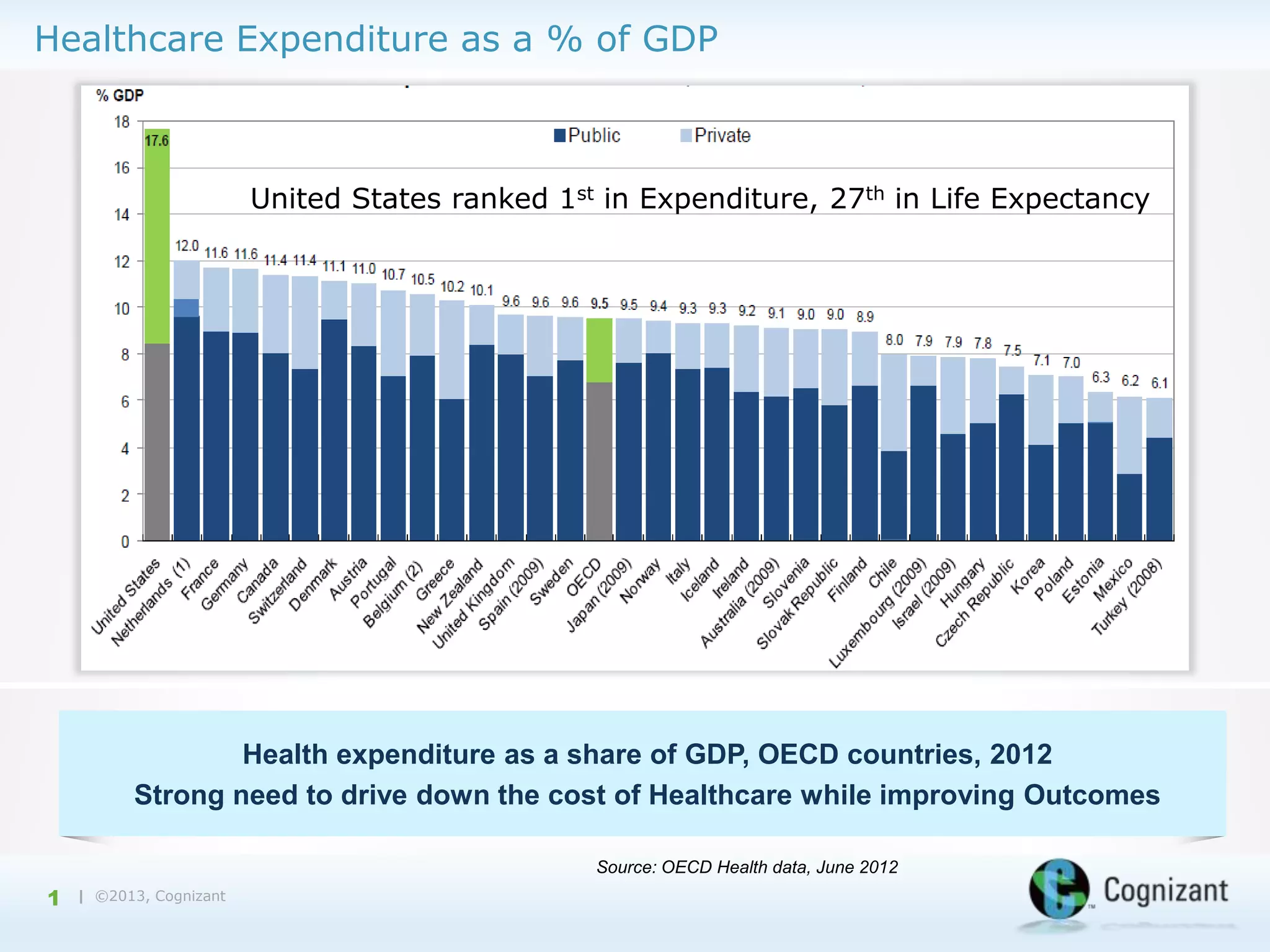
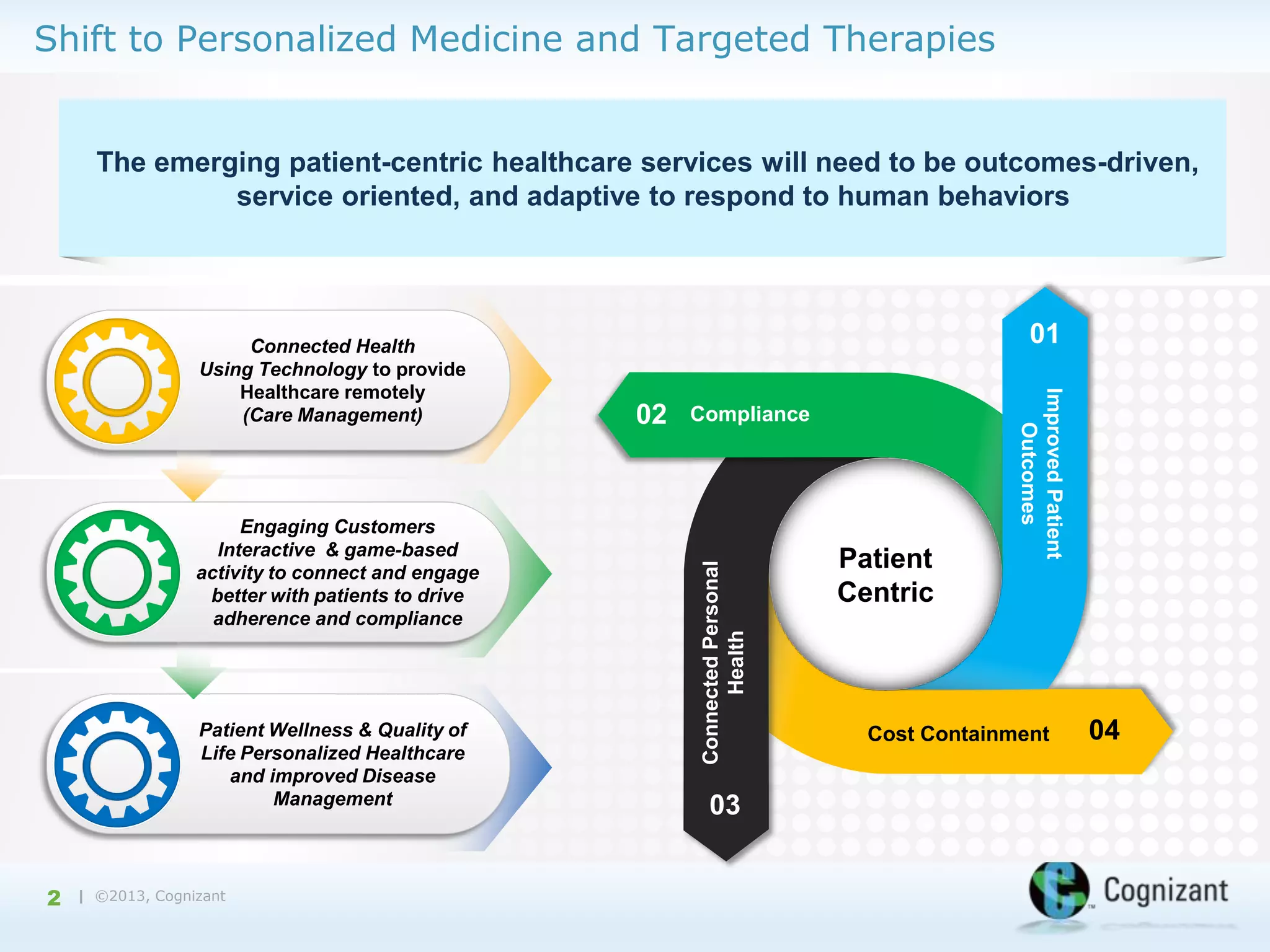
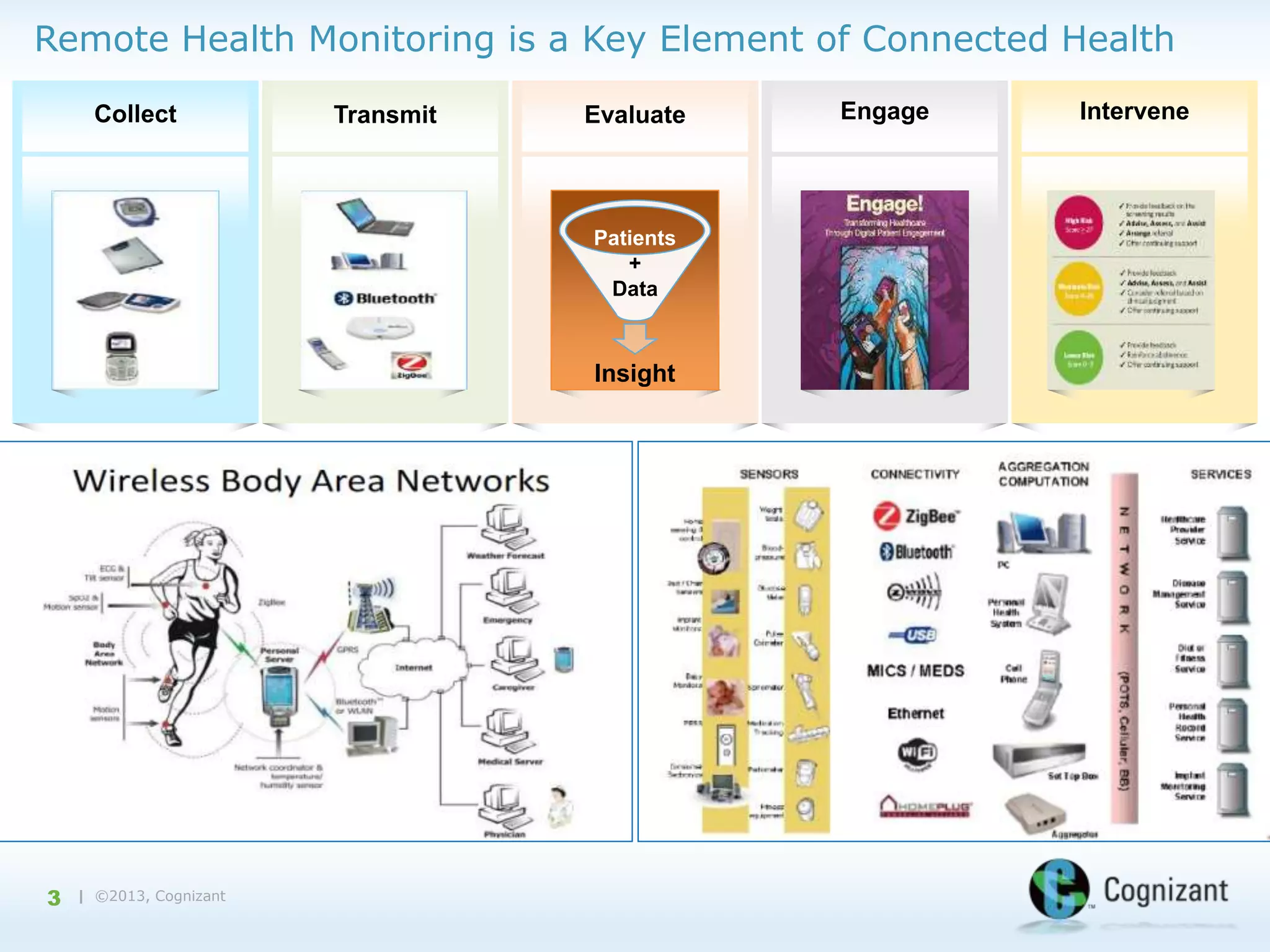
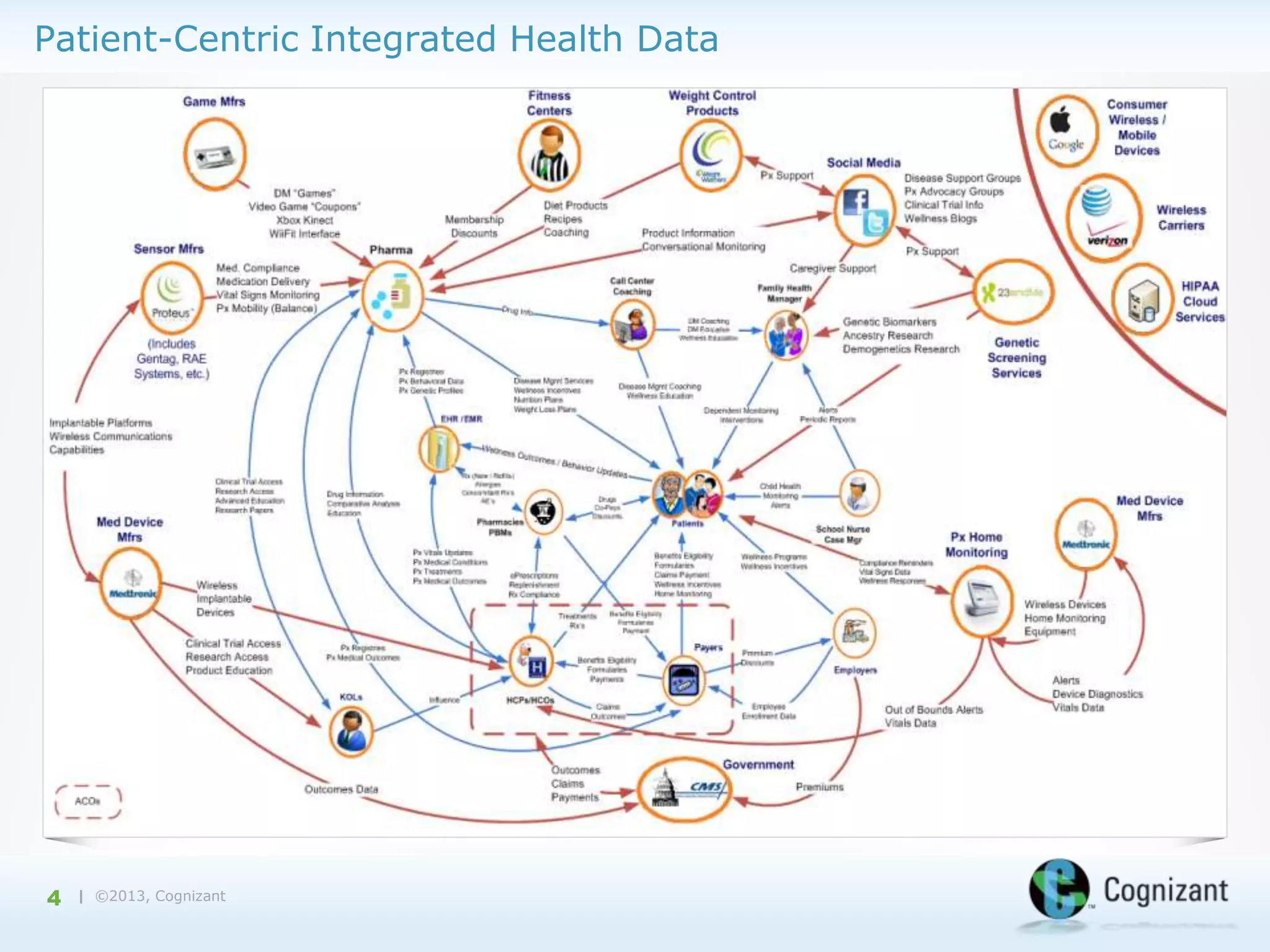
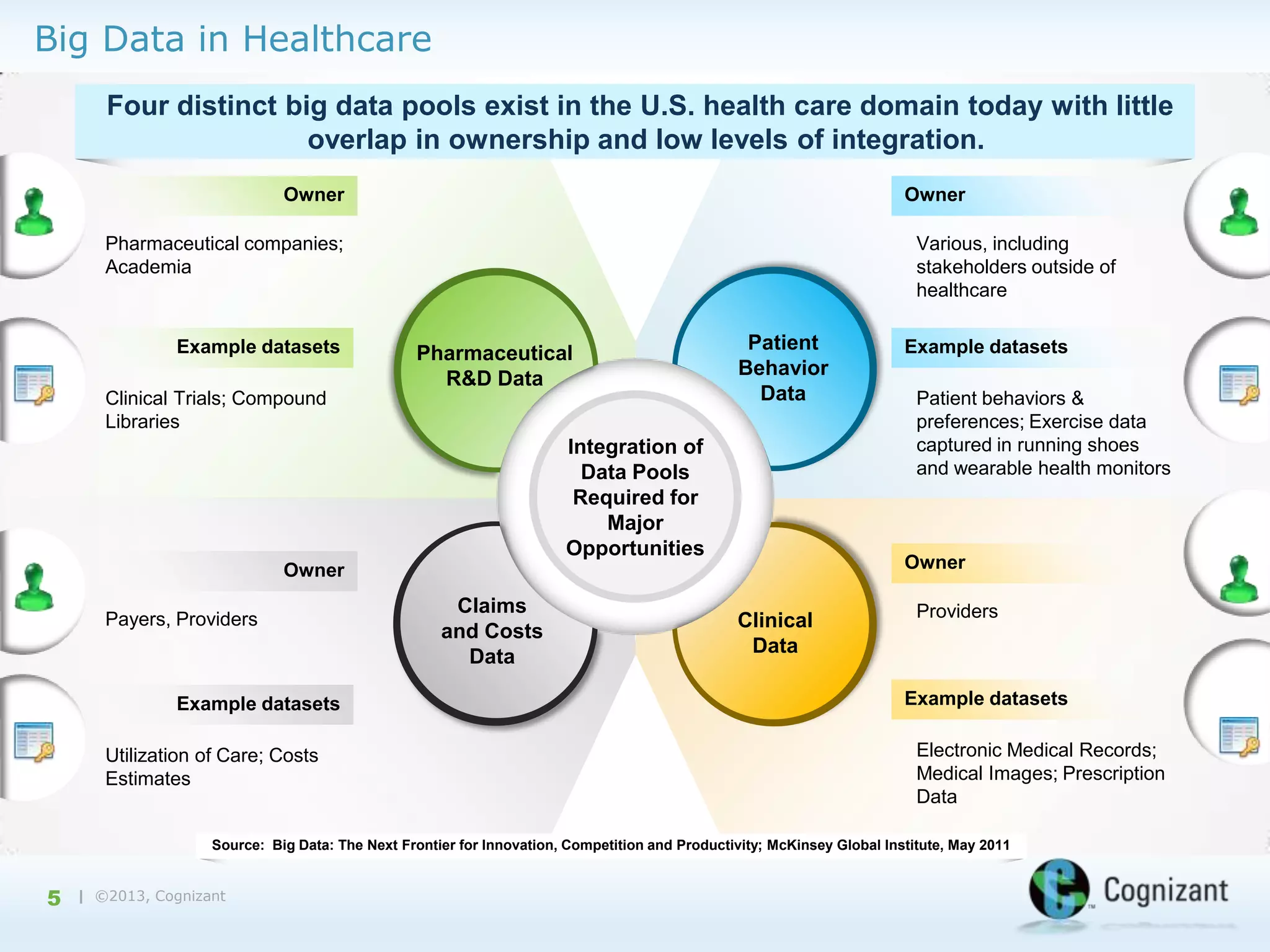
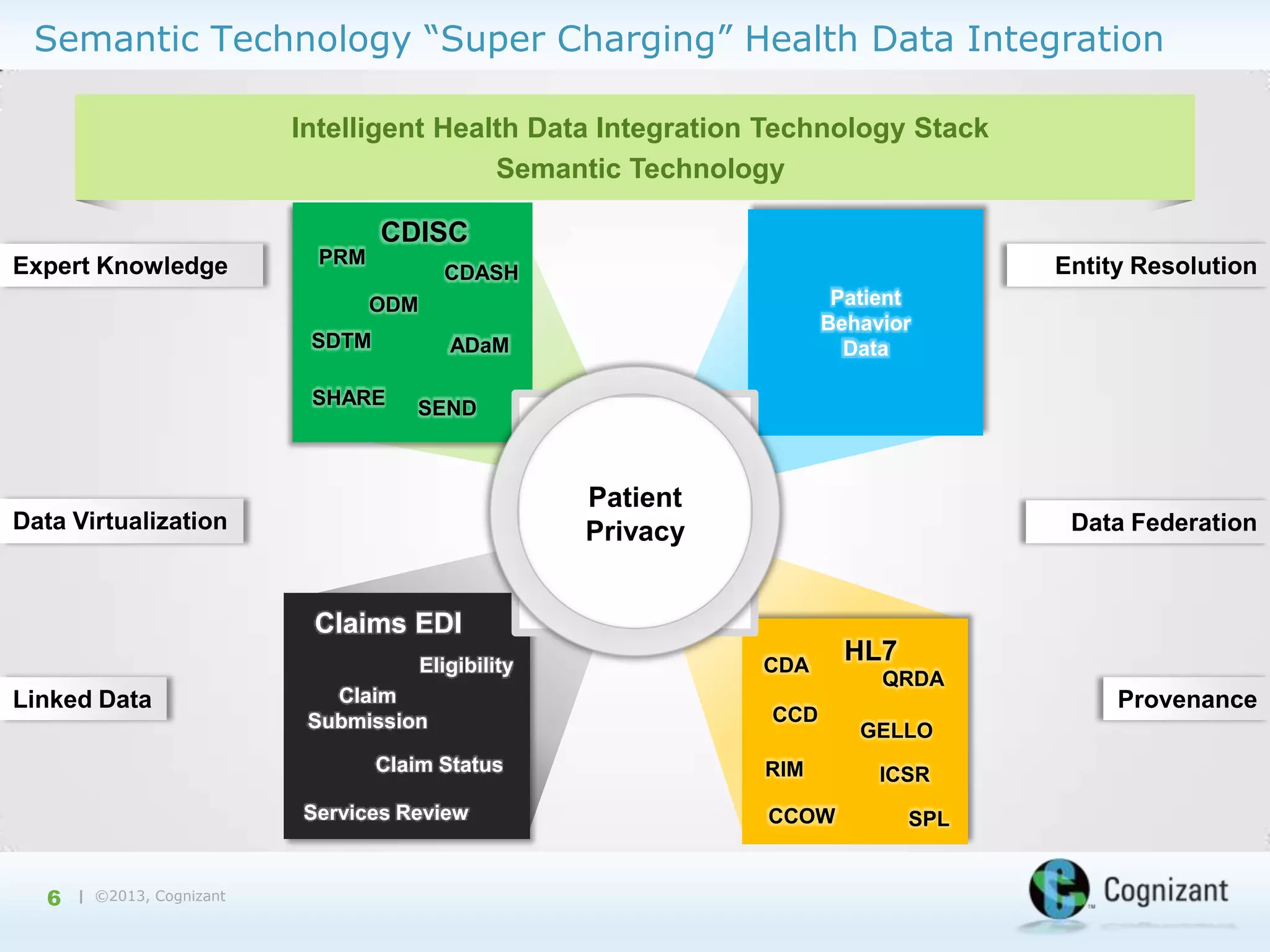
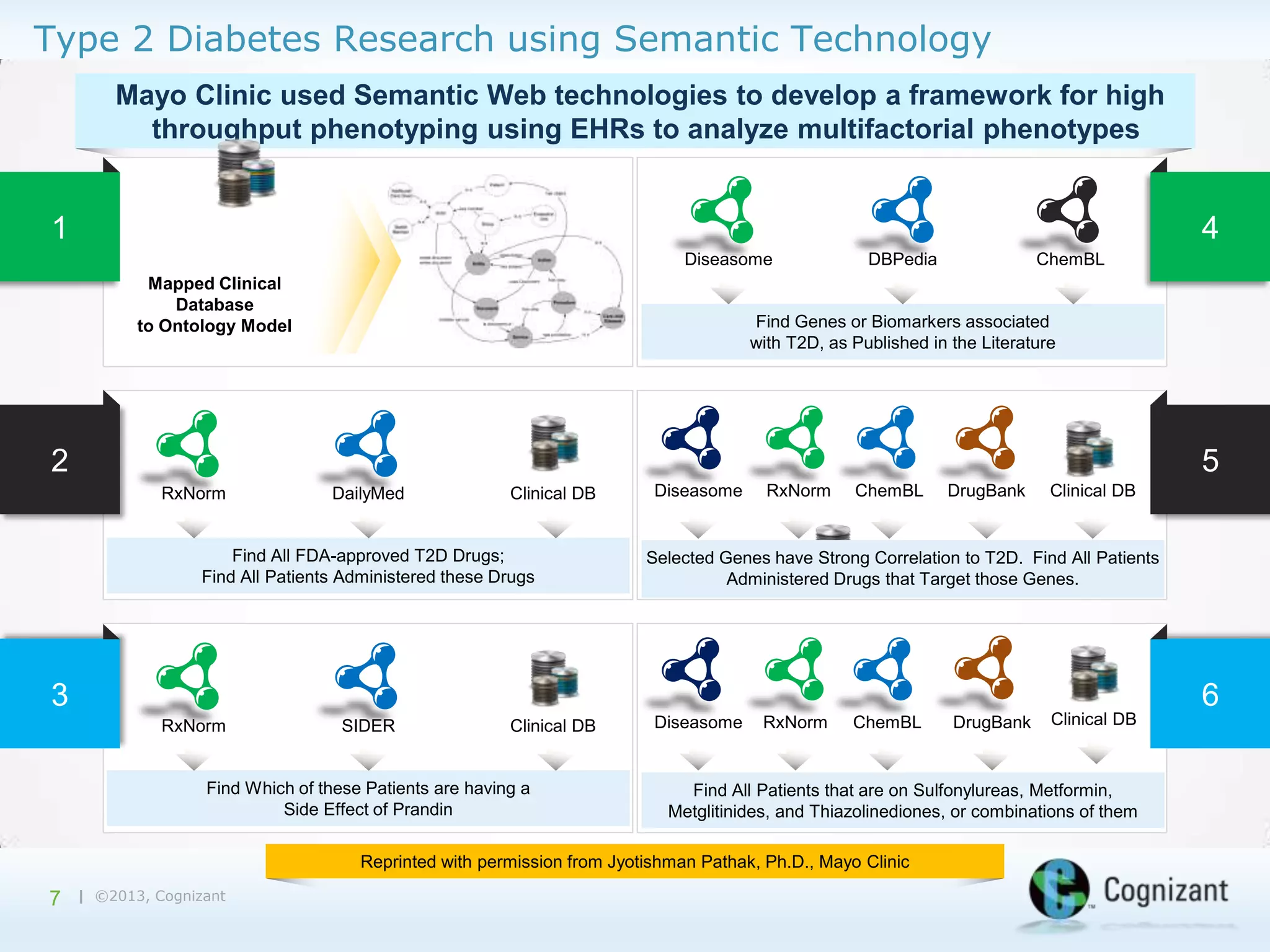
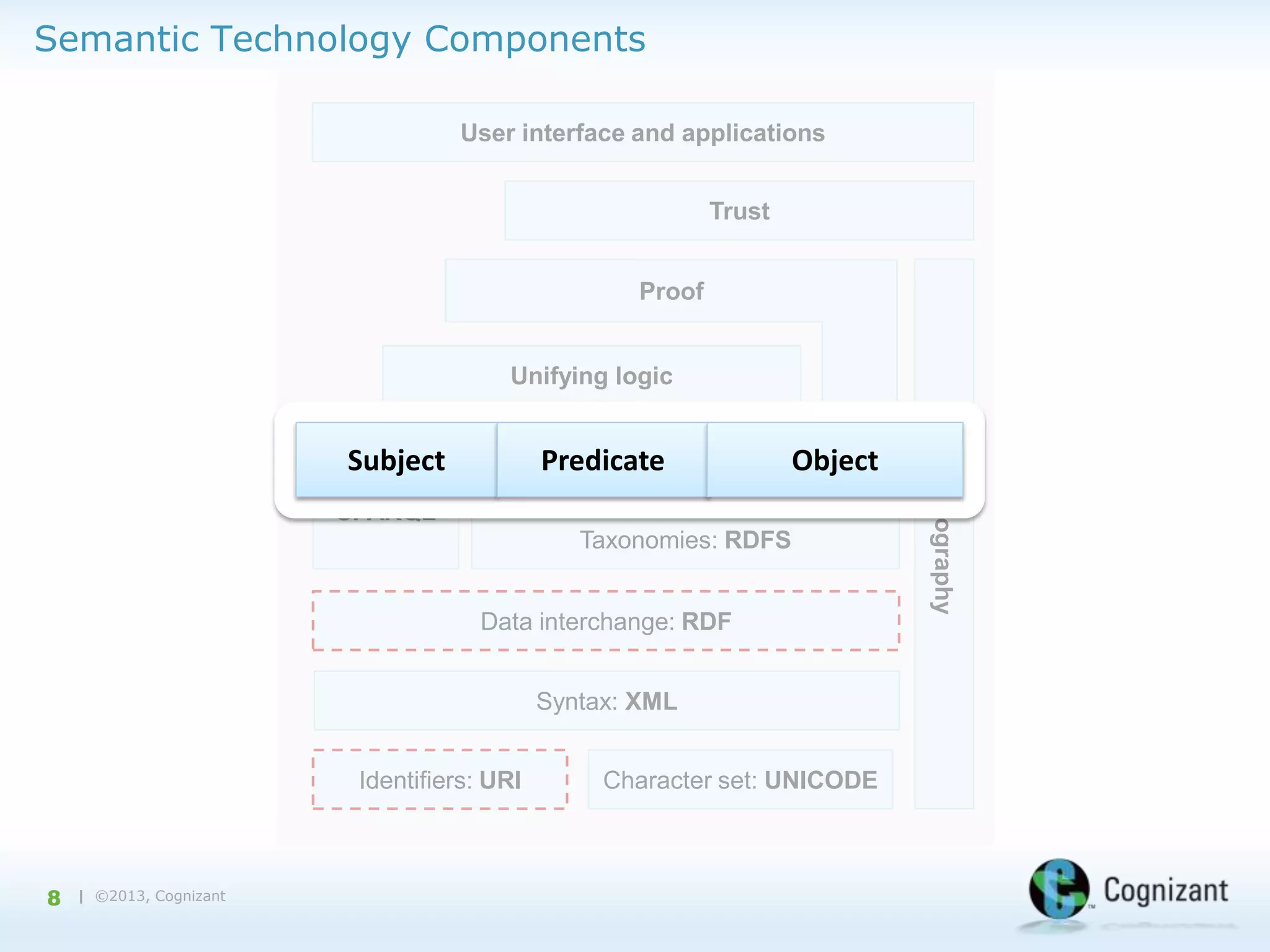
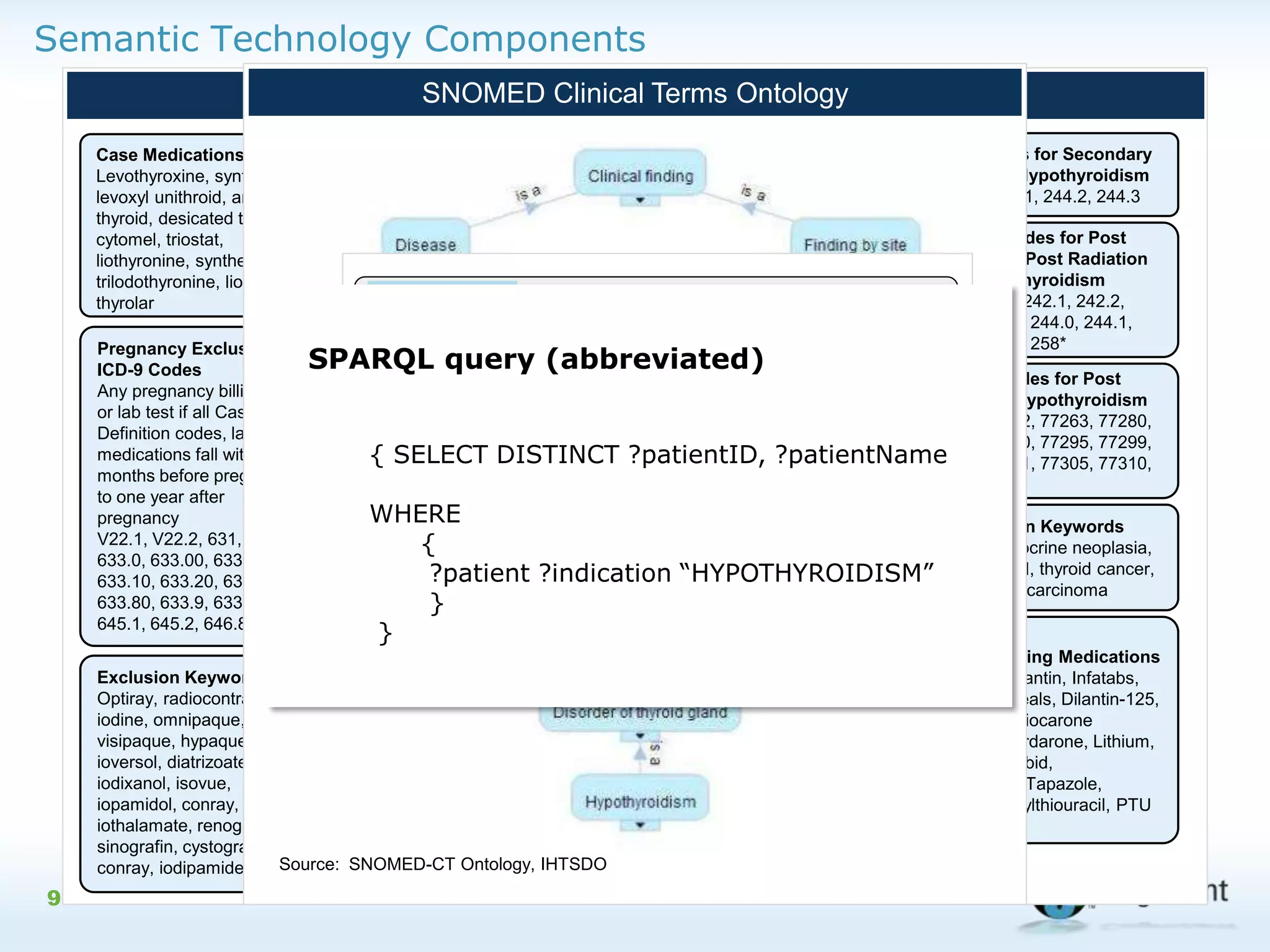
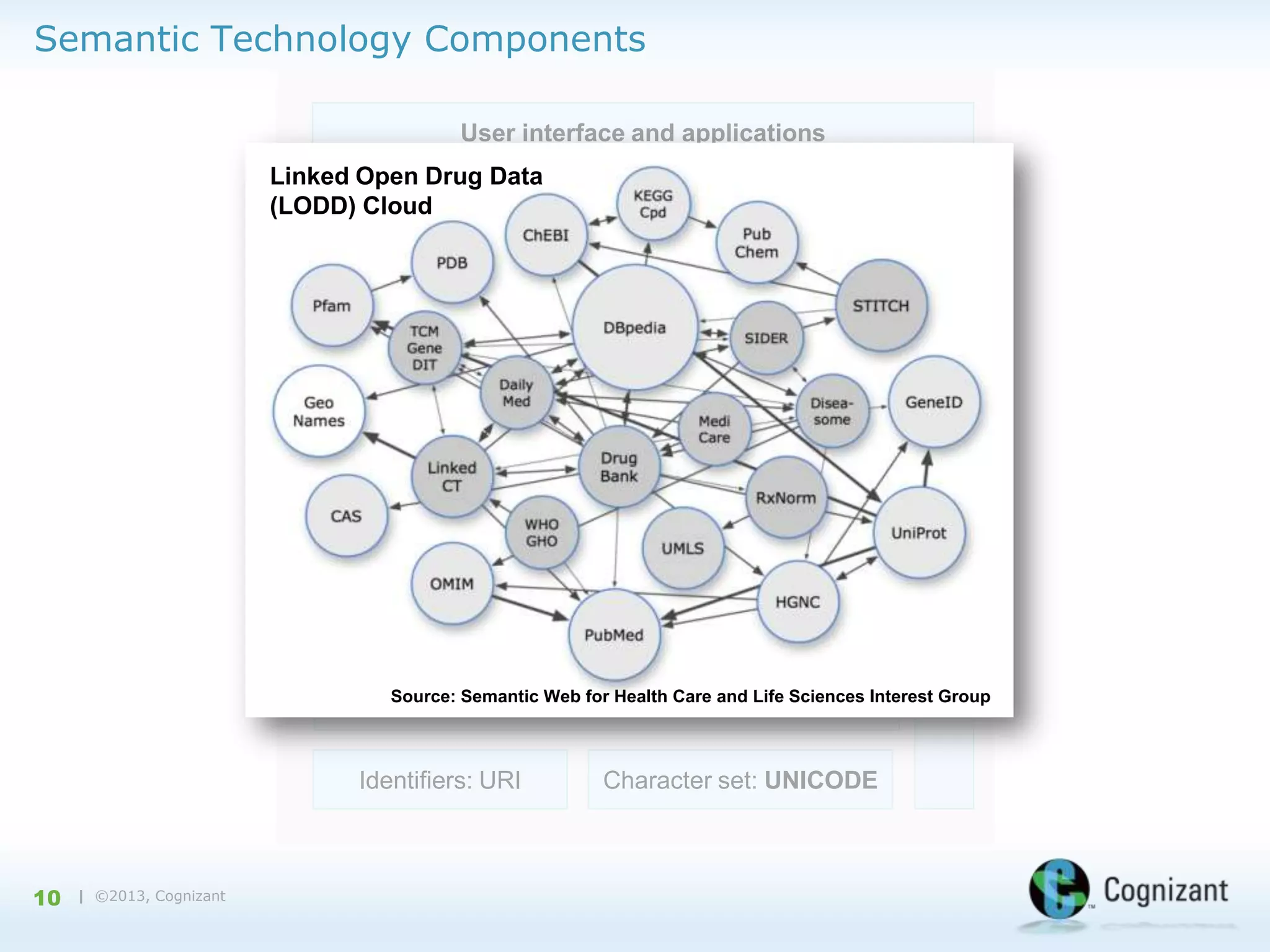
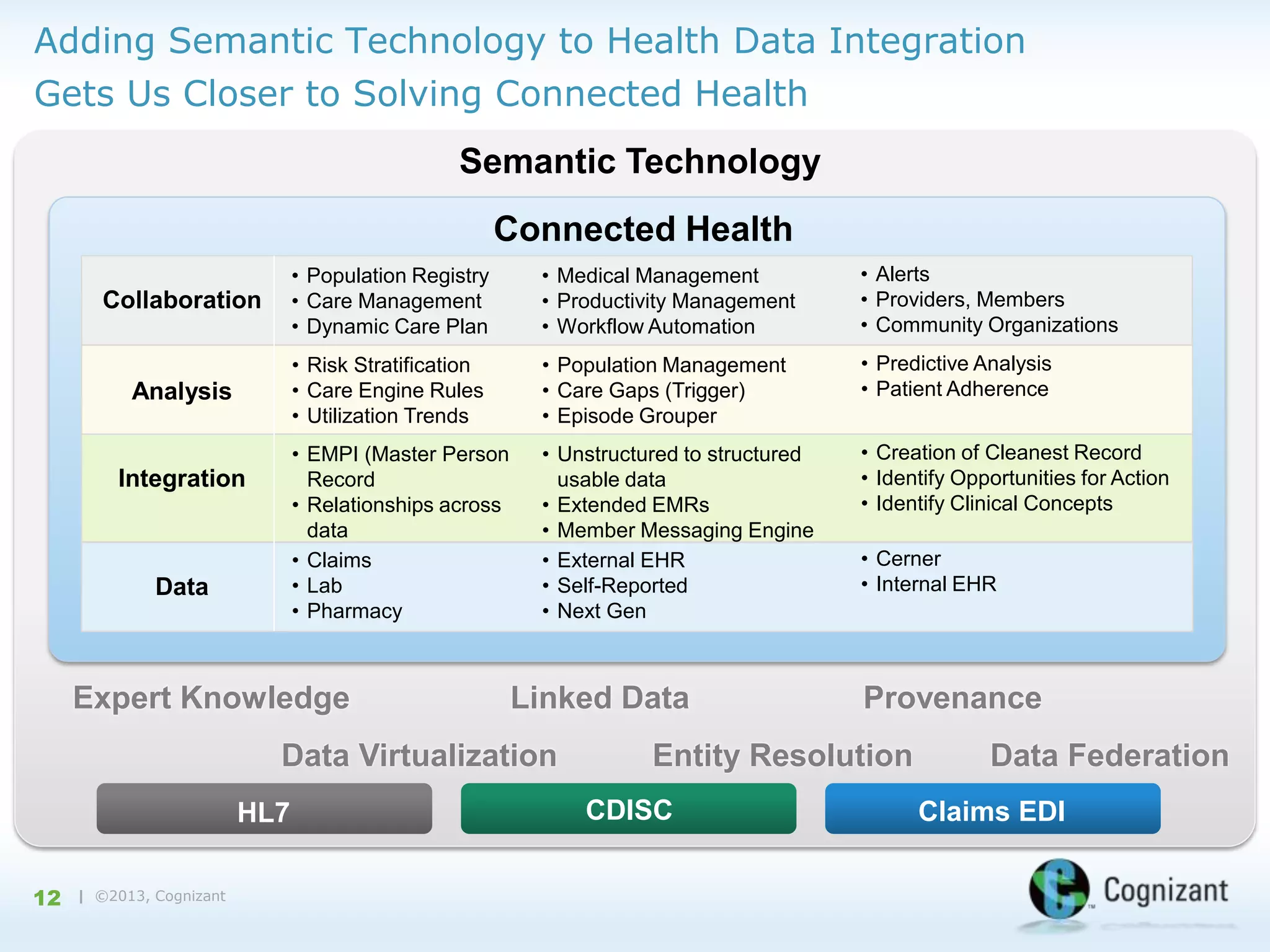
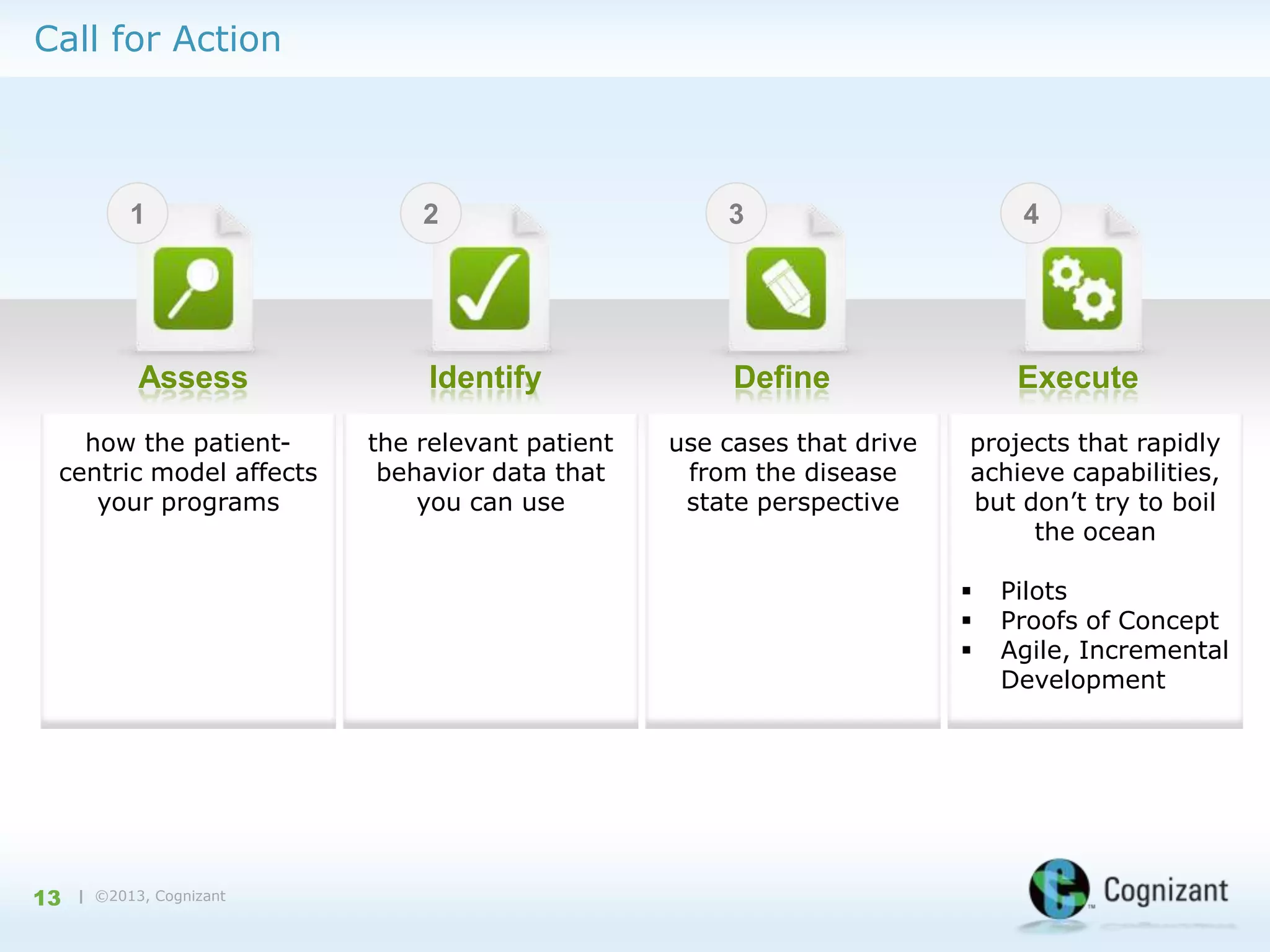
The document discusses the integration of semantic technology in healthcare to improve data collaboration between providers, payors, and pharmaceutical companies, addressing the need for personalized medicine and cost containment. It highlights the challenges of big data in healthcare, emphasizing the importance of data integration for better patient outcomes and disease management. The content includes case studies demonstrating the use of semantic technologies for enhanced data analysis and monitoring in health management.