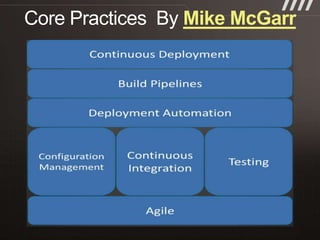
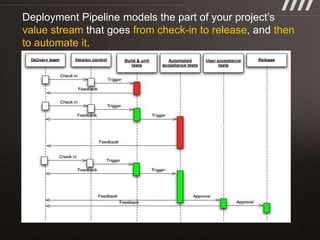
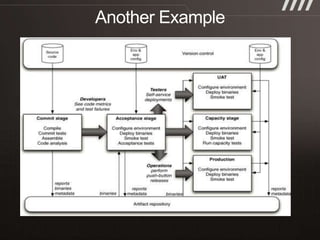
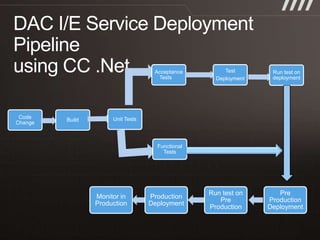
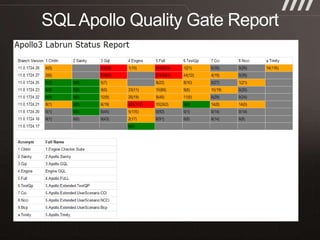
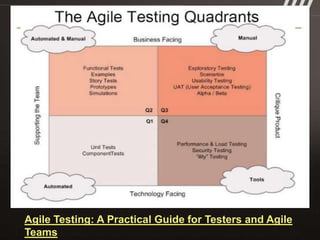
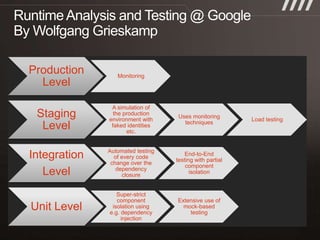
The document discusses key practices for software development, emphasizing continuous integration and continuous delivery to improve service quality and engineering agility. It advocates for a robust testing strategy, including testing in production and frequent automated deployments to enhance software release reliability. The focus is on creating efficient processes to ensure quality, reduce costs, and deliver customer value consistently.