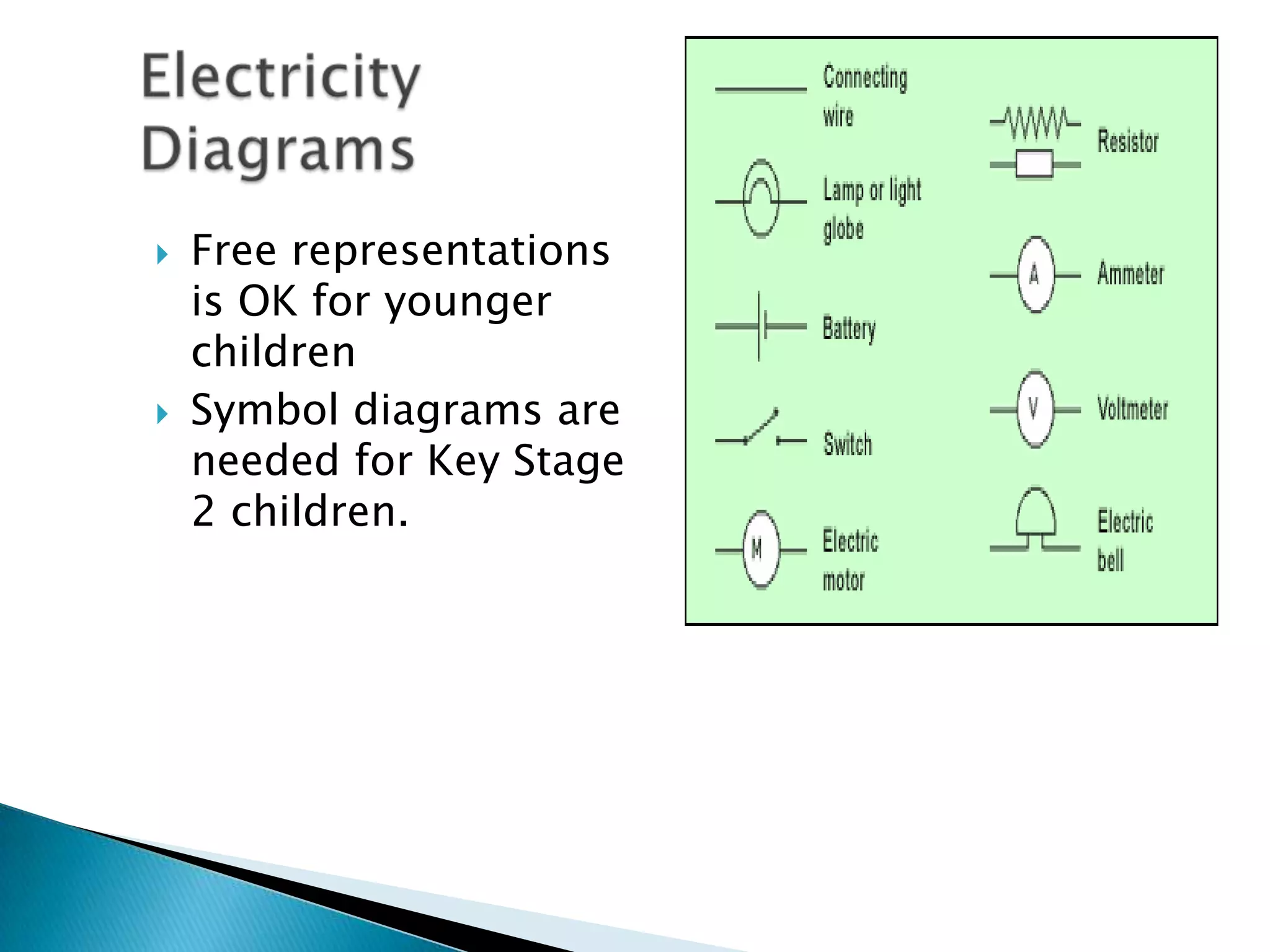
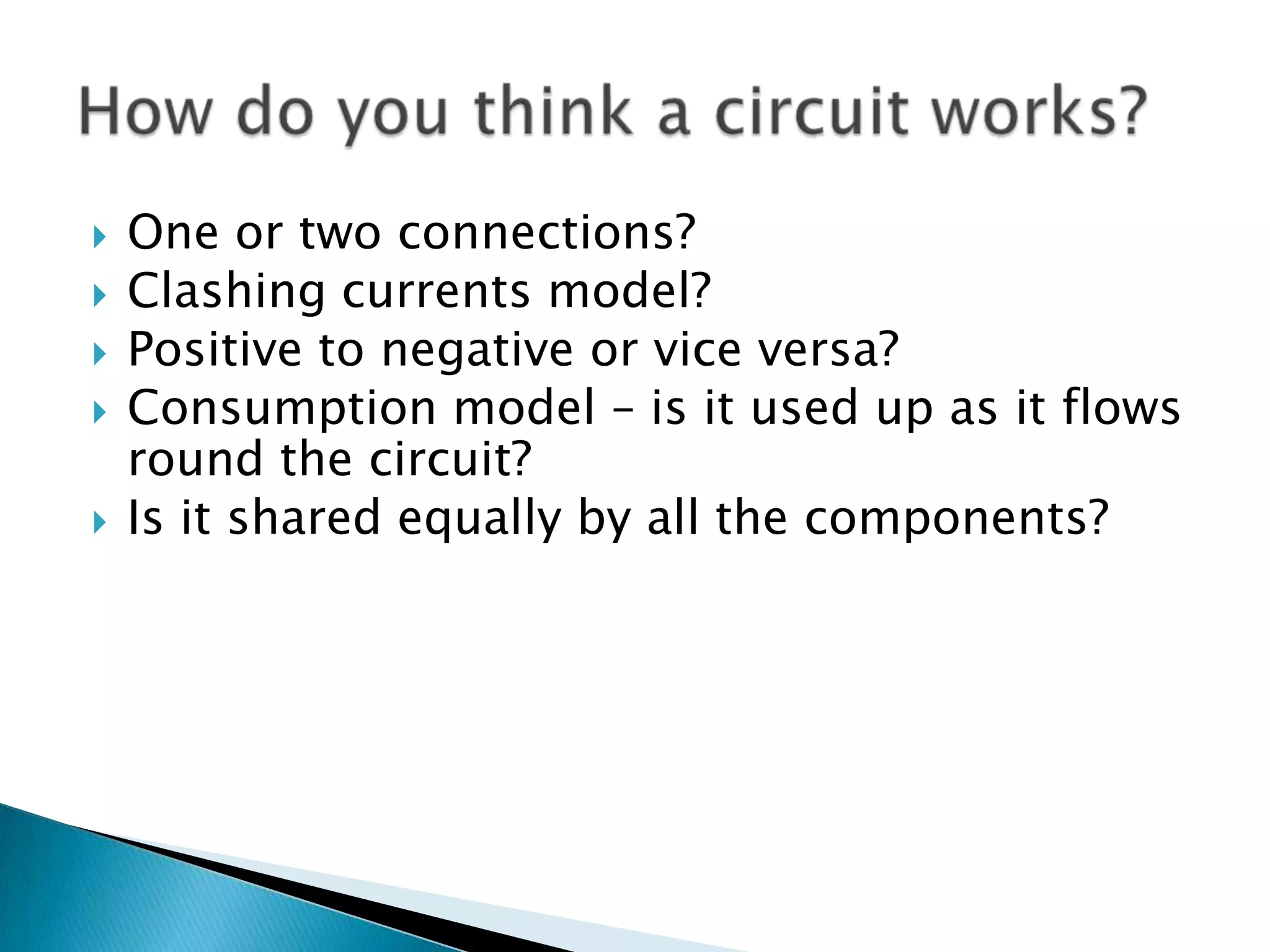
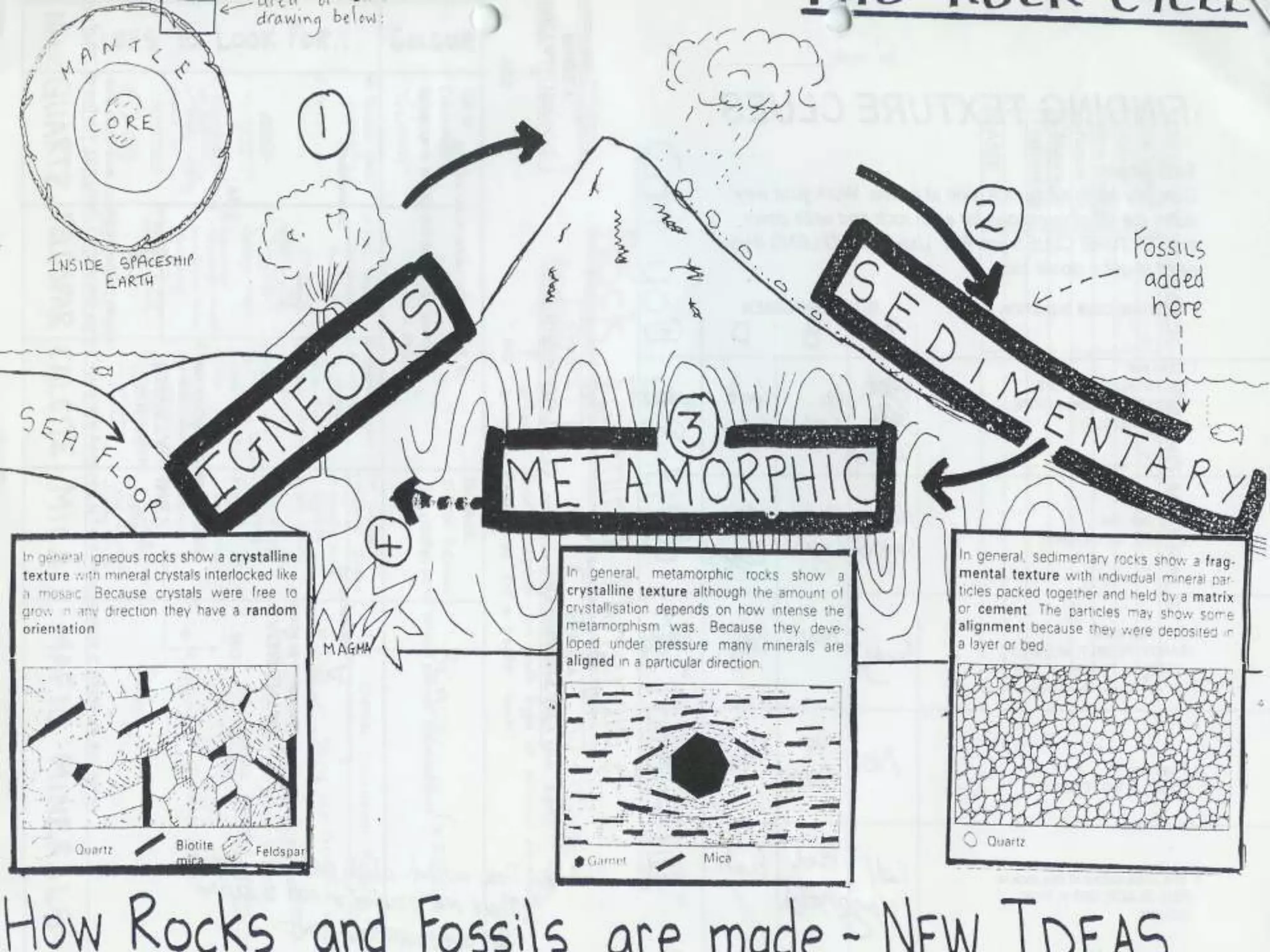
This document provides an overview of topics covered in a science lecture on electricity, magnetism, and rocks. It includes:
1. Objectives related to becoming familiar with teaching electricity, magnetism, and rocks as well as associated curriculum standards.
2. Suggested hands-on activities to teach concepts like circuits, static electricity, and the direction of electric current.
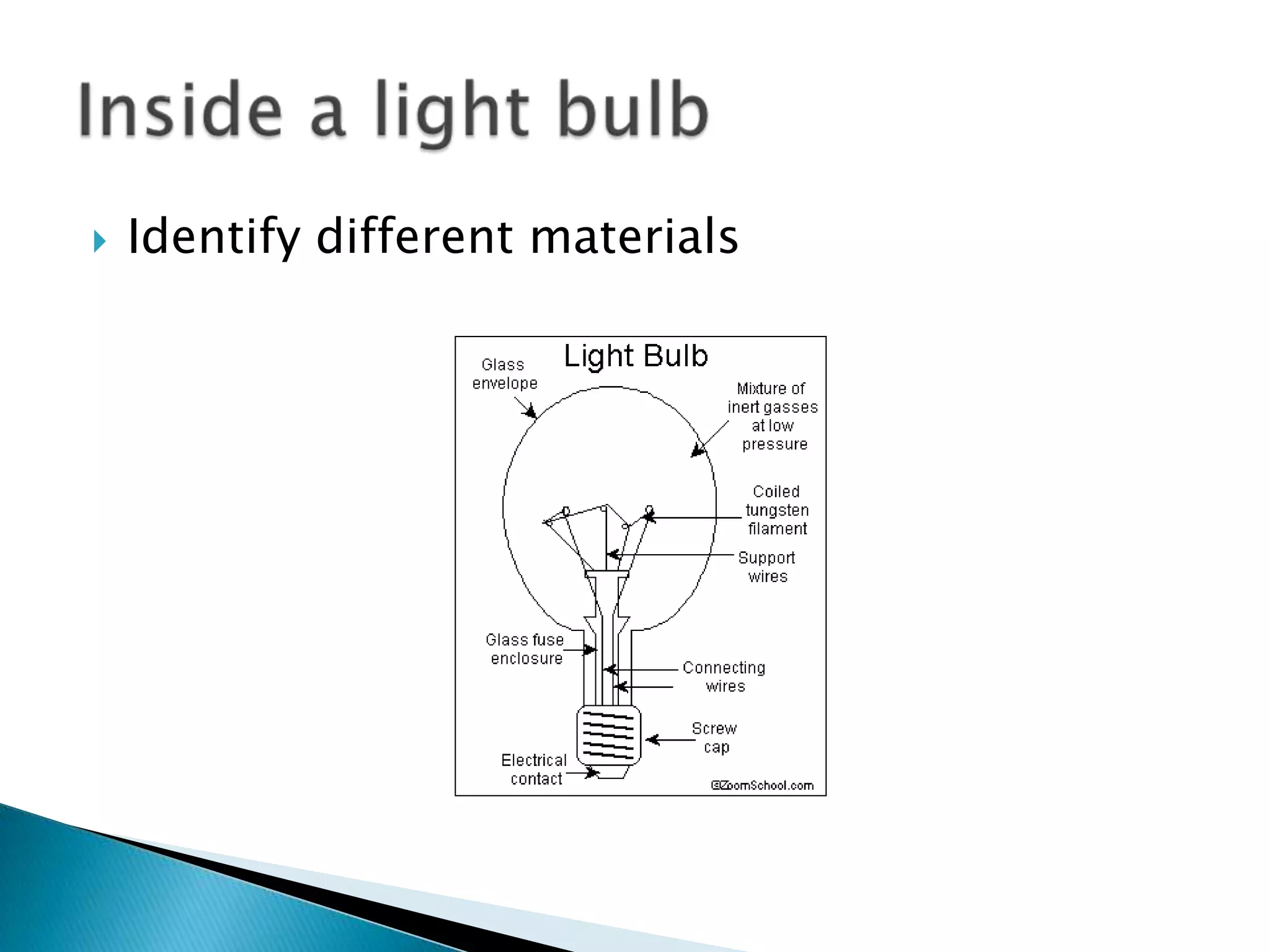
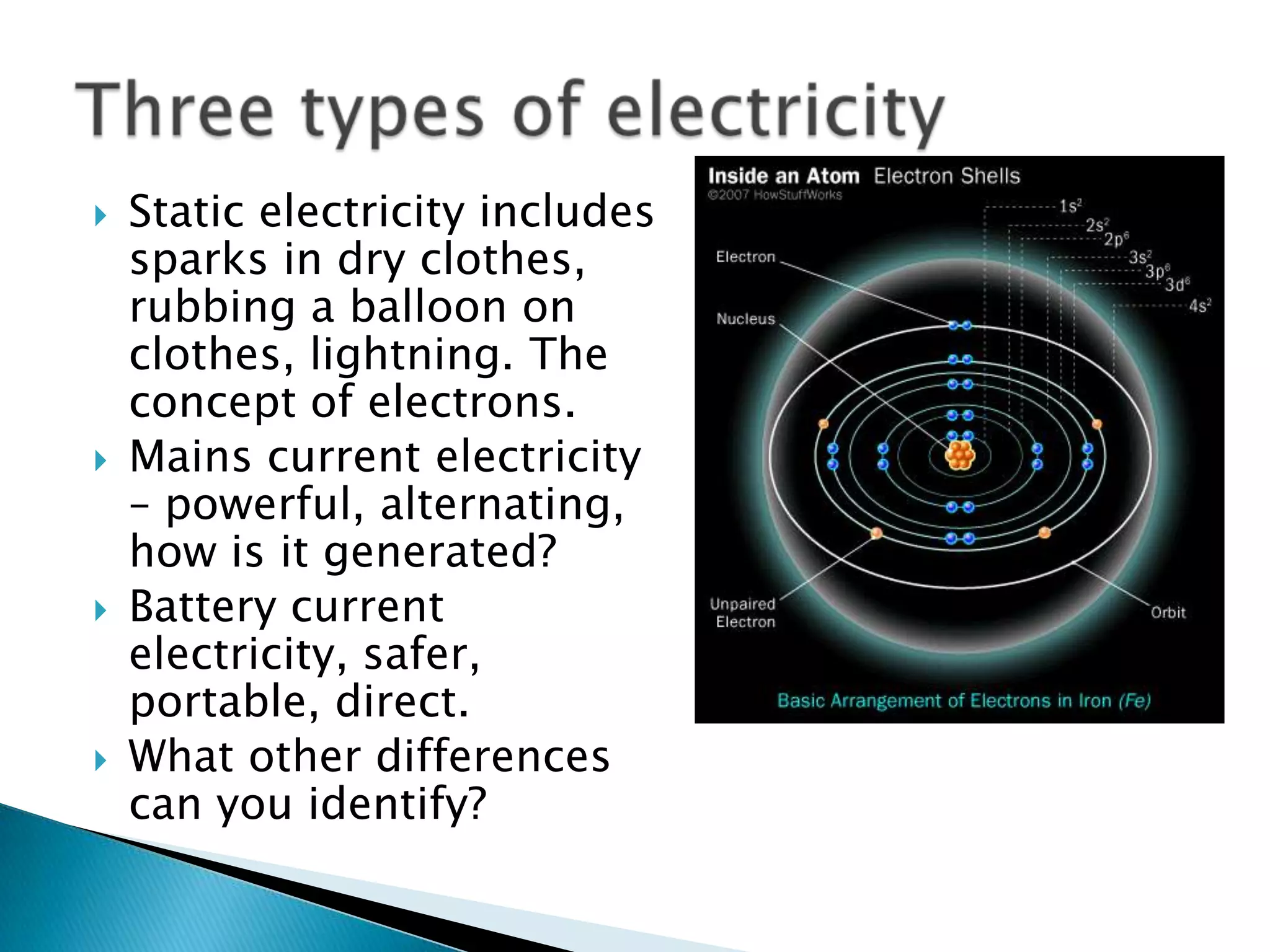
3. Information and misconceptions about concepts like conductors, insulators, atoms, and how circuits work.
4. Resources and investigations related to teaching topics like magnetism, types of rocks, and developing lesson plans. Criteria are provided for assessment of learning.