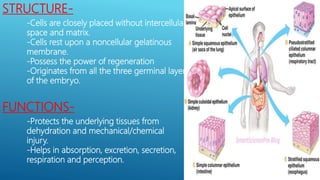
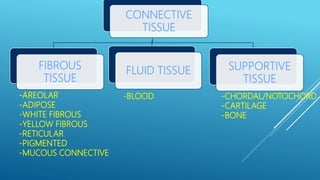
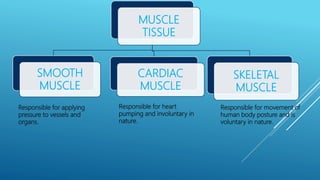
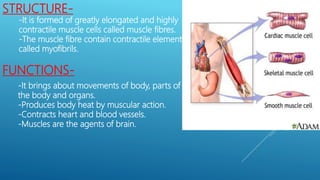
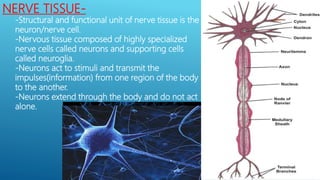
This document provides an overview of the four major types of animal tissue: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. It discusses the structure and functions of each tissue type. Epithelial tissue covers and lines body surfaces and forms glands. Connective tissue binds organs together and provides support. Muscle tissue enables movement and includes three types: smooth, cardiac, and skeletal. Nervous tissue is composed of neurons that sense stimuli and transmit electrical signals throughout the body.