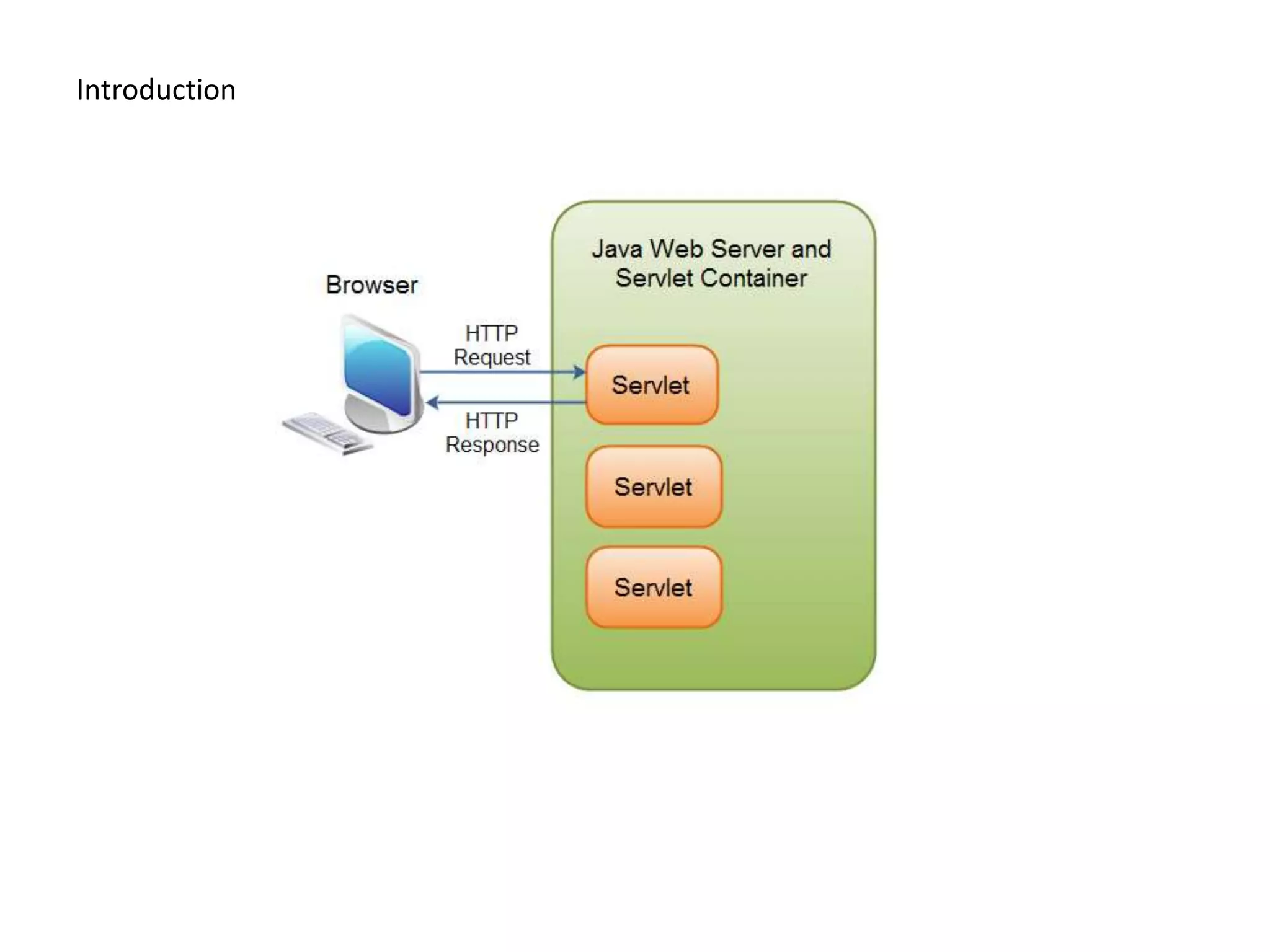
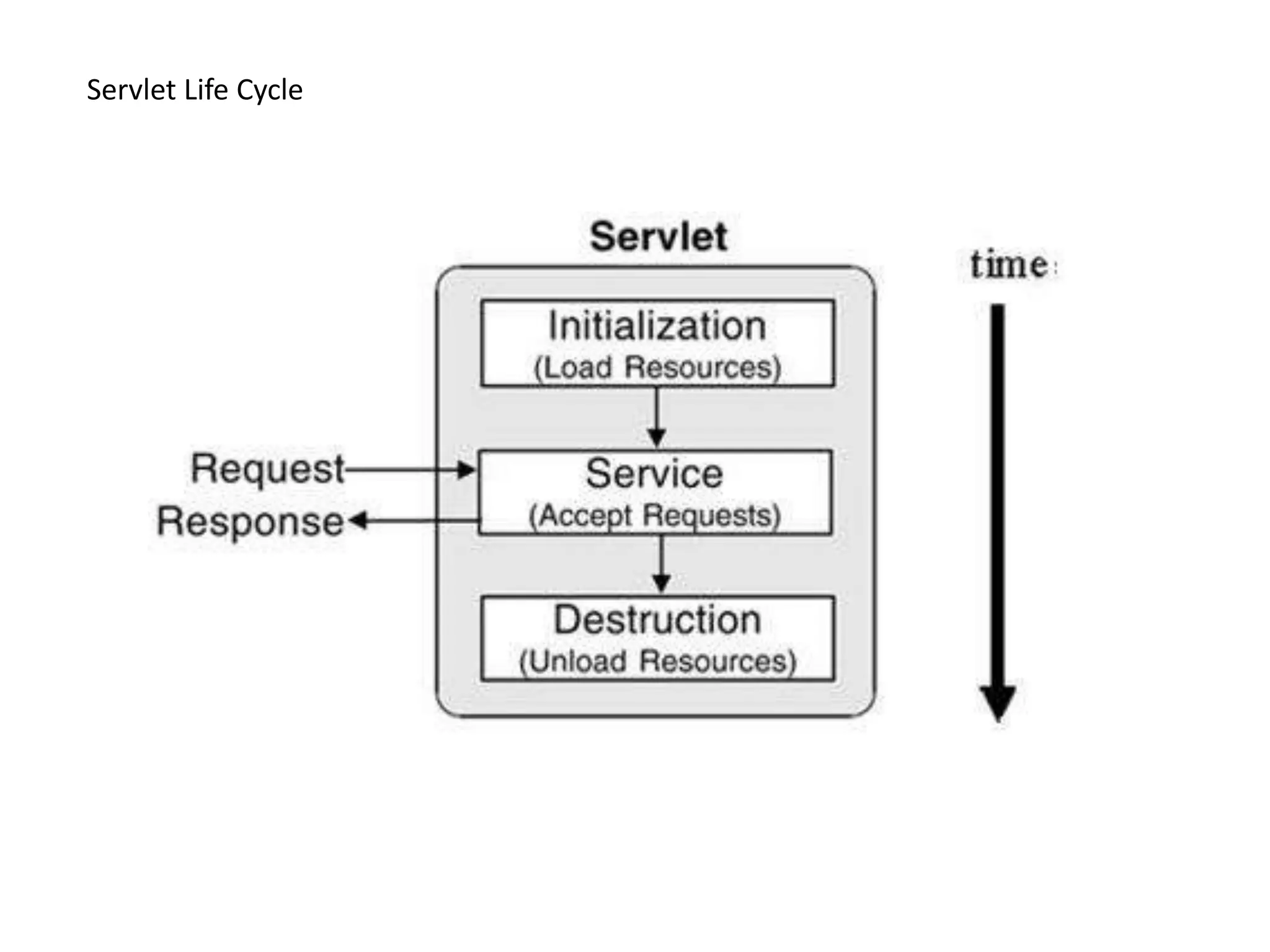
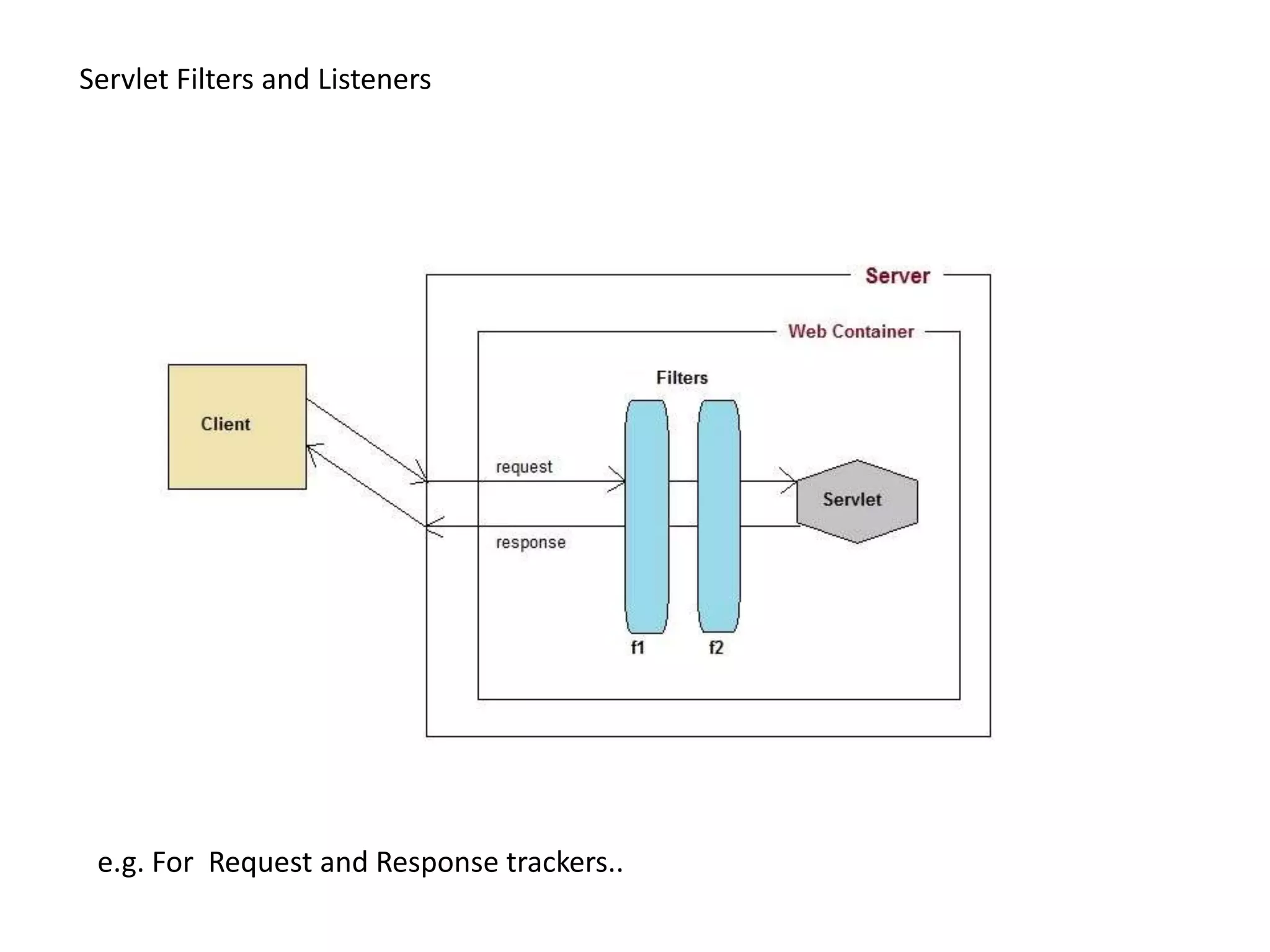
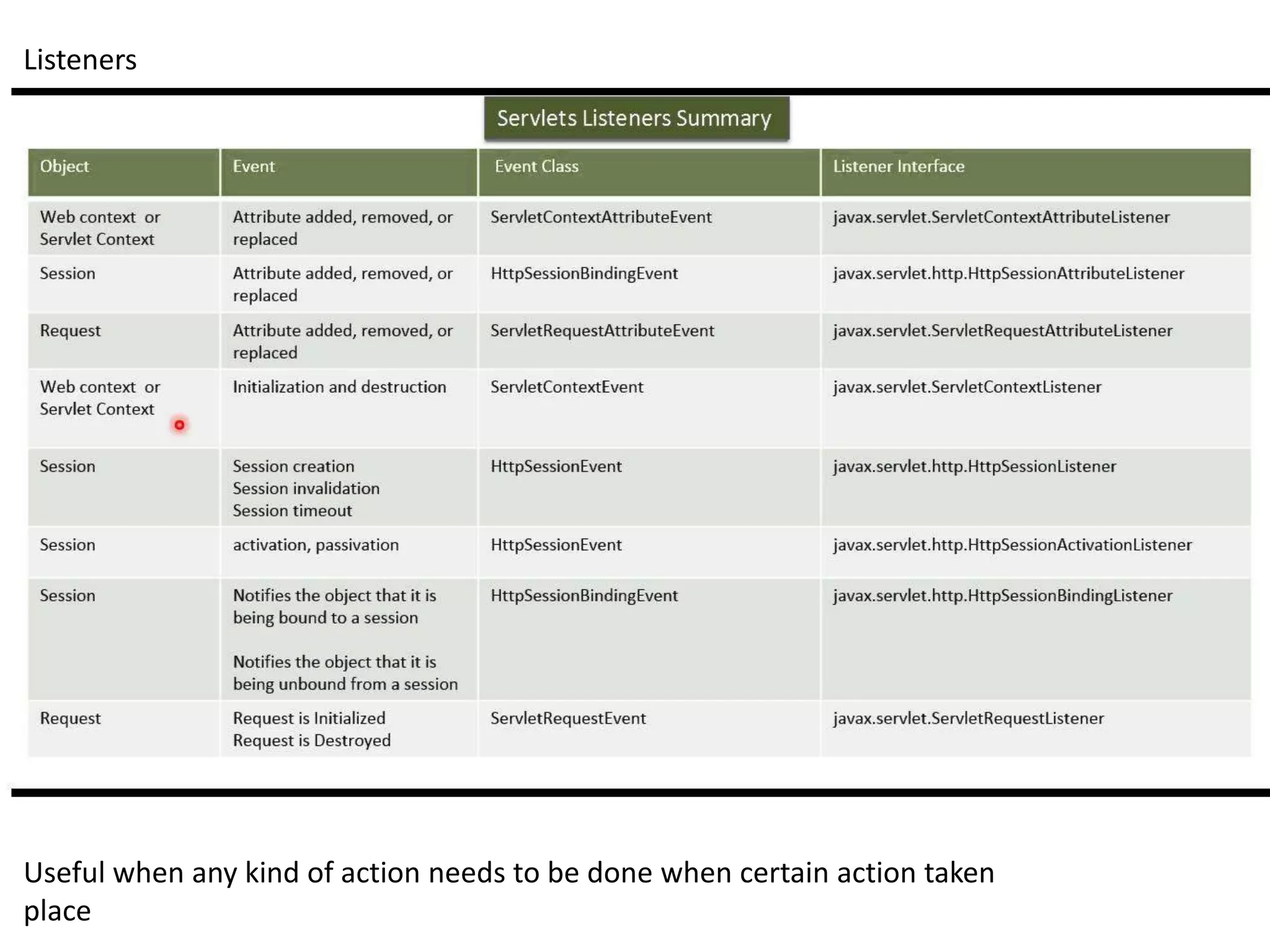
This document provides an overview of servlets and JSPs. It discusses the servlet lifecycle including loading, initialization, and configuration. It covers session management, filters, listeners, and the web.xml deployment descriptor. It also reviews the JSP lifecycle and implicit objects. The document uses examples to illustrate servlet initialization parameters, the servlet context, and communicating between servlets and JSPs. It concludes with potential assignments involving building login, file upload, and inter-component communication applications.