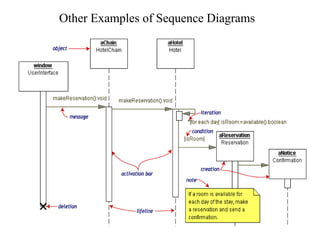
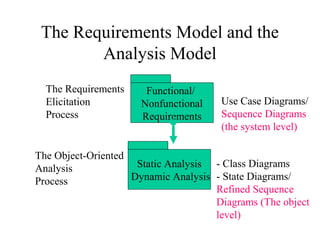
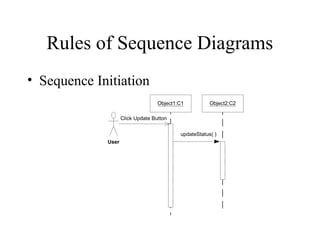
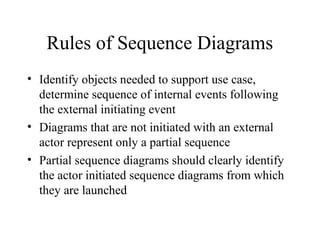
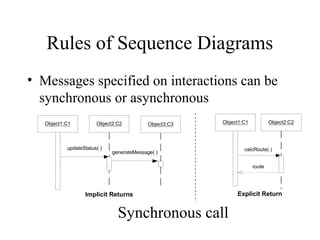
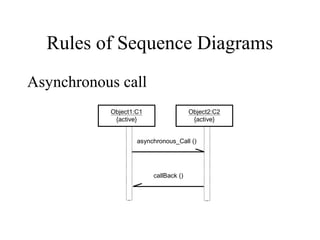
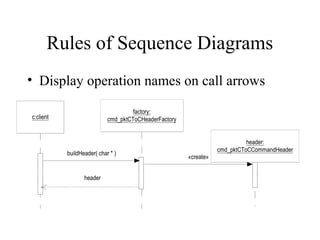
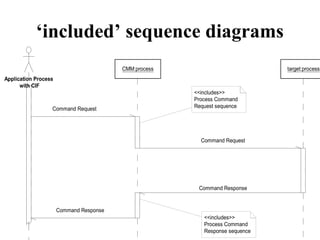
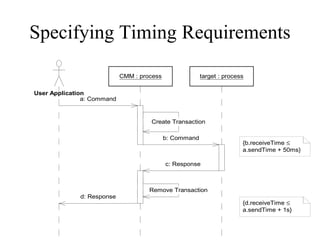
This document provides an overview of sequence diagrams and their use in UML modeling. It discusses the importance of sequence diagrams in depicting object interactions for use cases. The document outlines basic rules for constructing sequence diagrams, including identifying initiating events, messages, and synchronous/asynchronous calls. It provides examples of system sequence diagrams for various use cases of a vending machine system. These diagrams show object interactions and information flow over time to achieve the desired behaviors.


![Rules of Sequence Diagrams
Compound and Simple Iteration
* [for all
Interfaces in
Container] Find( )
amMasterSI( )
setState( )
getInterfaceContainer()
* [for all Interfaces in Container] publishState() setOn( ) / setOff( )
{
:DiscreteFD
:DiscreteFD
:Interface
:Interface:InterfaceContainer:Subsystem :Resource](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-10-320.jpg)
![Showing alternate behavior in a sequence
diagram
validateCommand( )
issueCommand( )
User Application
[if valid command] routeCommand( )
[if invalid command] logError( )
display(status)
:CmdHandler :CmdValidater :CmdRouter :EventLog :StatusDialog](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-12-320.jpg)
![Showing Extension Point
validateCommand( )
routeCommand( )
display( status)
Extension Point
[invalid command]
abort command
request and send
system message
:StatusDialog:CmdRouter:CmdValidater:CmdHandler
issueCommand( )
User Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-13-320.jpg)
![System Sequence Diagram
for Deposit Money Use Case
C u s t o m e r
M o n e y D e t e c t i o n
H a r d w a r e
C R T D i s p l a y
V e n d i n g M a c h i n e
C o n t r o l l e r
D e p o s i t M o n e y
[ I d l e S t a t e ]
D i s p l a y W e lc o m e
M e s s a g e
D i s p l a y A m o u n t
S e n d A m o u n t
P r o m p t f o r S e l e c t i o n
S t a r t T i m e r
[ I f T i m e r > 3 0 s e c o n d s a n d I n v a l i d o r N o S e l e c t i o n ]
R e t u r n M o n e y
M o n e y
D i s p e n s e r
S t o p
T i m e r[ I d l e S t a t e ]
D i s p l a y W e l c o m e
M e s s a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-15-320.jpg)
![System Sequence Diagram
for Make Selection Use Case
C u s t o m e r
N u m e r ic K e y p a d C R T D is p la y
V e n d in g M a c h in e
C o n t r o lle r
M o n e y
D is p e n s e r
P r o d u c t
D is p e n s e r
P r o m p t
f o r
S e le c t io n
E n t e r S e le c t io n
D is p la y S e le c t io n
S e n d S e le c t io n
P r o d u c t
D a t a b a s e
I n q u ir e D a t a b a s e
[ if I n v a lid S e le c t io n ]
P r o m p t f o r A n o t h e r S e le c t io n
D is p e n s e P r o d u c t
D is p e n s e C a lc u la t e d
C h a n g e[ I d le S t a t e ]
D i s p la y W e lc o m e
M e s s a g e
N o t e : I n s u f f i c i e n t
m o n e y , s e l e c t i o n
n o t a v a i l a b l e
N o t e : I f
R e l e a s e - I n p u t
B u t t o n P r e s s e d s e e
C a n c e l l a t i o n
S e q u e n c e D i a g r a m
R e t u r n R e s p o n s e
V a lid a t e
U p d a t e D a t a b a s e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-16-320.jpg)
![System Sequence Diagram
for Cancellation Use Case
C u s t o m e r
N u m e r ic K e y p a d C R T D is p la y
V e n d in g M a c h in e
C o n t r o lle r
M o n e y D is p e n s e r
P r o m p t
f o r
S e le c t io nR e le a s e - I n p u t
B u t t o n P r e s s e d
S e n d C a n c e lla t io n S ig n a l
[ I d le S t a t e ]
D is p la y W e lc o m e
M e s s a g e
R e t u r n M o n e y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-17-320.jpg)
![System Sequence Diagram
for Update Database Use Case
M a i n t e n a n c e
O p e r a t o r
A ll H a r d w a r e
E x c e p t C R T D i s p la y
C R T D i s p la y
V e n d i n g M a c h i n e
C o n t r o l l e r
P r o d u c t
D a t a b a s e
W ir e le s s K e y b o a r d
P o w e r O n
S e n d A c t i v e S i g n a l
D is p la y P r o g r a m m in g
I n f o r m a t i o n
D is a b le
E n a b l e
S e n d U p d a t e C o m m a n d s
U p d a t e D a t a b a s e
P o w e r O f f
[ I d l e S t a t e ]
D is p l a y W e l c o m e I n f o r m a t i o n
D is p la y U p d a t e
C o m m a n d s
T e r m i n a t e U p d a t e M o d e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequensediagram-180925090014/85/Sequense-diagram-18-320.jpg)