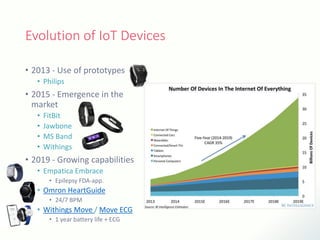
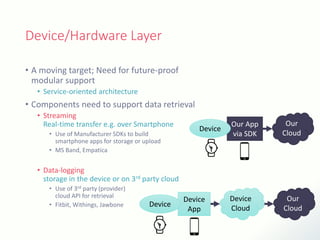
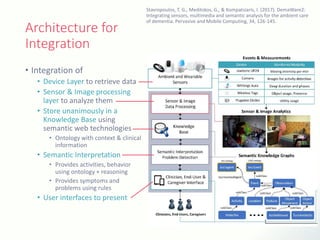
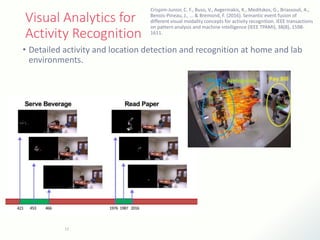
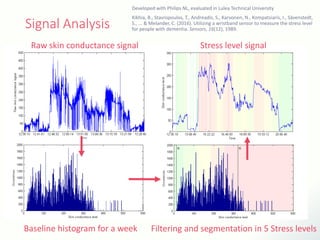
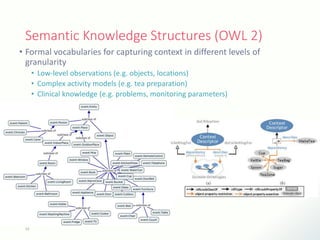
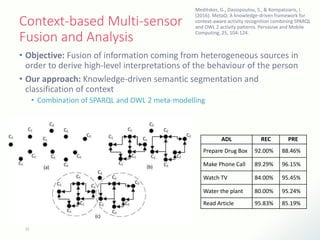
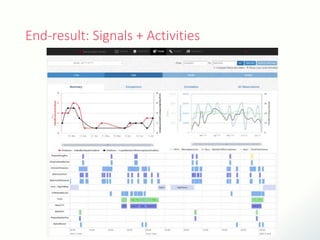
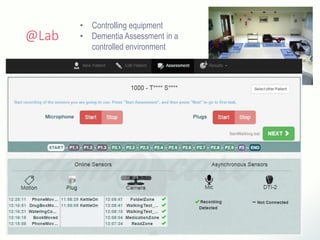
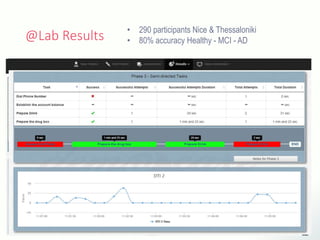
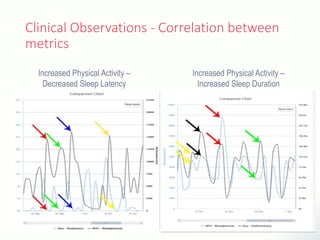
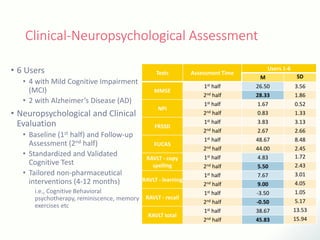
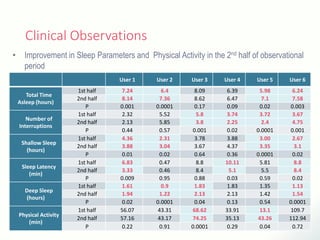
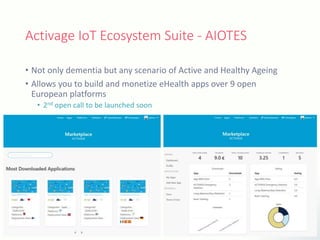
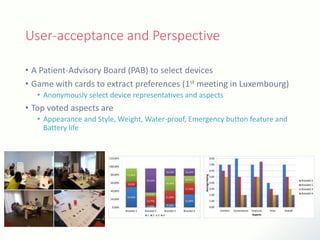
The document discusses innovative solutions for dementia care, emphasizing the integration of IoT and wearable sensors for continuous monitoring and personalized feedback to enhance patient safety and independence. It outlines various technological advancements, existing projects, and clinical interventions aimed at improving dementia care efficiency and effectiveness. Future directions include further integration of AI and big data to support cognitive and physical interventions for patients.