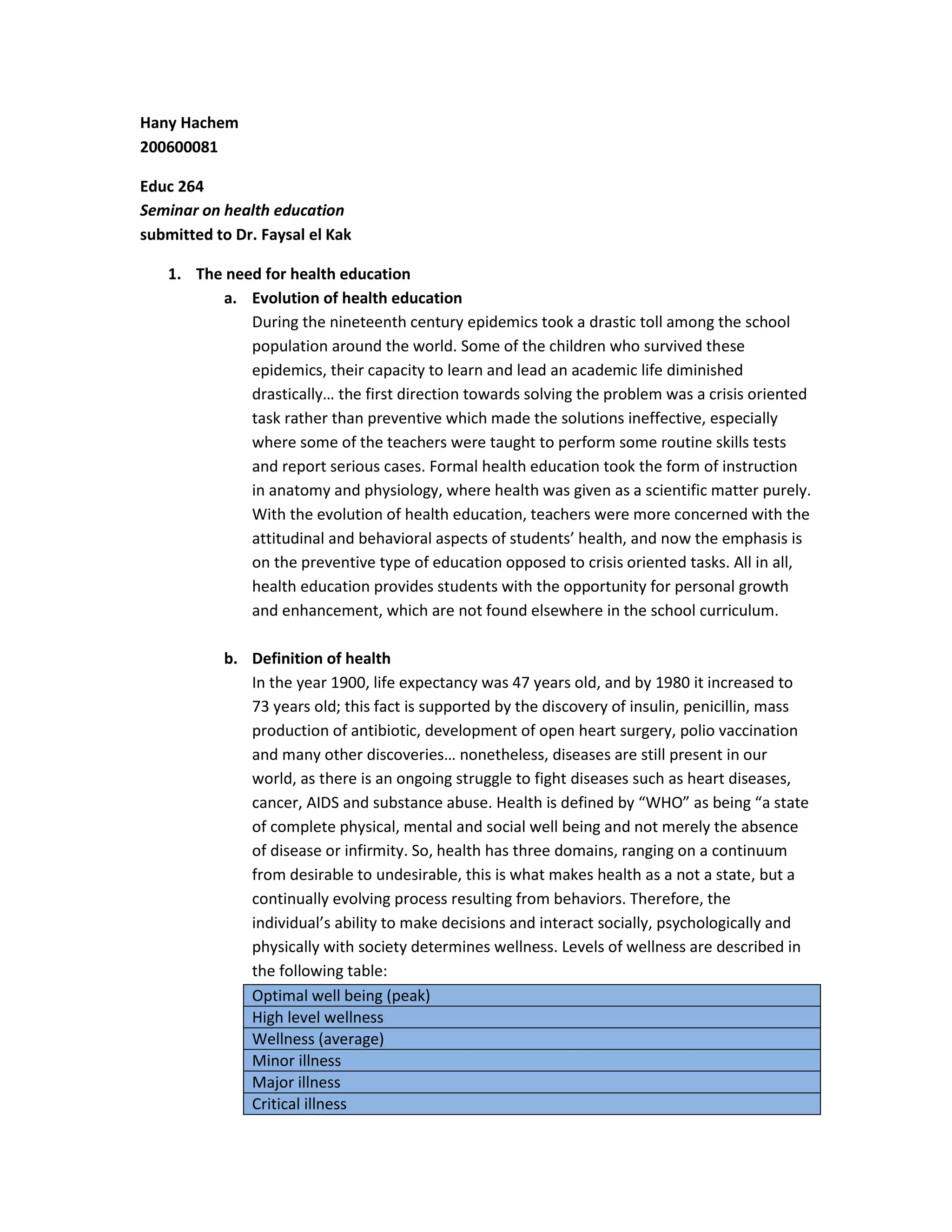
The document discusses the evolution of health education from a crisis-oriented approach focused on epidemics to a preventive model emphasizing students' health attitudes and behaviors. It also defines key terms like health, health education, and outlines the roles and responsibilities of teachers in developing and implementing comprehensive school health programs and instruction, including addressing controversial topics.