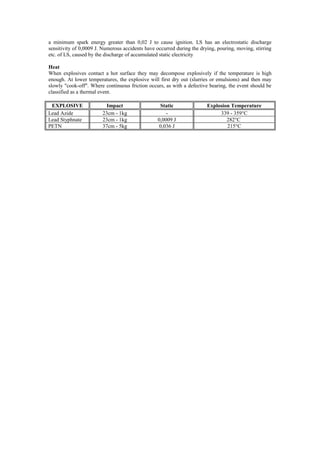
Initiating explosives like lead azide and lead styphnate are highly sensitive to mechanical shock and ignition by flame or static sparks. They are used to reliably detonate less sensitive secondary explosives. Lead azide detonates reliably under high pressures and in small amounts, while lead styphnate ignites easily but is a weaker explosive. Because of their sensitivity, initiating explosives must be handled with special precautions in small quantities. An impact involves two hard surfaces striking with explosive in between, while friction and static electricity can also initiate explosives through heating. Initiating explosives require only a small static spark while secondary explosives require more energy. Numerous accidents have occurred from static discharge during handling of lead styphnate.