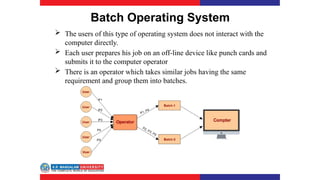
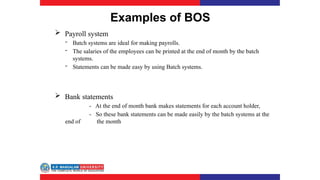
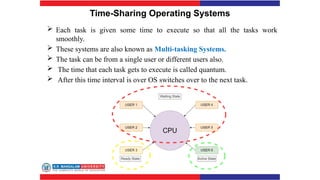
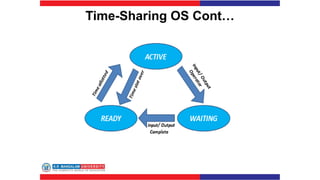
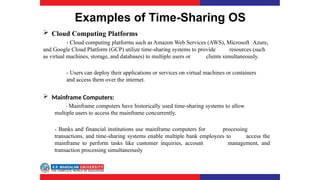
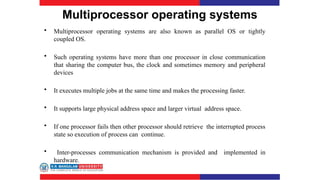
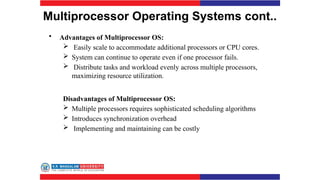
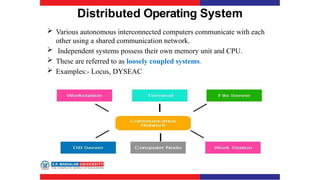
The document covers various types of operating systems, including their advantages and disadvantages, such as batch, time-sharing, multiprocessor, distributed, network, real-time, and embedded operating systems. Each type is described with examples and use cases, highlighting their functionalities and scenarios where they excel. Additionally, the document includes a test section with questions on operating system concepts and an answer key.