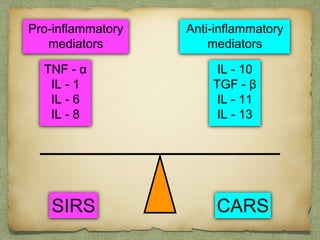
Sepsis is defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction due to a dysregulated host response to infection, and is a major cause of mortality and critical illness, with significant healthcare costs. Key diagnostic criteria include alterations in mentation and blood pressure, alongside the use of procalcitonin as a biomarker, despite it not being necessary for initiating treatment. Timely management involves implementing 3-hour and 6-hour treatment bundles focused on resuscitation and monitoring to improve patient outcomes.