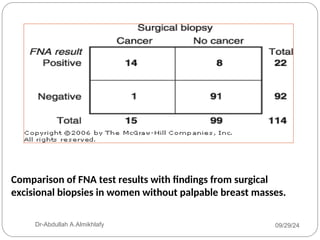
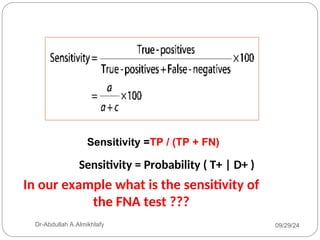
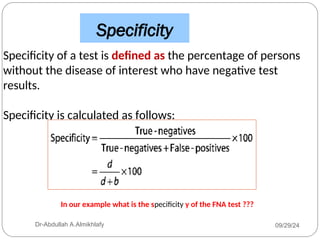
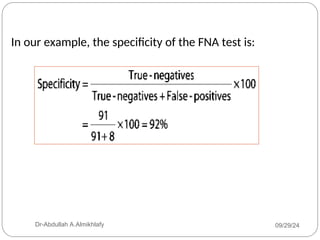
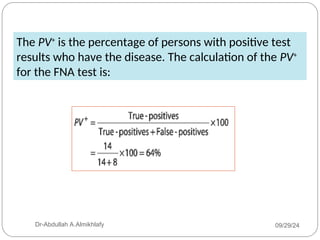
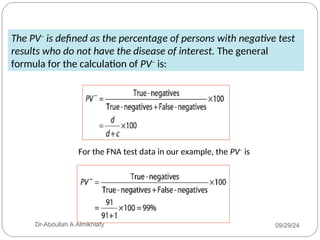
The document discusses the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tests, particularly focusing on a case study involving a 54-year-old teacher with an abnormal mammogram leading to a diagnosis of breast cancer through fine-needle aspiration (FNA). It explains key metrics like positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV), illustrating how these values change pre- and post-test. Ultimately, it emphasizes the importance of further testing, such as surgical biopsy, to confirm a diagnosis despite the predictive values of the FNA test.