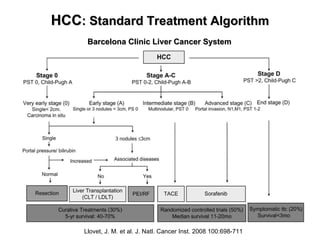
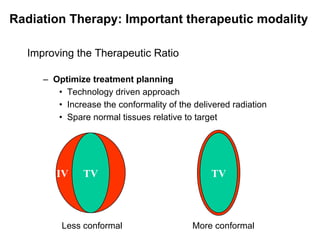
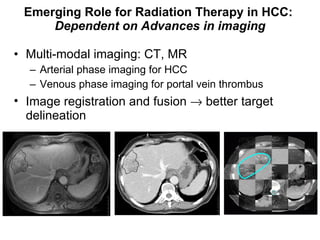
1) Radiation therapy has an emerging role in the multidisciplinary management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) due to advances that allow higher radiation doses to be safely delivered to small liver volumes.
2) Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) shows promise for HCC but questions remain about safety, effectiveness for bridging to transplant, and downsizing lesions.
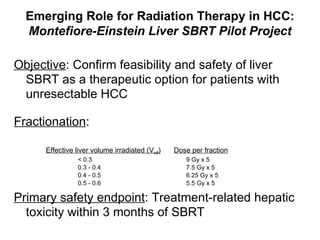
3) A pilot study is investigating the safety and feasibility of liver SBRT for HCC.