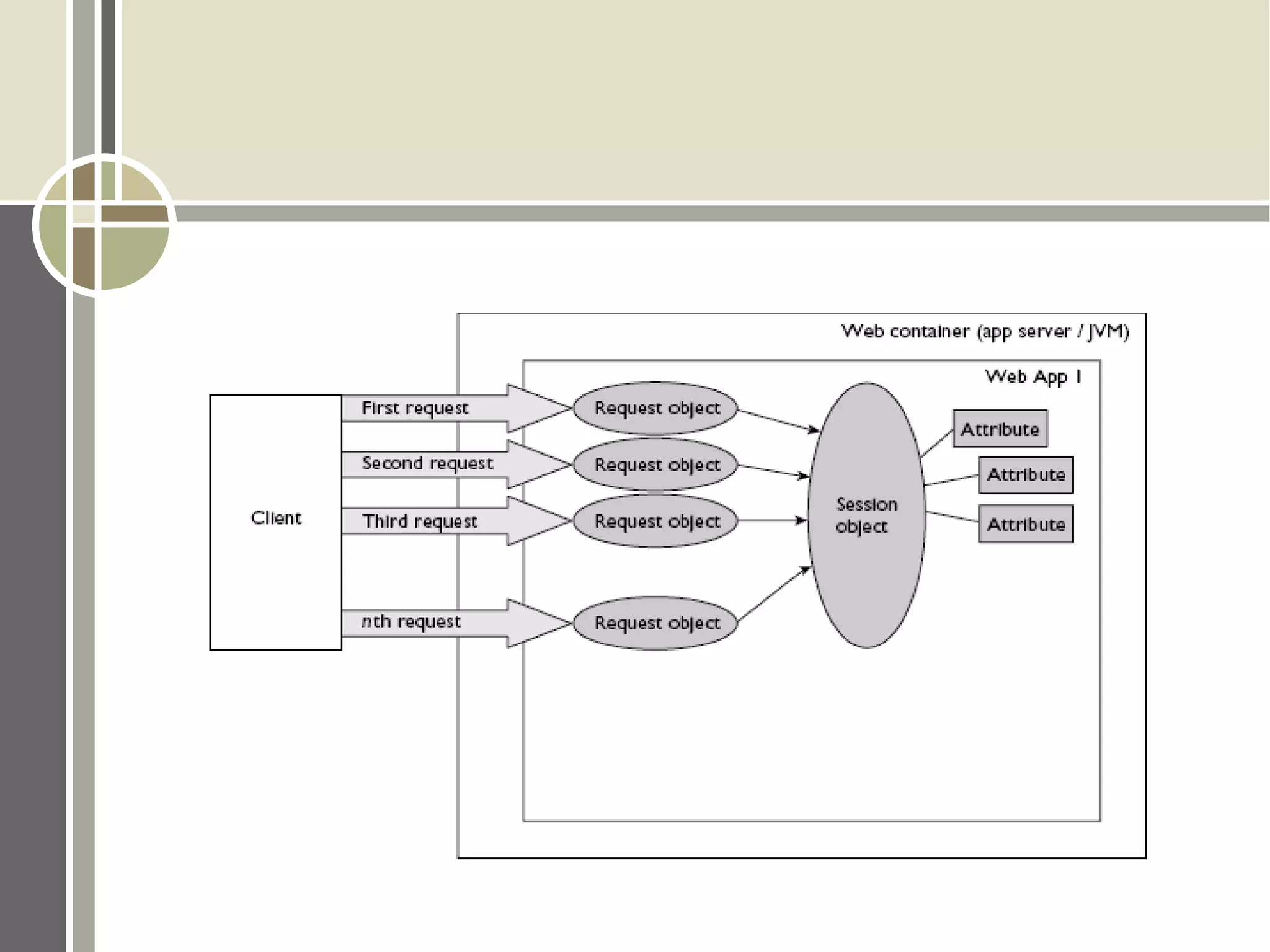
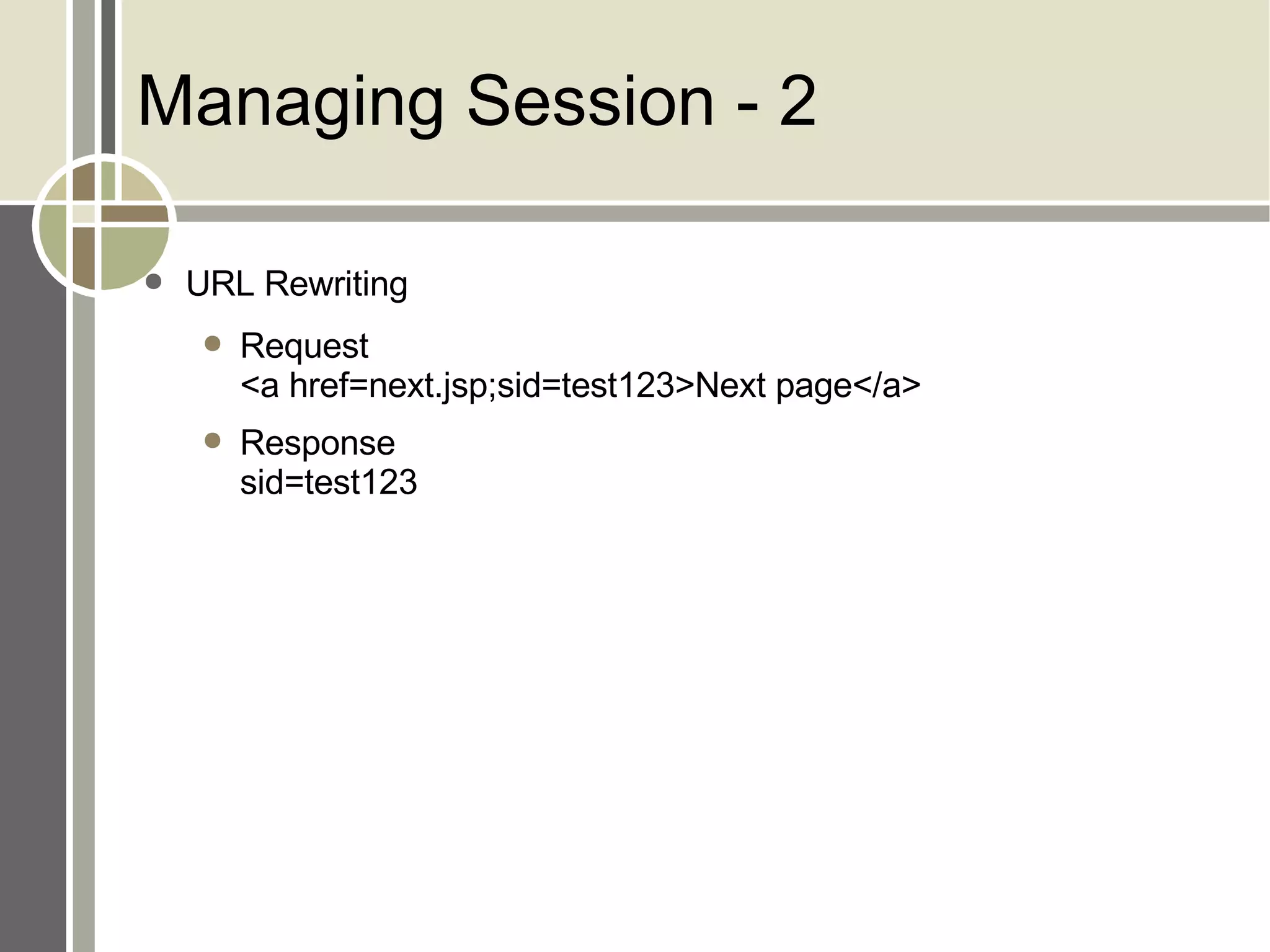
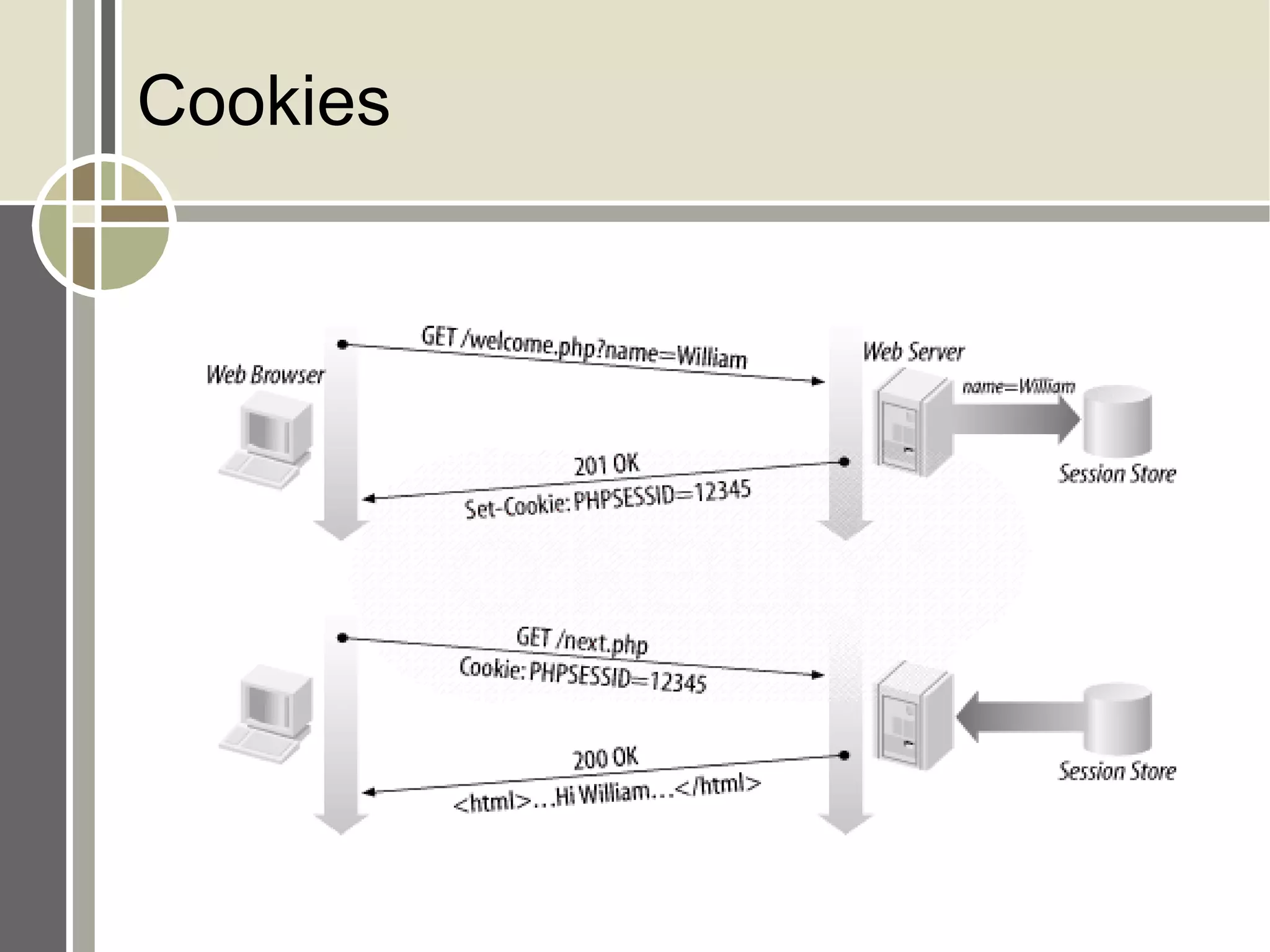
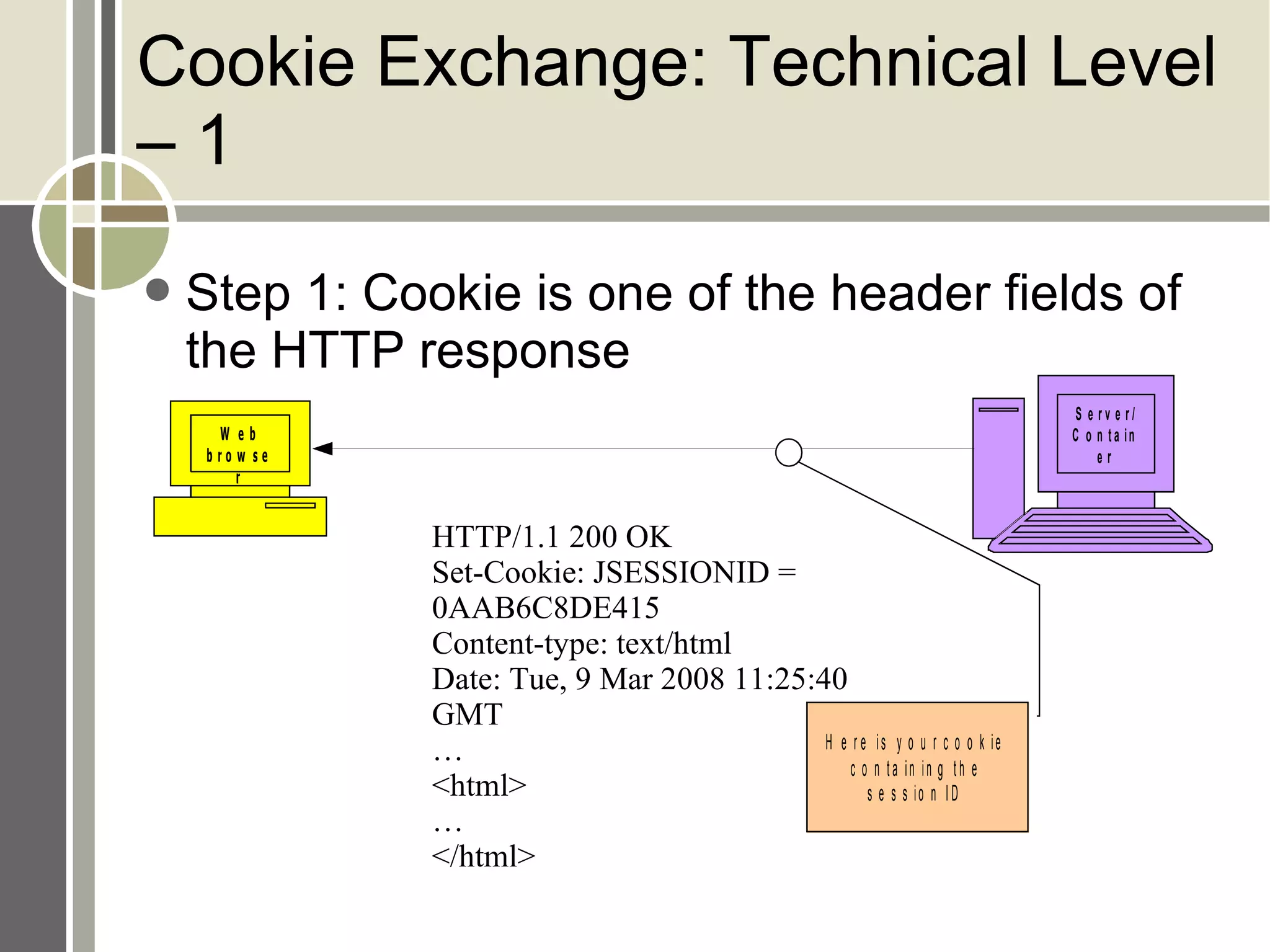
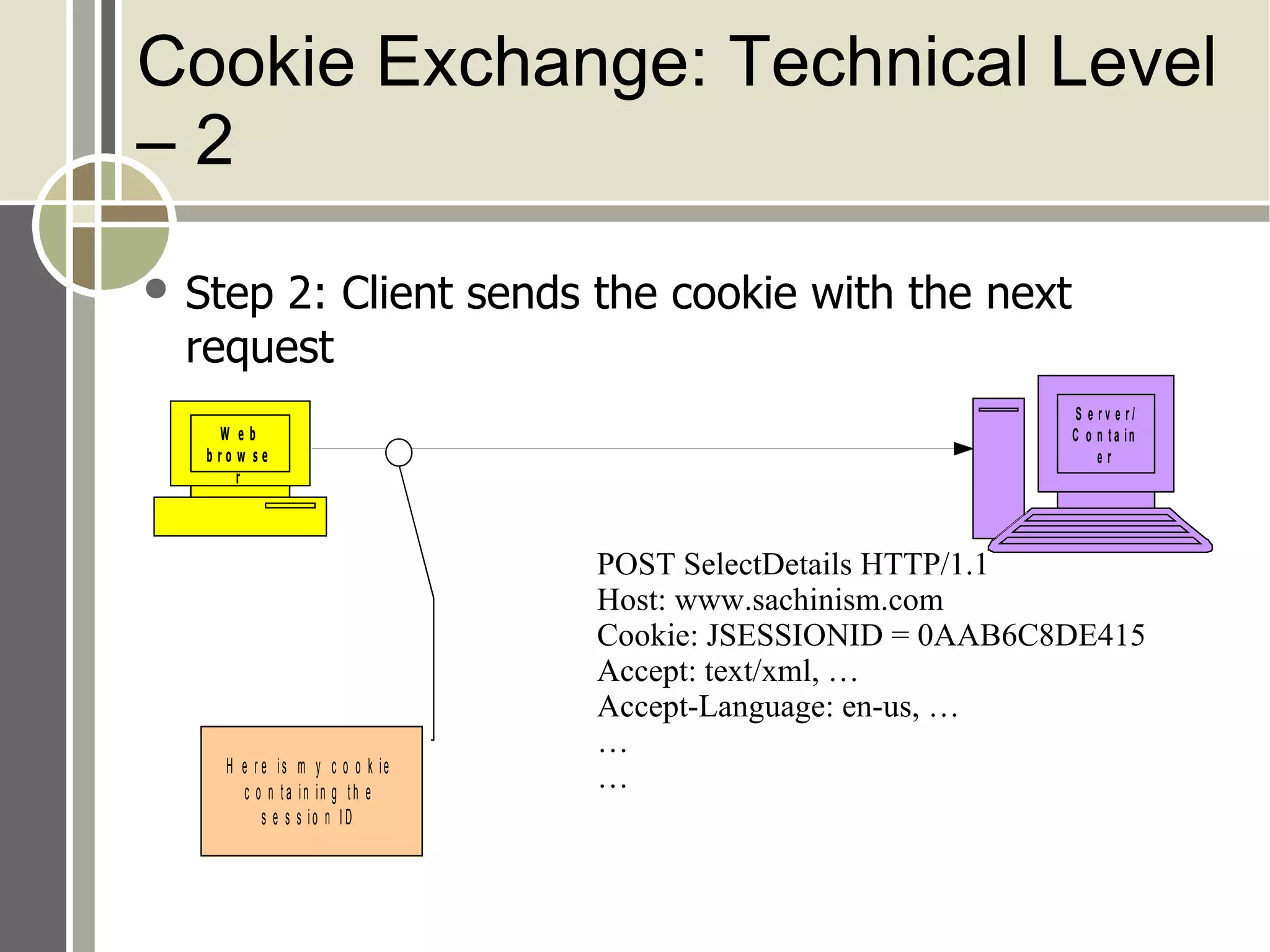
The document discusses session management and cookies in PHP. It describes how HTTP is stateless and sessions are used to maintain state across multiple requests. Sessions can be implemented using cookies, hidden form fields, or URL rewriting. Cookies are exchanged by setting a cookie header in the response and the client sending it back in subsequent requests. The document also outlines various PHP session functions like session_start(), session_register(), and setcookie() for managing sessions and cookies.
![PHP – Session Management & Cookies in PHP Harit Kothari [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-management-cookies-in-php-1205301153299811-2/75/Session-Management-Cookies-In-Php-1-2048.jpg)








![Session Management methods - 2 to avoid session mis-management!) string session_id([string id]) Can be used in two ways: to return the ID of an initialized session and to set the value of a session ID before a session is created. When used to return the session ID, the function must be called without arguments after a session has been initialized. When used to set the value of the session ID, the function must be called with the ID as the parameter before the session has been initialized.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-management-cookies-in-php-1205301153299811-2/75/Session-Management-Cookies-In-Php-17-2048.jpg)
![Session Management methods - 3 (to avoid session mis-management!) Boolean session_register(mixed name [, mixed ...]) Registers one or more variables in the session store. Each argument is the name of a variable, or an array of variable names, not the variable itself. Once a variable is registered, it becomes available to any script that identifies that session. This function calls the session_start( ) code internally if a session has not been initialized.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-management-cookies-in-php-1205301153299811-2/75/Session-Management-Cookies-In-Php-18-2048.jpg)



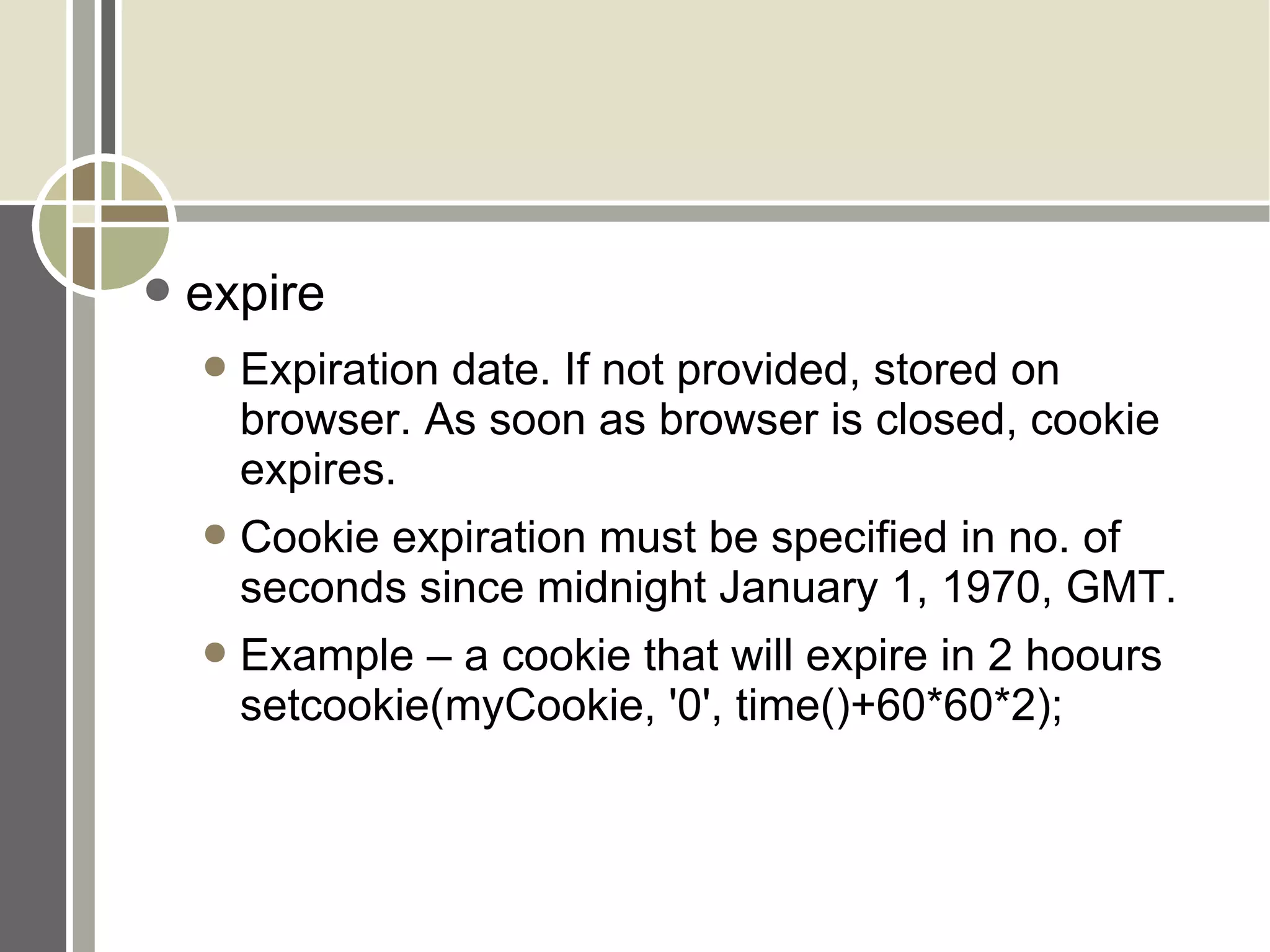
![Cookies Add / set cookie setcookie(name [, value [, expire [, path [, domain [, secure ]]]]]); Example : setcookie('accesses', '0'); Read cookie Manipulate $_COOKIE[] array Example : $pg_accesses = $_COOKIE['accesses'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-management-cookies-in-php-1205301153299811-2/75/Session-Management-Cookies-In-Php-22-2048.jpg)
![Understanding setcookie() setcookie(name [, value [, expire [, path [, domain [, secure ]]]]]); name Unique name to represent a cookie, like a variable value Value associated with cookie name, like variable value. Should not be too long. Appx. Max size for a cookie should be appx. 3.5KB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session-management-cookies-in-php-1205301153299811-2/75/Session-Management-Cookies-In-Php-23-2048.jpg)